Word
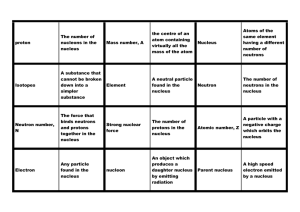
... small number were deflected through angles in excess of 90. Rutherford explained these results by picturing an atom as having a small massive positively charged nucleus. The fraction of particles scattered at different angles could be explained by assuming that the alpha particles and nucleus are p ...
... small number were deflected through angles in excess of 90. Rutherford explained these results by picturing an atom as having a small massive positively charged nucleus. The fraction of particles scattered at different angles could be explained by assuming that the alpha particles and nucleus are p ...
Bohr Theory in the Atomic Physics
... stationary state of the atom and the frequency rule of the radiation were a leap in the process that people explored the micro structure in the interior of atom, and they established the base of the modern atom model, and were excessively accepted by people, so Bohr was praised as the forerunner of ...
... stationary state of the atom and the frequency rule of the radiation were a leap in the process that people explored the micro structure in the interior of atom, and they established the base of the modern atom model, and were excessively accepted by people, so Bohr was praised as the forerunner of ...
Integrable Lattice Models From Gauge Theory
... Actually, there is a subtle but important difference between the R-matrix that solves the YangBaxter equation and the S-matrix that describes particle scattering in an integrable relativistic field theory. The reason for this is that the Yang-Baxter equation is not sensitive to an overall c-number f ...
... Actually, there is a subtle but important difference between the R-matrix that solves the YangBaxter equation and the S-matrix that describes particle scattering in an integrable relativistic field theory. The reason for this is that the Yang-Baxter equation is not sensitive to an overall c-number f ...
Motion in a Straight Line
... The screen of old fashioned TVs is coated on the inside surface with dots of chemicals called phosphors. When a beam of electrons hits a dot, it glows. These phosphor dots are in groups of three: Red, Green, and Blue which then create all the other colours by combining which dots are illuminated. Th ...
... The screen of old fashioned TVs is coated on the inside surface with dots of chemicals called phosphors. When a beam of electrons hits a dot, it glows. These phosphor dots are in groups of three: Red, Green, and Blue which then create all the other colours by combining which dots are illuminated. Th ...
Nordheim, L. “Electron emission in intense electric fields,”
... his work has a bearing on the emission of electrons in strong fields, but he does not pursue the matter further. For our purposes the calculations can be shorn of irrelevancies and made so much simpler that it is worth while attacking the problem de novo. ? 2. The Reflection of Electrons at a Potent ...
... his work has a bearing on the emission of electrons in strong fields, but he does not pursue the matter further. For our purposes the calculations can be shorn of irrelevancies and made so much simpler that it is worth while attacking the problem de novo. ? 2. The Reflection of Electrons at a Potent ...
AP® Physics C: Electricity and Magnetism 2009 Free
... E&M. 3. A square conducting loop of side L contains two identical lightbulbs, 1 and 2, as shown above. There is a magnetic field directed into the page in the region inside the loop with magnitude as a function of time t given by B (t ) = at + b , where a and b are positive constants. The lightbulbs ...
... E&M. 3. A square conducting loop of side L contains two identical lightbulbs, 1 and 2, as shown above. There is a magnetic field directed into the page in the region inside the loop with magnitude as a function of time t given by B (t ) = at + b , where a and b are positive constants. The lightbulbs ...
Variation of the Gravitational Constant and its Consequences
... The Gravitational Electron Another derived constant from the era of quantum mechanics is the ‘classical radius of the electron’. This object arose as a necessary adjustment to quantum electrodynamics when it was still very young. In the early days of QED some problems had an unfortunate tendency to ...
... The Gravitational Electron Another derived constant from the era of quantum mechanics is the ‘classical radius of the electron’. This object arose as a necessary adjustment to quantum electrodynamics when it was still very young. In the early days of QED some problems had an unfortunate tendency to ...
Renormalization

In quantum field theory, the statistical mechanics of fields, and the theory of self-similar geometric structures, renormalization is any of a collection of techniques used to treat infinities arising in calculated quantities.Renormalization specifies relationships between parameters in the theory when the parameters describing large distance scales differ from the parameters describing small distances. Physically, the pileup of contributions from an infinity of scales involved in a problem may then result in infinities. When describing space and time as a continuum, certain statistical and quantum mechanical constructions are ill defined. To define them, this continuum limit, the removal of the ""construction scaffolding"" of lattices at various scales, has to be taken carefully, as detailed below.Renormalization was first developed in quantum electrodynamics (QED) to make sense of infinite integrals in perturbation theory. Initially viewed as a suspect provisional procedure even by some of its originators, renormalization eventually was embraced as an important and self-consistent actual mechanism of scale physics in several fields of physics and mathematics. Today, the point of view has shifted: on the basis of the breakthrough renormalization group insights of Kenneth Wilson, the focus is on variation of physical quantities across contiguous scales, while distant scales are related to each other through ""effective"" descriptions. All scales are linked in a broadly systematic way, and the actual physics pertinent to each is extracted with the suitable specific computational techniques appropriate for each.