Exam description The exam is written and divided into two parts
... The present simple The present continuous (including action and non-action verbs) The past simple: regular and irregular verbs The past continuous The past perfect The future forms: going to for intentions and predictions; the present continuous for future arrangements; will/won’t for predictions; p ...
... The present simple The present continuous (including action and non-action verbs) The past simple: regular and irregular verbs The past continuous The past perfect The future forms: going to for intentions and predictions; the present continuous for future arrangements; will/won’t for predictions; p ...
Grammar Lesson Five Verbs and Verbals
... in a sentence. An infinitive is a verbal consisting of the word to plus a verb (in its simplest "stem" form) and functioning as a noun, adjective, or adverb. The term verbal indicates that an infinitive, like the other two kinds of verbals, is based on a verb and therefore expresses action or a stat ...
... in a sentence. An infinitive is a verbal consisting of the word to plus a verb (in its simplest "stem" form) and functioning as a noun, adjective, or adverb. The term verbal indicates that an infinitive, like the other two kinds of verbals, is based on a verb and therefore expresses action or a stat ...
Infinitives The gerunds
... the infinitive can also be used without to. Read the examples given below. She wants to go. (Here the phrase ‘to go’ is an example of a to-infinitive.) She made me cry. (Here the infinitive ‘cry’ is used without the marker to.) The infinitive is a non-finite verb. In other words, it does not change ...
... the infinitive can also be used without to. Read the examples given below. She wants to go. (Here the phrase ‘to go’ is an example of a to-infinitive.) She made me cry. (Here the infinitive ‘cry’ is used without the marker to.) The infinitive is a non-finite verb. In other words, it does not change ...
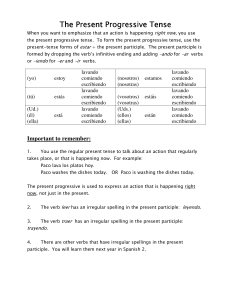
The Present Progressive Tense The Present
... When you want to emphasize that an action is happening right now, you use the present progressive tense. To form the present progressive tense, use the present-tense forms of estar + the present participle. The present participle is formed by dropping the verb’s infinitive ending and adding –ando fo ...
... When you want to emphasize that an action is happening right now, you use the present progressive tense. To form the present progressive tense, use the present-tense forms of estar + the present participle. The present participle is formed by dropping the verb’s infinitive ending and adding –ando fo ...
Park Walk Primary School Year 6 Writing Passport Practise Apply
... I can choose the writing tool that is best suited for a task. Vocabulary Grammar Punctuation I can recognise vocabulary and structures that are appropriate for formal speech and writing, including subjunctive forms. I can use passive verbs to affect the presentation of information in a sentence. I c ...
... I can choose the writing tool that is best suited for a task. Vocabulary Grammar Punctuation I can recognise vocabulary and structures that are appropriate for formal speech and writing, including subjunctive forms. I can use passive verbs to affect the presentation of information in a sentence. I c ...
The Tense and Aspect System: Chapter 7, Part 1
... inflectionally in language, such as tense, aspect, mood, number, gender, and person. As a result, a non-finite verb cannot generally serve as the main verb in an independent clause; rather, it heads a non-finite clause.” http://dictionary.babylon.com/ You can find another nice explanation of non-f ...
... inflectionally in language, such as tense, aspect, mood, number, gender, and person. As a result, a non-finite verb cannot generally serve as the main verb in an independent clause; rather, it heads a non-finite clause.” http://dictionary.babylon.com/ You can find another nice explanation of non-f ...
07.10 Indirect Statement Indirect Statement
... on having the correct verb tense of the main verb. Take the time now to insure that you have the four principal parts firmly in mind before going any further. 3. In Latin, an infinitive with an _______________subject is used instead of a that clause to express an indirect statement. Notice the subje ...
... on having the correct verb tense of the main verb. Take the time now to insure that you have the four principal parts firmly in mind before going any further. 3. In Latin, an infinitive with an _______________subject is used instead of a that clause to express an indirect statement. Notice the subje ...
PerfectTenses - Ector County ISD.
... state as having occurred – and been completed – at a time before another past action, state, or time. It is used in almost exactly the same way as we use it in English. The wedding started at 3. By then, all the guests ...
... state as having occurred – and been completed – at a time before another past action, state, or time. It is used in almost exactly the same way as we use it in English. The wedding started at 3. By then, all the guests ...
Verbals - Santa Ana College
... Trembling with fear, I opened the door. (Here, trembling is modifying the subject I. It is a participle). The stolen car was never located. (Stolen is a past participle form of the verb steal. It is functioning as an adjective modifying the noun car). *Note – the words accompanying the participle ar ...
... Trembling with fear, I opened the door. (Here, trembling is modifying the subject I. It is a participle). The stolen car was never located. (Stolen is a past participle form of the verb steal. It is functioning as an adjective modifying the noun car). *Note – the words accompanying the participle ar ...
The Infinitive
... There is a special class of words that are made from verbs but are not used as verbs. They are called verbals. There are three kinds of verbals: infinitives, participles, and gerunds. Verbals are used as various parts of speech. An infinitive is a verb form that is usually preceded by the word fo. W ...
... There is a special class of words that are made from verbs but are not used as verbs. They are called verbals. There are three kinds of verbals: infinitives, participles, and gerunds. Verbals are used as various parts of speech. An infinitive is a verb form that is usually preceded by the word fo. W ...
CH33 Objectives
... to say that on the adjective side, they modify nouns, yet on the verb side, they can take objects (as in the example below). ...
... to say that on the adjective side, they modify nouns, yet on the verb side, they can take objects (as in the example below). ...
GMAS Crash Couse
... Personal pronoun refers to the one speaking (first person – I, we, us), to one spoken to ( second person- you, your) the one spoken about( third person- he, she, they, him) Reflexive – refers to the subject and functions as a compliment ( yourself, myself, herself) Intensive – emphasizes a noun or a ...
... Personal pronoun refers to the one speaking (first person – I, we, us), to one spoken to ( second person- you, your) the one spoken about( third person- he, she, they, him) Reflexive – refers to the subject and functions as a compliment ( yourself, myself, herself) Intensive – emphasizes a noun or a ...
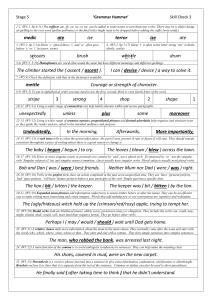
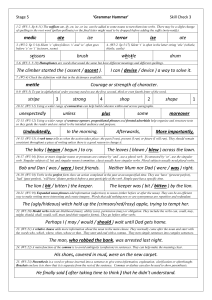
Stage 5 Check 3 – Answers
... The (ugly/hideous) witch held up the (crimson/red/rosy) apple, trying to tempt her. 22. (W5:20) Modal verbs indicate likelihood (must), ability (can), permission (may) or obligation. They include the verbs can, could, may, might, should, shall, would, will, must (and their negative forms). They go b ...
... The (ugly/hideous) witch held up the (crimson/red/rosy) apple, trying to tempt her. 22. (W5:20) Modal verbs indicate likelihood (must), ability (can), permission (may) or obligation. They include the verbs can, could, may, might, should, shall, would, will, must (and their negative forms). They go b ...
medic ate ize terror ize ate scissors brush whistle drum The climber
... The (ugly/hideous) witch held up the (crimson/red/rosy) apple, trying to tempt her. 22. (W5:20) Modal verbs indicate likelihood (must), ability (can), permission (may) or obligation. They include the verbs can, could, may, might, should, shall, would, will, must (and their negative forms). They go b ...
... The (ugly/hideous) witch held up the (crimson/red/rosy) apple, trying to tempt her. 22. (W5:20) Modal verbs indicate likelihood (must), ability (can), permission (may) or obligation. They include the verbs can, could, may, might, should, shall, would, will, must (and their negative forms). They go b ...
Grammar Definition Example Conjunction Used to join two ideas
... The object in a sentence that is having the action done to it, what the verb is acting upon. ...
... The object in a sentence that is having the action done to it, what the verb is acting upon. ...
Editing for Comma Splices and Run-Ons
... He learned how to study, and he learned how to manage his time. (a sentence with two independent clauses) He had the time to complete his schoolwork properly and time to spend with his friends.(a sentence with one IC and a pair of infinitive phrases. ...
... He learned how to study, and he learned how to manage his time. (a sentence with two independent clauses) He had the time to complete his schoolwork properly and time to spend with his friends.(a sentence with one IC and a pair of infinitive phrases. ...
Parts of Speech Review WS
... 5. Past Perfect Tensea. To express an action that was completed in the past before some other past occurrance. b. ____________________________________________ 6. Future Perfect Tense- used to express an action that will be completed in the future. __________________________________________ have or s ...
... 5. Past Perfect Tensea. To express an action that was completed in the past before some other past occurrance. b. ____________________________________________ 6. Future Perfect Tense- used to express an action that will be completed in the future. __________________________________________ have or s ...
1 Foundations of Syntax Spr14 Handout One [CGEL: Quirk, R
... conducted the next experiment] >> obligatory, complement clause, subordinate clause is required by the transitive verb predict >> that subordinating conjunction, introducing complement clauses/when subordinating conjunction, introducing adverbial/adjunct clauses >>> that/when: ambiguous III) syntact ...
... conducted the next experiment] >> obligatory, complement clause, subordinate clause is required by the transitive verb predict >> that subordinating conjunction, introducing complement clauses/when subordinating conjunction, introducing adverbial/adjunct clauses >>> that/when: ambiguous III) syntact ...
Linking Verbs
... Linking/Action Verbs: (can be either depending on how used in the sentence) become appear remain stay grow seem turn sound look taste feel smell Linking Verb test – Substitute “is” for singular subjects or “are” for plural subjects. If the sentence makes sense, then it is a linking verb. If it does ...
... Linking/Action Verbs: (can be either depending on how used in the sentence) become appear remain stay grow seem turn sound look taste feel smell Linking Verb test – Substitute “is” for singular subjects or “are” for plural subjects. If the sentence makes sense, then it is a linking verb. If it does ...
CRY - OER Commons
... Regular verbs are those whose past tense and past participles are formed by adding a -d or an -ed to the end of the verb. "To roll" is a good example of a regular verb: roll, rolled, rolled. ...
... Regular verbs are those whose past tense and past participles are formed by adding a -d or an -ed to the end of the verb. "To roll" is a good example of a regular verb: roll, rolled, rolled. ...
Ling 222 (Hedberg) – Types of Embedded Clauses in
... Ling 222 (Hedberg) – Types of Embedded Clauses in English 1. Finite clauses The verb in the embedded clause is finite and has a subject. Relative clauses See handout on relative clauses. o The man [whose car we crashed into] called the police. o We’ll rent the apartment to the person [that we like ...
... Ling 222 (Hedberg) – Types of Embedded Clauses in English 1. Finite clauses The verb in the embedded clause is finite and has a subject. Relative clauses See handout on relative clauses. o The man [whose car we crashed into] called the police. o We’ll rent the apartment to the person [that we like ...
Phrases - Huber Heights City Schools
... preposition (n. or pron.) A prepositional phrase always acts like a modifier (adj. or adv.) Examples = of the room, by the way, with us, to him, under the bed ...
... preposition (n. or pron.) A prepositional phrase always acts like a modifier (adj. or adv.) Examples = of the room, by the way, with us, to him, under the bed ...