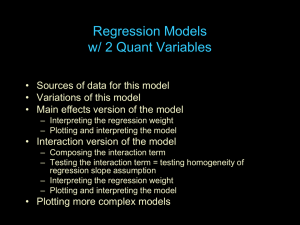
The Simple Linear Regression Model
... estimators. Are they unbiased? What are their standard errors? Section 2.4 of ALR, and the associated appendix sections, A.3 and A.4, develop formulas for these properties that are given in many traditional regression textbooks. These formulas can be confusing to someone with an intermediate level o ...
... estimators. Are they unbiased? What are their standard errors? Section 2.4 of ALR, and the associated appendix sections, A.3 and A.4, develop formulas for these properties that are given in many traditional regression textbooks. These formulas can be confusing to someone with an intermediate level o ...
IOSR Journal of Computer Engineering (IOSR-JCE)
... classification and simple tree arrangement. Ridor algorithm is used for best performance. He compared various algorithms and finally concluded that J48 and RepTree algorithm improves accuracy, Ridor improves performance and JRip improves performance in terms of complexity [2]. Goyal Anshul et al. (2 ...
... classification and simple tree arrangement. Ridor algorithm is used for best performance. He compared various algorithms and finally concluded that J48 and RepTree algorithm improves accuracy, Ridor improves performance and JRip improves performance in terms of complexity [2]. Goyal Anshul et al. (2 ...
Analyzing beta diversity: partitioning the spatial variation of
... the environmental variables explain a significant proportion of the community composition variation. In this contribution, we explain how hypotheses about the origin of beta diversity can be tested by partitioning the spatial variation of community composition (presence– absence or abundance data) w ...
... the environmental variables explain a significant proportion of the community composition variation. In this contribution, we explain how hypotheses about the origin of beta diversity can be tested by partitioning the spatial variation of community composition (presence– absence or abundance data) w ...
Can longitudinal generalized estimating equation models
... and friendship, these models are not constructed so as to closely mimic physiology or some other applicationspecific characteristic. The agents, in fact, simply have one continuous-valued attribute with an intrinsic rate of growth of that attribute (which may be mean zero), and a propensity to devel ...
... and friendship, these models are not constructed so as to closely mimic physiology or some other applicationspecific characteristic. The agents, in fact, simply have one continuous-valued attribute with an intrinsic rate of growth of that attribute (which may be mean zero), and a propensity to devel ...
theory of errors
... will exist inconsistency or 00contradiction00 among measurements, also called misclosure. One of the tasks of geodetic and photogrammetric computations is to get rid of misclosures among measurements in an optimal way according to some estimation criteria (such as the least squares principle). These ...
... will exist inconsistency or 00contradiction00 among measurements, also called misclosure. One of the tasks of geodetic and photogrammetric computations is to get rid of misclosures among measurements in an optimal way according to some estimation criteria (such as the least squares principle). These ...
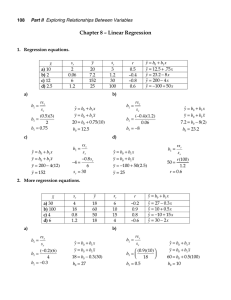
CHAPTER 3 CLASSICAL LINEAR REGRESSION MODELS
... where Xt = (1; Yt 1 )0 : Obviously, E(Xt "t ) = E(Xt )E("t ) = 0 but E(Xt+1 "t ) 6= 0: Thus, we have E("t jX) 6= 0; and so Assumption 3.2 does not hold. In Chapter 5, we will consider linear regression models with dependent observations, which will include this example as a special case. In fact, th ...
... where Xt = (1; Yt 1 )0 : Obviously, E(Xt "t ) = E(Xt )E("t ) = 0 but E(Xt+1 "t ) 6= 0: Thus, we have E("t jX) 6= 0; and so Assumption 3.2 does not hold. In Chapter 5, we will consider linear regression models with dependent observations, which will include this example as a special case. In fact, th ...
GWmodel: an R Package for Exploring Spatial Heterogeneity
... described well by some universal or global model, but where there are spatial regions where a suitably localised model calibration provides a better description. The approach uses a moving window weighting technique, where localised models are found at target locations. Here, for an individual model ...
... described well by some universal or global model, but where there are spatial regions where a suitably localised model calibration provides a better description. The approach uses a moving window weighting technique, where localised models are found at target locations. Here, for an individual model ...