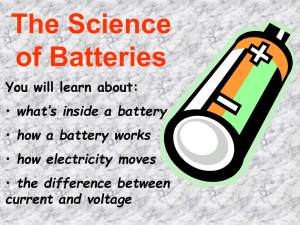
The Photoelectric Effect
... wavelength, such that photons of short wavelength (blue light) carry more energy than long wavelength (red light) photons. To release an electron from a metal plate required a minimal energy that could only be transferred by a photon of energy equal or greater than that minimal threshold energy (i.e ...
... wavelength, such that photons of short wavelength (blue light) carry more energy than long wavelength (red light) photons. To release an electron from a metal plate required a minimal energy that could only be transferred by a photon of energy equal or greater than that minimal threshold energy (i.e ...
Feb20_modified
... • The atom has a nucleus at its center containing protons and neutrons • Outside of the nucleus, electrons whiz around in clouds called orbitals – Electrons can also be described using wave or particle models – Electron orbitals are quantized – that is, they exist only at very particular energies ...
... • The atom has a nucleus at its center containing protons and neutrons • Outside of the nucleus, electrons whiz around in clouds called orbitals – Electrons can also be described using wave or particle models – Electron orbitals are quantized – that is, they exist only at very particular energies ...
Spectrophotometry Chapter 18
... • Therefore, electrons in higher energy levels spend more time farther away from the nucleus. • The higher energy levels are larger so they can hold more electrons. • Electrons are not orbiting the nucleus like planets! • The energy levels of the electrons are divided into sublevels and orbitals. Li ...
... • Therefore, electrons in higher energy levels spend more time farther away from the nucleus. • The higher energy levels are larger so they can hold more electrons. • Electrons are not orbiting the nucleus like planets! • The energy levels of the electrons are divided into sublevels and orbitals. Li ...
nakuru district sec. schools trial examination – 2014
... Hard x-rays have very short wavelength, thus high penetrating power while soft x-rays have longer wavelength, hence less penetrating power ...
... Hard x-rays have very short wavelength, thus high penetrating power while soft x-rays have longer wavelength, hence less penetrating power ...
Abstract - Heidelberger Life
... Today, there are three different methods used to detect photons: semiconductor detectors, vacuum detectors or gas detectors. The semiconductor devices have the disadvantage of limited size. Semiconductors have large background noise at room ambient temperature, which falsifies the results of the mea ...
... Today, there are three different methods used to detect photons: semiconductor detectors, vacuum detectors or gas detectors. The semiconductor devices have the disadvantage of limited size. Semiconductors have large background noise at room ambient temperature, which falsifies the results of the mea ...
______ is the ability to do work
... light waves have more _______ than low frequency light waves. Light is a _________ wave produced by accelerating electrons. Light is the only type of wave that can travel through a __________. The reason you can see a book is because light is _________ off the book to your eyes. When light reflects ...
... light waves have more _______ than low frequency light waves. Light is a _________ wave produced by accelerating electrons. Light is the only type of wave that can travel through a __________. The reason you can see a book is because light is _________ off the book to your eyes. When light reflects ...
forward-biased
... Triode Vacuum Tube • Inside the envelope is a vacuum. • Feature common to both transistors and tubes is that they can amplify signals. • A triode vacuum tube might be used because instead of a transistor because it may be able to handle higher power. • Can amplify a small signal but must use high v ...
... Triode Vacuum Tube • Inside the envelope is a vacuum. • Feature common to both transistors and tubes is that they can amplify signals. • A triode vacuum tube might be used because instead of a transistor because it may be able to handle higher power. • Can amplify a small signal but must use high v ...
Electron gun - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
... A direct current, electrostatic thermionic electron gun is formed from several parts: a hot cathode, which is heated to create a stream of electrons via thermionic emission, electrodes generating an electric field which focus the beam (such as a Wehnelt cylinder), and one or more anode electrodes wh ...
... A direct current, electrostatic thermionic electron gun is formed from several parts: a hot cathode, which is heated to create a stream of electrons via thermionic emission, electrodes generating an electric field which focus the beam (such as a Wehnelt cylinder), and one or more anode electrodes wh ...
Photomultiplier

Photomultiplier tubes (photomultipliers or PMTs for short), members of the class of vacuum tubes, and more specifically vacuum phototubes, are extremely sensitive detectors of light in the ultraviolet, visible, and near-infrared ranges of the electromagnetic spectrum. These detectors multiply the current produced by incident light by as much as 100 million times (i.e., 160 dB), in multiple dynode stages, enabling (for example) individual photons to be detected when the incident flux of light is very low. Unlike most vacuum tubes, they are not obsolete.The combination of high gain, low noise, high frequency response or, equivalently, ultra-fast response, and large area of collection has maintained photomultipliers an essential place in nuclear and particle physics, astronomy, medical diagnostics including blood tests, medical imaging, motion picture film scanning (telecine), radar jamming, and high-end image scanners known as drum scanners. Elements of photomultiplier technology, when integrated differently, are the basis of night vision devices.Semiconductor devices, particularly avalanche photodiodes, are alternatives to photomultipliers; however, photomultipliers are uniquely well-suited for applications requiring low-noise, high-sensitivity detection of light that is imperfectly collimated.