Applied quantum mechanics 1 Applied Quantum Mechanics
... (d) Show that E kinetic = – E potential 2 (which is a result predicted by the virial theorem). (e) Show that the peak in radial probability occurs at r = a B Z . (f) Show that the expectation value r = 3a B 2Z . (g) Show that the expectation value of momentum p = 0 . Problem 11.3 T ...
... (d) Show that E kinetic = – E potential 2 (which is a result predicted by the virial theorem). (e) Show that the peak in radial probability occurs at r = a B Z . (f) Show that the expectation value r = 3a B 2Z . (g) Show that the expectation value of momentum p = 0 . Problem 11.3 T ...
File
... 41.Atoms are made up of tiny particles called molecules. 42.Atoms are not created or destroyed in chemical reactions. A chemical reaction simply changes the way atoms are grouped together. 43.The nucleus of an atom contains the electrons and the neutrons. 44.A proton is equal to one atomic mass unit ...
... 41.Atoms are made up of tiny particles called molecules. 42.Atoms are not created or destroyed in chemical reactions. A chemical reaction simply changes the way atoms are grouped together. 43.The nucleus of an atom contains the electrons and the neutrons. 44.A proton is equal to one atomic mass unit ...
Chemical reactions occur with outer level electrons so that is the
... A Na atom has 11+ and 11- IF it loses one electron then 11+ and 10Atoms with more than 4 electrons will gain electrons For Oxygen it is easier to gain 2 electrons than to lose 6 electrons An O atom has 8+ and 8- IF it gains two electrons then 8+ and 10- ...
... A Na atom has 11+ and 11- IF it loses one electron then 11+ and 10Atoms with more than 4 electrons will gain electrons For Oxygen it is easier to gain 2 electrons than to lose 6 electrons An O atom has 8+ and 8- IF it gains two electrons then 8+ and 10- ...
the atomic theory
... Elements are made of tiny particles called atoms. All atoms of a given element are identical. The atoms of a given element are different from those of any other element; the atoms of different elements can be distinguished from one another by their respective relative weights. Atoms of one element c ...
... Elements are made of tiny particles called atoms. All atoms of a given element are identical. The atoms of a given element are different from those of any other element; the atoms of different elements can be distinguished from one another by their respective relative weights. Atoms of one element c ...
Part One: Molecular Geometry and Directional Bonding A
... Valence Bond Theory (VB) provides a more detailed picture of what happens to electron wave functions (orbitals) in molecules. ...
... Valence Bond Theory (VB) provides a more detailed picture of what happens to electron wave functions (orbitals) in molecules. ...
Chapter 1 - Atoms: The Quantum World
... the 4p-subshell. The first will enter the vacant 4pz-orbital and the second must pair with one of the three. The 4p-subshell will appear as ↑↓ ↑ ↑ . Like Ge, the Se atom also has two unpaired electrons in the ground state. 4px 4py 4pz ...
... the 4p-subshell. The first will enter the vacant 4pz-orbital and the second must pair with one of the three. The 4p-subshell will appear as ↑↓ ↑ ↑ . Like Ge, the Se atom also has two unpaired electrons in the ground state. 4px 4py 4pz ...
Population_analysis_Ranjit
... molecules into atoms called the Quantum Theory of Atoms in Molecules (QTAIM). His definition of an atom is based purely on the electronic charge density. Bader uses what are called zero flux surfaces to divide atoms. A zero flux surface is a 2-D surface on which the charge density is a minimum perpe ...
... molecules into atoms called the Quantum Theory of Atoms in Molecules (QTAIM). His definition of an atom is based purely on the electronic charge density. Bader uses what are called zero flux surfaces to divide atoms. A zero flux surface is a 2-D surface on which the charge density is a minimum perpe ...
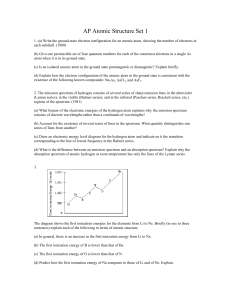
Chemistry 102B What`s in an atom? Before “Chemistry” Other Early
... Developed the “Law of conservation of Mass”. • Joseph Proust (early 1800s) – discovered that a given compound always contained the same proportions of certain elements by mass. “Law of Definite Proportions” • John Dalton (early 1800s) – noted that elements that combined to form more than one kind of ...
... Developed the “Law of conservation of Mass”. • Joseph Proust (early 1800s) – discovered that a given compound always contained the same proportions of certain elements by mass. “Law of Definite Proportions” • John Dalton (early 1800s) – noted that elements that combined to form more than one kind of ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 19. (a) The point group of staggered confirmation of ethane is D3d. What do these letters D, 3 and d in this point group represent? (b) Formulate the term symbols for the ground state configuration of F atom. ...
... 19. (a) The point group of staggered confirmation of ethane is D3d. What do these letters D, 3 and d in this point group represent? (b) Formulate the term symbols for the ground state configuration of F atom. ...
HW / Unit 2
... 9. What is unique about the electron configurations of the noble gases and what bearing does this have on their chemical properties? 10. Give the symbols of three atoms and/or ions which are isoelectronic. ...
... 9. What is unique about the electron configurations of the noble gases and what bearing does this have on their chemical properties? 10. Give the symbols of three atoms and/or ions which are isoelectronic. ...
Document
... (C) The catalyst speeds up the reaction. (D) two of these (E) none of these 30. Which of the following should have the lowest boiling point? (A) CH4 (B) C2H6 (C) C3H8 (D) C4H10 (E) C5H12 31. The process of sublimation happens when which of the following occurs? (A) A solid becomes a liquid. (B) A li ...
... (C) The catalyst speeds up the reaction. (D) two of these (E) none of these 30. Which of the following should have the lowest boiling point? (A) CH4 (B) C2H6 (C) C3H8 (D) C4H10 (E) C5H12 31. The process of sublimation happens when which of the following occurs? (A) A solid becomes a liquid. (B) A li ...
Chapter 28 Atoms
... radius can be calculated, and a threedimensional plot can be constructed that shows regions of equal probability. The region in which there is a high probability of finding the electron is called the Electron Cloud. ...
... radius can be calculated, and a threedimensional plot can be constructed that shows regions of equal probability. The region in which there is a high probability of finding the electron is called the Electron Cloud. ...
Final Review
... how to “build-up” the order of occupation of hydrogenic orbitals, that is the atomic electronic configuration for the ground state of a many-electron or ion. Remember the special exceptions and that the s electrons are lost before the d electrons for a metal cation. Why do the s, p, and d orbitals w ...
... how to “build-up” the order of occupation of hydrogenic orbitals, that is the atomic electronic configuration for the ground state of a many-electron or ion. Remember the special exceptions and that the s electrons are lost before the d electrons for a metal cation. Why do the s, p, and d orbitals w ...
Course Syllabus - Honors Chemistry
... and identified in laboratory experiments. g.* The position of an element in the periodic table relates to its quantum electron configuration and to its reactivity with other elements in the table. h.* The experimental basis for Thomson’s discovery of the electron, Rutherford’s nuclear atom, Millikan ...
... and identified in laboratory experiments. g.* The position of an element in the periodic table relates to its quantum electron configuration and to its reactivity with other elements in the table. h.* The experimental basis for Thomson’s discovery of the electron, Rutherford’s nuclear atom, Millikan ...
Electron configuration
In atomic physics and quantum chemistry, the electron configuration is the distribution of electrons of an atom or molecule (or other physical structure) in atomic or molecular orbitals. For example, the electron configuration of the neon atom is 1s2 2s2 2p6.Electronic configurations describe electrons as each moving independently in an orbital, in an average field created by all other orbitals. Mathematically, configurations are described by Slater determinants or configuration state functions.According to the laws of quantum mechanics, for systems with only one electron, an energy is associated with each electron configuration and, upon certain conditions, electrons are able to move from one configuration to another by the emission or absorption of a quantum of energy, in the form of a photon.Knowledge of the electron configuration of different atoms is useful in understanding the structure of the periodic table of elements. The concept is also useful for describing the chemical bonds that hold atoms together. In bulk materials, this same idea helps explain the peculiar properties of lasers and semiconductors.