Logistic Regression Models for Ordinal Response Variables
... and in fact, much of the recent literature on application and development of ordinal regression techniques is found within the research of the larger public health community. Results of many of these statistical or comparative studies are mentioned here. Educational and social scientists may not typ ...
... and in fact, much of the recent literature on application and development of ordinal regression techniques is found within the research of the larger public health community. Results of many of these statistical or comparative studies are mentioned here. Educational and social scientists may not typ ...
Document
... minimum extreme value, normal, logistic. • Estimation and Inference Consider data with right censoring only: {(Ti, ci) : i = 1, · · · , n.} Likelihood function: n ...
... minimum extreme value, normal, logistic. • Estimation and Inference Consider data with right censoring only: {(Ti, ci) : i = 1, · · · , n.} Likelihood function: n ...
IBM SPSS Advanced Statistics 22
... v A polynomial regression model in which any lower-order terms are specified before any higher-order terms. v A purely nested model in which the first-specified effect is nested within the second-specified effect, the second-specified effect is nested within the third, and so on. (This form of nesti ...
... v A polynomial regression model in which any lower-order terms are specified before any higher-order terms. v A purely nested model in which the first-specified effect is nested within the second-specified effect, the second-specified effect is nested within the third, and so on. (This form of nesti ...
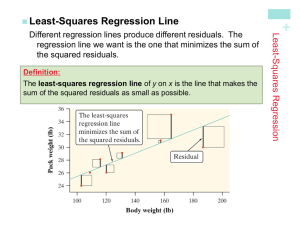
Least-Squares Regression Line
... The number of miles (in thousands) for the 11 used Hondas have a mean of 50.5 and a standard deviation of 19.3. The asking prices had a mean of $14,425 and a standard deviation of $1,899. The correlation for these variables is r = -0.874. Find the equation of the least-squares regression line and ...
... The number of miles (in thousands) for the 11 used Hondas have a mean of 50.5 and a standard deviation of 19.3. The asking prices had a mean of $14,425 and a standard deviation of $1,899. The correlation for these variables is r = -0.874. Find the equation of the least-squares regression line and ...
Including Measurement Error in the Regression Model: A First Try
... Yi is an q × 1 random vector of observable response variables, so the regression can be multivariate; there are q response variables. β 0 is a q × 1 vector of unknown constants, the intercepts for the q regression equations. There is one for each response variable. Xi is a p × 1 observable random ve ...
... Yi is an q × 1 random vector of observable response variables, so the regression can be multivariate; there are q response variables. β 0 is a q × 1 vector of unknown constants, the intercepts for the q regression equations. There is one for each response variable. Xi is a p × 1 observable random ve ...
5-8
... Chapters 3 or 4 to solve the system of three equations in three variables. For example, you can use a matrix equation as shown. ...
... Chapters 3 or 4 to solve the system of three equations in three variables. For example, you can use a matrix equation as shown. ...
Applying Generalized Linear Models
... such an approach is decidedly outdated, not in the sense that it is no longer useful, but in its limiting restrictions as compared to what statistical models are needed and possible with modern computing power. What are now required, and feasible, are nonlinear models with dependence structures amon ...
... such an approach is decidedly outdated, not in the sense that it is no longer useful, but in its limiting restrictions as compared to what statistical models are needed and possible with modern computing power. What are now required, and feasible, are nonlinear models with dependence structures amon ...
Models for Mapping Potential Habitat at Landscape Scales: An
... habitat pattern and area using landscape-scale estimates of habitat capability. The method was designed to be adaptable to goals, constraints, and future conditions not currently represented on landscapes but that might result from new approaches imposed by land managers. Further, it allows comparis ...
... habitat pattern and area using landscape-scale estimates of habitat capability. The method was designed to be adaptable to goals, constraints, and future conditions not currently represented on landscapes but that might result from new approaches imposed by land managers. Further, it allows comparis ...