Effective Field Theory, Past and Future
... Then some time late in 1966 I was sitting at the counter of a café in Harvard Square, scribbling on a napkin the amplitudes I had found for emitting two or three soft pions in nucleon collisions, and it suddenly occurred to me that these results looked very much like what would be given by lowest o ...
... Then some time late in 1966 I was sitting at the counter of a café in Harvard Square, scribbling on a napkin the amplitudes I had found for emitting two or three soft pions in nucleon collisions, and it suddenly occurred to me that these results looked very much like what would be given by lowest o ...
PHYS 4011, 5050: Atomic and Molecular Physics
... = −13.6 eV = −0.5 a.u. = −0.5 hartree = −1 Rydberg 2me a20 ...
... = −13.6 eV = −0.5 a.u. = −0.5 hartree = −1 Rydberg 2me a20 ...
Triadic Quantum Energy
... going to change the understanding of the spontaneous self organization phenomena in nature. Therefore aiming to develop the interpretation of this quantum effect , we propose to think about what happen when two Quantum Particles are closed in a box and the wall of the box are gradually restricted ...
... going to change the understanding of the spontaneous self organization phenomena in nature. Therefore aiming to develop the interpretation of this quantum effect , we propose to think about what happen when two Quantum Particles are closed in a box and the wall of the box are gradually restricted ...
CH 27 – Quantum Physics
... Quantum mechanics is the branch of physics that deals with systems at the atomic level. Some of the consequences of quantum mechanics are that energy is quantized, particles have wave-like characteristics, and there are inherent uncertainties with which we can determine the position, momentum, and e ...
... Quantum mechanics is the branch of physics that deals with systems at the atomic level. Some of the consequences of quantum mechanics are that energy is quantized, particles have wave-like characteristics, and there are inherent uncertainties with which we can determine the position, momentum, and e ...
Creating Entanglement
... The Hamiltonian The Hamiltonian operator is a function of operators concerning degrees of freedom (dynamical variables) of the system. Eg. if quantum information is encoded in positions x1 and x2 of two particles, then with … representing other relevant operators. Momentum p is conjugate to p ...
... The Hamiltonian The Hamiltonian operator is a function of operators concerning degrees of freedom (dynamical variables) of the system. Eg. if quantum information is encoded in positions x1 and x2 of two particles, then with … representing other relevant operators. Momentum p is conjugate to p ...
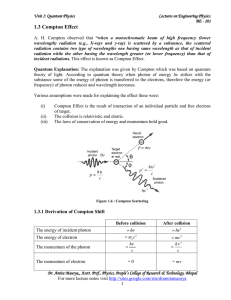
1.3 Compton Effect - IndiaStudyChannel.com
... wavelength) radiation (e.g., X-rays and γ-ray) is scattered by a substance, the scattered radiation contains two type of wavelengths one having same wavelength as that of incident radiation while the other having the wavelength greater (or lower frequency) than that of incident radiations. This effe ...
... wavelength) radiation (e.g., X-rays and γ-ray) is scattered by a substance, the scattered radiation contains two type of wavelengths one having same wavelength as that of incident radiation while the other having the wavelength greater (or lower frequency) than that of incident radiations. This effe ...
Chapter 18 – Potential and Capacitance
... charge from one point in a field to another, the external agent must do work. This work is equal to the increase in potential energy of the charge. It is also the NEGATIVE of the work done BY THE FIELD in moving the charge from the same points. ...
... charge from one point in a field to another, the external agent must do work. This work is equal to the increase in potential energy of the charge. It is also the NEGATIVE of the work done BY THE FIELD in moving the charge from the same points. ...
quantum mechanics and real events - Heriot
... system and the environment, or the quantum part and the classical part. The classical part is described in terms of the familar ideas of everyday life, according to which the world consists of objects which have definite positions at all times (even though we may not know these positions). The quant ...
... system and the environment, or the quantum part and the classical part. The classical part is described in terms of the familar ideas of everyday life, according to which the world consists of objects which have definite positions at all times (even though we may not know these positions). The quant ...
Renormalization

In quantum field theory, the statistical mechanics of fields, and the theory of self-similar geometric structures, renormalization is any of a collection of techniques used to treat infinities arising in calculated quantities.Renormalization specifies relationships between parameters in the theory when the parameters describing large distance scales differ from the parameters describing small distances. Physically, the pileup of contributions from an infinity of scales involved in a problem may then result in infinities. When describing space and time as a continuum, certain statistical and quantum mechanical constructions are ill defined. To define them, this continuum limit, the removal of the ""construction scaffolding"" of lattices at various scales, has to be taken carefully, as detailed below.Renormalization was first developed in quantum electrodynamics (QED) to make sense of infinite integrals in perturbation theory. Initially viewed as a suspect provisional procedure even by some of its originators, renormalization eventually was embraced as an important and self-consistent actual mechanism of scale physics in several fields of physics and mathematics. Today, the point of view has shifted: on the basis of the breakthrough renormalization group insights of Kenneth Wilson, the focus is on variation of physical quantities across contiguous scales, while distant scales are related to each other through ""effective"" descriptions. All scales are linked in a broadly systematic way, and the actual physics pertinent to each is extracted with the suitable specific computational techniques appropriate for each.