Scale, structure and behaviour
... Discreteness of energy It is the fact that electrons can only exist at discrete energy levels that prevents them from spiraling into the nucleus, as classical models predict. This quantization of energy, along with some other atomic properties that are quantized, give quantum mechanics its name. In ...
... Discreteness of energy It is the fact that electrons can only exist at discrete energy levels that prevents them from spiraling into the nucleus, as classical models predict. This quantization of energy, along with some other atomic properties that are quantized, give quantum mechanics its name. In ...
StandardModel
... What will happen if we try to bring it all together ? ----This synthesis of current knowledge, without any doubt is known as ---“The Standard Model ” A glimpse into the Big Bang! It is clear from the figure that all 4 forces were created from a super force during the Big-Bang! In reverse way, we are ...
... What will happen if we try to bring it all together ? ----This synthesis of current knowledge, without any doubt is known as ---“The Standard Model ” A glimpse into the Big Bang! It is clear from the figure that all 4 forces were created from a super force during the Big-Bang! In reverse way, we are ...
The Quantum-Mechanical Model of the Atom
... Matter as a wave! • If light is both particles and waves and • quantum mechanics is the theory of the very small, • then, maybe small particles act as waves. • This was shown by Prince Louis de Broglie! ...
... Matter as a wave! • If light is both particles and waves and • quantum mechanics is the theory of the very small, • then, maybe small particles act as waves. • This was shown by Prince Louis de Broglie! ...
CH4 PT1 Arrangement of Electrons
... • Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle (1927) – it is impossible to determine simultaneously both the position and velocity of an electron or any other particle. • Schrodinger Wave Equation (1926) - developed an equation that treated electrons in atoms as waves. • Heisenberg and Schrodinger laid the fo ...
... • Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle (1927) – it is impossible to determine simultaneously both the position and velocity of an electron or any other particle. • Schrodinger Wave Equation (1926) - developed an equation that treated electrons in atoms as waves. • Heisenberg and Schrodinger laid the fo ...
chapter 7 – cyu
... show up. 3. Crookes put an iron cross in the middle. The cross blocked the rays coming from the cathode end. The shadow on the one end (anode) allowed him to see where the electrons were coming from. Crookes also had another experiment using a pinwheel in which electric currents, when switched on, w ...
... show up. 3. Crookes put an iron cross in the middle. The cross blocked the rays coming from the cathode end. The shadow on the one end (anode) allowed him to see where the electrons were coming from. Crookes also had another experiment using a pinwheel in which electric currents, when switched on, w ...
MODEL EXAM physics-Sem1 29-11-2013 SET 2
... (ii).For a rubber tube, internal radius is 0.25 cm and external radius is 0.35cm. The inner temperature is 370C and outer temperature is 300C. What is the temperature at a distance of 0.5 cm from the axis of rubber tube? (12+4) 13(a)(i).What is Compton effect? Derive an expression for the frequency ...
... (ii).For a rubber tube, internal radius is 0.25 cm and external radius is 0.35cm. The inner temperature is 370C and outer temperature is 300C. What is the temperature at a distance of 0.5 cm from the axis of rubber tube? (12+4) 13(a)(i).What is Compton effect? Derive an expression for the frequency ...
Quantum phenomena
... The end of the mechanical age 1. Things move in a continuous manner. All motion, both in the large and small, exhibits continuity. 2. Things move for reasons. All motion has a history, is determinable and predictable. 3. The universe and all its constituents can be understood as complex machinery, ...
... The end of the mechanical age 1. Things move in a continuous manner. All motion, both in the large and small, exhibits continuity. 2. Things move for reasons. All motion has a history, is determinable and predictable. 3. The universe and all its constituents can be understood as complex machinery, ...
The Standard Model or Particle Physics 101
... – Small mass (almost zero, evidence for mass discovered in past few years, UMD group on experiment) – Only feel weak force (and gravity) – N -> p e ν ...
... – Small mass (almost zero, evidence for mass discovered in past few years, UMD group on experiment) – Only feel weak force (and gravity) – N -> p e ν ...
Prentice Hall Chemistry Worksheets
... 8. the distance between two adjacent crests of an electromagnetic wave ...
... 8. the distance between two adjacent crests of an electromagnetic wave ...
5 ELECTRONS IN ATOMS Vocabulary Review Name ___________________________
... 8. the distance between two adjacent crests of an electromagnetic wave ...
... 8. the distance between two adjacent crests of an electromagnetic wave ...
Photosynthesis Stores Energy in Organic Compounds
... replaced by an electron from the end of the electron transport system ...
... replaced by an electron from the end of the electron transport system ...
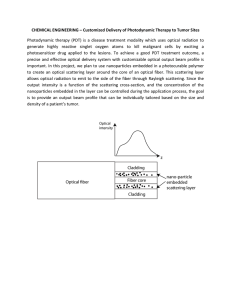
Customized Delivery of Photodynamic Therapy to Tumor Sites
... precise and effective optical delivery system with customizable optical output beam profile is important. In this project, we plan to use nanoparticles embedded in a photocurable polymer to create an optical scattering layer around the core of an optical fiber. This scattering layer allows optical r ...
... precise and effective optical delivery system with customizable optical output beam profile is important. In this project, we plan to use nanoparticles embedded in a photocurable polymer to create an optical scattering layer around the core of an optical fiber. This scattering layer allows optical r ...
Photosynthesis Stores Energy in Organic Compounds
... replaced by an electron from the end of the electron transport system ...
... replaced by an electron from the end of the electron transport system ...
13. Particle physics
... This means that there is no meson or baryon, which properties cannot be explained by a suitable combination of quarks. In the same way there does not exist any quark combination that does not correspond to an observed meson or baryon. Until the mid-70-ies there were only three quarks known. Up today ...
... This means that there is no meson or baryon, which properties cannot be explained by a suitable combination of quarks. In the same way there does not exist any quark combination that does not correspond to an observed meson or baryon. Until the mid-70-ies there were only three quarks known. Up today ...
Ch 4 – Atoms: Building Blocks of Matter
... _____________________ ___________________: the entire space that electrons occupy __________________ _________________: the most likely location in an electron cloud in which an electron can be found ...
... _____________________ ___________________: the entire space that electrons occupy __________________ _________________: the most likely location in an electron cloud in which an electron can be found ...
- dr
... spin is a fundamental characteristic property of elementary particles in particle physics and quantum physics ...
... spin is a fundamental characteristic property of elementary particles in particle physics and quantum physics ...
Handout. Using the Fine Structure Constant to Push on the Standard
... o Renormalization yields a correction to the coupling constants which depends on energy. So, the coupling constants “run”, i.e. change with energy. o We expect that if the four forces are unified, the running coupling constants will converge at some high energy. (This is one of the motivations for s ...
... o Renormalization yields a correction to the coupling constants which depends on energy. So, the coupling constants “run”, i.e. change with energy. o We expect that if the four forces are unified, the running coupling constants will converge at some high energy. (This is one of the motivations for s ...
Particles & Strings - University of Southampton
... • The missing element is the higgs that generates mass (plus explanation of why the building blocks are what they are) • Our theories of particles don’t fit with theories of gravity • String Theory is an attempt to construct a sensible theory of both • We are realizing it predicts wild possibilities ...
... • The missing element is the higgs that generates mass (plus explanation of why the building blocks are what they are) • Our theories of particles don’t fit with theories of gravity • String Theory is an attempt to construct a sensible theory of both • We are realizing it predicts wild possibilities ...
High_intensity_beam_diagnostics_system_(EURISOL)
... and proton beam intensity up to 1010 protons·s-1·mm-2. Conversion factor of MMD – electrons/particle: ranges from 0.1 (for MIP) to few hundreds (for the fast Heavy Ion), noise – Determined by the connecting cable and readout electronics – ENC: 100 – 500 electrons. Metal detectors are suitable for me ...
... and proton beam intensity up to 1010 protons·s-1·mm-2. Conversion factor of MMD – electrons/particle: ranges from 0.1 (for MIP) to few hundreds (for the fast Heavy Ion), noise – Determined by the connecting cable and readout electronics – ENC: 100 – 500 electrons. Metal detectors are suitable for me ...
Electron scattering

Electron scattering occurs when electrons are deviated from their original trajectory. This is due to the electrostatic forces within matter interaction or, if an external magnetic field is present, the electron may be deflected by the Lorentz force. This scattering typically happens with solids such as metals, semiconductors and insulators; and is a limiting factor in integrated circuits and transistors.The application of electron scattering is such that it can be used as a high resolution microscope for hadronic systems, that allows the measurement of the distribution of charges for nucleons and nuclear structure. The scattering of electrons has allowed us to understand that protons and neutrons are made up of the smaller elementary subatomic particles called quarks.Electrons may be scattered through a solid in several ways:Not at all: no electron scattering occurs at all and the beam passes straight through.Single scattering: when an electron is scattered just once.Plural scattering: when electron(s) scatter several times.Multiple scattering: when electron(s) scatter very many times over.The likelihood of an electron scattering and the proliferance of the scattering is a probability function of the specimen thickness to the mean free path.