PowerPoint Presentation - Particle Physics Group
... We know x,y starting momenta is zero, but along the z axis it is not, so many of our measurements are in the xy plane, or transverse ...
... We know x,y starting momenta is zero, but along the z axis it is not, so many of our measurements are in the xy plane, or transverse ...
Electric Potential in Uniform Electric Fields +
... A potential difference is generated any time we have areas of high and low potential energy, just like those generated by gravitational fields. ...
... A potential difference is generated any time we have areas of high and low potential energy, just like those generated by gravitational fields. ...
Variation of the Gravitational Constant and its Consequences
... a fluctuating or intermittent effect of something local but quite outside our experience.1 It is reasonable to extrapolate and suggest that in the limit of zero time, gravity could have been infinitely strong or at least extremely large.2 Enough to say that at some early moment after t = 0 it would ...
... a fluctuating or intermittent effect of something local but quite outside our experience.1 It is reasonable to extrapolate and suggest that in the limit of zero time, gravity could have been infinitely strong or at least extremely large.2 Enough to say that at some early moment after t = 0 it would ...
The statistical interpretation of quantum mechanics
... the basis for a new mode of thought in regard to natural phenomena. This way of thinking has permeated both experimental and theoretical physics to such a degree that it hardly seems possible to say anything more about it that has not been already so often said. However, there are some particular as ...
... the basis for a new mode of thought in regard to natural phenomena. This way of thinking has permeated both experimental and theoretical physics to such a degree that it hardly seems possible to say anything more about it that has not been already so often said. However, there are some particular as ...
URL - StealthSkater
... It just happens to turn out that when we use Niobium (which is a superconductor) with the temperatures of outer space on our hull … It turns out if you put electrons on Niobium … Well, the electrons line up in this triangular array where they’re all at a certain distance one from another. That dista ...
... It just happens to turn out that when we use Niobium (which is a superconductor) with the temperatures of outer space on our hull … It turns out if you put electrons on Niobium … Well, the electrons line up in this triangular array where they’re all at a certain distance one from another. That dista ...
Document
... X-ray tube Types of X-ray tube and power supplies Compton scattering Absorption process – matter & materials Dosimetry ...
... X-ray tube Types of X-ray tube and power supplies Compton scattering Absorption process – matter & materials Dosimetry ...
What is Light?
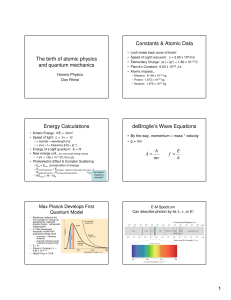
... • Combined planetary model and quantum mechanics • Electrons orbit nucleus, but only certain orbits allowed • Angular momentum quantized: L = (mr)v = n(h/2π) n=1,2,3… • Fit mathematical prediction of H spectra by Balmer (1885) • Electrons in atoms cannot lose/gain energy continuously (Planck/Einstei ...
... • Combined planetary model and quantum mechanics • Electrons orbit nucleus, but only certain orbits allowed • Angular momentum quantized: L = (mr)v = n(h/2π) n=1,2,3… • Fit mathematical prediction of H spectra by Balmer (1885) • Electrons in atoms cannot lose/gain energy continuously (Planck/Einstei ...
Renormalization

In quantum field theory, the statistical mechanics of fields, and the theory of self-similar geometric structures, renormalization is any of a collection of techniques used to treat infinities arising in calculated quantities.Renormalization specifies relationships between parameters in the theory when the parameters describing large distance scales differ from the parameters describing small distances. Physically, the pileup of contributions from an infinity of scales involved in a problem may then result in infinities. When describing space and time as a continuum, certain statistical and quantum mechanical constructions are ill defined. To define them, this continuum limit, the removal of the ""construction scaffolding"" of lattices at various scales, has to be taken carefully, as detailed below.Renormalization was first developed in quantum electrodynamics (QED) to make sense of infinite integrals in perturbation theory. Initially viewed as a suspect provisional procedure even by some of its originators, renormalization eventually was embraced as an important and self-consistent actual mechanism of scale physics in several fields of physics and mathematics. Today, the point of view has shifted: on the basis of the breakthrough renormalization group insights of Kenneth Wilson, the focus is on variation of physical quantities across contiguous scales, while distant scales are related to each other through ""effective"" descriptions. All scales are linked in a broadly systematic way, and the actual physics pertinent to each is extracted with the suitable specific computational techniques appropriate for each.