MARKETING TERMINOLOGY
... Clearly identified group of consumers with needs that business wants to satisfy. ...
... Clearly identified group of consumers with needs that business wants to satisfy. ...
MARKETINGTERMINOLOGY
... Clearly identified group of consumers with needs that business wants to satisfy. ...
... Clearly identified group of consumers with needs that business wants to satisfy. ...
List 3
... f) Suppose the publisher were not profit-maximizing but were concerned with maximizing economic efficiency. What price would it charge for the book? How much profit would it make at this price? Exercise 2. Suppose that a natural monopolist were required by law to charge average total cost. On a diag ...
... f) Suppose the publisher were not profit-maximizing but were concerned with maximizing economic efficiency. What price would it charge for the book? How much profit would it make at this price? Exercise 2. Suppose that a natural monopolist were required by law to charge average total cost. On a diag ...
File
... After building customer loyalty, prices may gradually increase. Increase Market Share Strategy: lower prices or offer premiums to get more customers. used to lure customers away from competitors’ products Similar to maximizing sales strategy. Meet Competition Strategy: set prices in relation to co ...
... After building customer loyalty, prices may gradually increase. Increase Market Share Strategy: lower prices or offer premiums to get more customers. used to lure customers away from competitors’ products Similar to maximizing sales strategy. Meet Competition Strategy: set prices in relation to co ...
the free enterprise system
... cars, most of them would not have the money to buy them. Moreover, the few people who could afford such cars might prefer to spend their money on something else. Producers, therefore, have to take into account not only whether consumers will want their product, but also whether potential consumers w ...
... cars, most of them would not have the money to buy them. Moreover, the few people who could afford such cars might prefer to spend their money on something else. Producers, therefore, have to take into account not only whether consumers will want their product, but also whether potential consumers w ...
Directions: - Heath
... 13. If you buy an item wholesale for $9.00 and keystone it, what is the price you will be charging at the retail level? ...
... 13. If you buy an item wholesale for $9.00 and keystone it, what is the price you will be charging at the retail level? ...
PES-Introduction
... Price Elasticity of Supply – practice exercises 1. In each of the following cases, calculate the price elasticity of supply to 2 decimal places; decide whether this makes the supply of this product elastic or inelastic: a. The price of a product falls from 60p to 40p, causing supply to contract from ...
... Price Elasticity of Supply – practice exercises 1. In each of the following cases, calculate the price elasticity of supply to 2 decimal places; decide whether this makes the supply of this product elastic or inelastic: a. The price of a product falls from 60p to 40p, causing supply to contract from ...
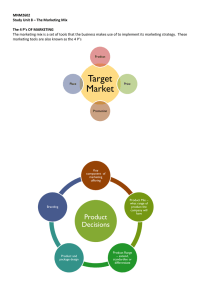
The Marketing Mix
... How much is this product sold for Where is this product sold How is it promoted ...
... How much is this product sold for Where is this product sold How is it promoted ...
Notes
... § Identify three methods that firms use to set their prices. § EDLP versus a high/low strategy § How do consumers process and evaluate prices? § Market penetration and market skimming § How should a co ...
... § Identify three methods that firms use to set their prices. § EDLP versus a high/low strategy § How do consumers process and evaluate prices? § Market penetration and market skimming § How should a co ...