* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Worksheet 38 (7
Big O notation wikipedia , lookup
Location arithmetic wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
History of mathematical notation wikipedia , lookup
List of important publications in mathematics wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics of radio engineering wikipedia , lookup
Vincent's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Large numbers wikipedia , lookup
Recurrence relation wikipedia , lookup
Factorization wikipedia , lookup
Quadratic reciprocity wikipedia , lookup
Fundamental theorem of algebra wikipedia , lookup
System of polynomial equations wikipedia , lookup
Elementary mathematics wikipedia , lookup
Elementary algebra wikipedia , lookup
Partial differential equation wikipedia , lookup
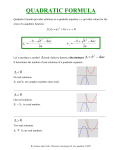
Worksheet 38 (7.1) Chapter 7 Quadratic Equations and Inequalities 7.1 Complex Numbers A complex number is any number that can be expressed in the form a + bi, where a and b are real numbers. The standard form of a complex number is a + bi. The real number a is called the real part of the complex number and the real number b is called the imaginary part of the complex number. Important definitions involving i: 1. i = - 1 2. i2 = - 1 3. - b = i b Note: The square root of any negative real number must be rewritten as an imaginary number before doing any computation. Summary 1: Warm-up 1. a) Give the real part and imaginary part of -2 + 5i. a = _____ b = _____ b) Give the standard form of -5i. _______________ c) Rewrite - 49 as an imaginary number. - 49 = i =i ( ) = ______ d) Rewrite - 45 as an imaginary number. - 45 = i ) or 3 i =i ( Worksheet 38 (7.1) Problems 151 1. Give the real part and imaginary part of 2 - 5i. 2. Give the standard form of 7. 3. Rewrite - 100 as an imaginary number. 4. Rewrite - 48 as an imaginary number. Summary 2: 1. Add the realnumbers: parts. Adding complex (a + bi) + (c + di) = (a + c) + (b + d)i 2. Add the imaginary parts. 3. Express in standard form. Subtracting complex numbers: (a + bi) - (c + di) = (a - c) + (b - d)i 1. Subtract the real parts. 2. Subtract the imaginary parts. 3. Express in standard form. Warm-up 2. Add or subtract as indicated: a) (4 - 9i) + (-8 + 3i) = (4 + ____) + (-9 + ____)i = _____ + _____i or ___________ b) (-2 - i) - (-1 - 4i) = (-2 - ____) + (-1 - ____)i = _____ + _____i Problems - Add or subtract as indicated: 5. (3 + 2i) + (-5 + 7i) 6. (3 + i) - (9 + 4i) Worksheet 38 (7.1) Summary 3: Multiplying complex numbers: 152 1. Follow summary 2 in section 3.3 for multiplying two binomials. Note: A complex number has a binomial form. 2. Replace i2 with -1. 3. Simplify to express the result in standard form. Warm-up 3. Find the following products: a) (2 + 5i)(4 + 3i) = 2( ) + 5i( ) = _____ + 6i + _____ + 15i2 = 8 + 26i - _____ = ___________ b) (3 - 5i)2 = ( = 3( )( ) ) - 5i( ) = _____ - 15i - 15i + _____ = 9 - 30i - _____ = ___________ c) (2 - 7i)(2 + 7i) = 2( ) - 7i( ) = _____ + 14i - _____ - 49i2 = _____ + 0i + _____ = ___________ Problems - Find the following products: 7. (-2 + 6i)(4 - 3i) 8. (4 - 2i)2 Worksheet 38 (7.1) 9. (1 - 3i)(1 + 3i) 153 Two complex numbers a + bi and a - bi are called conjugates of each other. Note: The product of a complex number and its conjugate is always a real number - see warm-up 3c and problem 9 in above summary. Dividing complex numbers: 1. Determine the conjugate of the denominator. 2. Multiply both numerator and denominator by this conjugate to obtain an equivalent fraction with a real-number denominator. 3. Express the result in standard form when directed to do so. Summary 4: Warm-up 4. Find the following quotients: a) b) 2i 5 - 4i 4 - 3i 7 - 2i ( 2i )( ) (5 - 4i)( ) 2i( ) + 2i( ) = 2 25 - 16 i ( )- 8 = 25 - ( ) - 8 + 10i = ( ) = = (standard form) (4 - 3i)( ) (7 - 2i)( ) 28 + ( ) - ( ) - 6 i 2 = 49 - 4 i 2 28 - ( ) + ( ) = 49 + ( ) = Worksheet 38 (7.1) = ( ) - 13i 53 = c) 7 (7)( = 5i (5i)( (standard form) ) ) 154 ( ) ( ) - 35i = ( ) = = Note: In warm-up 4c, the numerator and denominator could have been multiplied by i to produce the same result. Problems - Find the following quotients: 10. 5i - 3 + 2i 11. 3 - 4i 2+i 12. - 3 + 2i 5i Worksheet 39 (7.2) 7.2 Quadratic Equations A quadratic equation is a second-degree equation in one variable that contains a variable with an exponent of two. Summary 1: 155 For quadratic equations of the form x2 = a, where x is a variable and a is any real number, the following square root property holds true: For any real number a, x2 = a if and only if x = a or x = - a . Solving quadratic equations of the form x2 = a: 1. If necessary, rewrite the equation in the form x2 = a. 2. Apply the above square root property: x = a 3. Solve for x. 4. Write an appropriate solution set. 5. Check when directed to do so. Warm-up 1. Solve each of the following quadratic equations by applying the square root property: a) x 2 = - 16 x= The solution set is __________. x= 2 b) (n - 1 ) = 36 n - 1= n - 1= n - 1 =______ or n - 1 =______ n =______ or n =______ The solution set is __________. Worksheet 39 (7.2) 2 c) (2y - 3 ) = - 45 2y - 3 = 2y - 3 = i 2y - 3 = 3 i 3i 5 2y = y= The solution set is ___________. 2 2 d) 2(y + 5 ) - 9 = 41 2 2(y + 5 ) = (y + 5 )2 = y+5 = or y + 5 = y +5= 156 y= or y = The solution set is __________. Problems - Solve each of the following quadratic equations by applying the square root property: 1. y 2 = - 49 2. (m - 2 )2 = 16 3. (3x - 2 )2 = - 48 Worksheet 39 (7.2) 4. 3(x + 1 )2 - 10 = 65 Summary 2: Using the Pythagorean Theorem, summary 3 in section 3.7, can also lead to solving quadratic equations in the form x2 = a. Warm-up 2. Set up and write an algebraic equation, then solve: Note: Drawing a figure is helpful in the word problem which follows. a) A rectangular parking lot is 25 yards wide. Find, to the nearest yard, the length of the parking lot if the diagonal is 50 yards long. Let x = length of rectangular lot a2 + b2 = c2 ( )2 + 252 = 50 2 2 = 2500 x + 2 x = x = 157 x The length of the parking lot is _______ yards. Problem - Set up and write an algebraic equation, then solve: 5. Find, to the nearest tenth, the length of one side of a square with a diagonal that is 20 meters long. Worksheet 40 (7.3) 7.3 Completing the Square Summary 1: The coefficient is often referred to as the2 leading TheNote: standard form of a aquadratic equation is ax + bx + ccoefficient. = 0, where a, b, and c are real numbers and a0. A perfect square trinomial results from squaring a binomial: (x + a)2 = x2 + 2ax + a2 Note: The constant in a perfect square trinomial is equal to the square one-half of the coefficient of the x-term. Rewriting a quadratic equation in the form x2 = a: 1. Put the given equation in standard form. 2. If the leading coefficient is not 1, apply the multiplication property of equality by dividing each term on both sides by the given leading coefficient. 3. Apply the addition property of equality to move the constant to the right side of the equation. 4. Examine the remaining terms on the left side to determine what value must be added to obtain a perfect square trinomial on the left side of the equation. This is done by finding the square of one-half of the coefficient of the x-term. 5. Apply the addition property of equality by adding the result from step 4 to both sides of the equation. 6. Express the perfect square trinomial found in step 5 as the square of a binomial. 7. The quadratic equation is now in the form x2 = a where x represents a binomial and a represents a real number. 158 of Warm-up 1. Rewrite the given equation in the form x2 = a: 2 y 2 + 8y + 10 = 0 a) 0 2 y2 8y 10 = + + ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) 2 y +( =0 )+ 5 2 =( y + 4y ) Worksheet 40 (7.3) To complete the square for y2 + 4y: a) ½(4) = 2 b) (2)2 = 4 2 y + 4y + ( ) = - 5 +( 2 y + 4y + 4 ( b) 2 x -( )-( =( 2 159 ) =-1 ) x )=0 ) 2 = 3x + 10 2 x - 3x = ( ) 2 To complete the square for x - 3x: a) ½(-3) = -32 2 b) -32 = 94 2 x - 3x + ( ) = 10 + ( ) 2 = ( 4 ) + 94 x - 3x + 94 ( 2 = ) 49 4 Problems - Rewrite the given equation in the form x2 = a: 1. y 2 - 10y + 28 = 0 2. 2 x2 = 5x + 3 Worksheet 40 (7.3) Completing the square refers to the method used to solve any quadratic equation by rewriting it first in the form x2 = a. Solving quadratic equations by completing the square: 1. Rewrite the quadratic equation in the form x2 = a - see summary 1 above. 2. Apply the square root property: x2 = a if and only if x = a - see summary 1 in section 6.2. 3. Solve for x. 4. Write an appropriate solution set. 5. Check when directed to do so. Summary 2: Warm-up 2.Solve by completing the square: 160 a) 2 y - 10y + 28 2 =0 =( y - 10y 2 y - 10y + ( ) ) = - 28 + ( 2 y - 10y + 25 ( ) =( ) 2 ) =-3 y -5 = ) -3 y =( y =5i The solution set is _____________. b) 2 x2 2 x2 - ( ) - ( ) = 0 2 x2 5x 3 0 = ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) = 5x + 3 Worksheet 40 (7.3) 2 x - 52 x - ( 2 x - 52 x ) =0 = 32 2 ) = 32 + ( x - 52 x + ( 2 25 = ( 16 x - 52 x + 16 ( ) ) 2 49 ) = 16 x - 45 = ) x - 45 = ( 5 5 x- 4= or x - 4 = or x= The solution set is __________. Problems - Solve by completing the square: 3. 3 x2 = 14x + 5 161 x= 4. y 2 + 8y + 25 = 0 Worksheet 41 (7.4) 7.4 The Quadratic Formula Summary 1: The quadratic formula is derived from completing the square to solve ax2 + bx + c = 0 for x. The quadratic formula is used to solve any quadratic equation in standard form. The Quadratic Formula: - b b2 - 4ac 2a Note: Since the quadratic formula is frequently used in algebra, it is common to memorize the formula for instant recall. Given ax2 + bx + c = 0, x = Using the quadratic formula to solve any quadratic equation: 1. If necessary, rewrite the given equation in standard form: ax2 + bx + c = 0 2. Identify a, b, and c from the standard form. - b b2 - 4ac 2a 4. Substitute a, b, and c in the quadratic formula to evaluate x. 5. Write an appropriate solution set. 6. Check when directed to do so. 3. Recall the quadratic formula: x = 162 Warm-up 1. Solve using the quadratic formula: 2 a) x + 2x = 2 2 x + 2x - 2 = ( ) ; a = ____, b = ____, c = ____ x= x= - b b2 - 4ac 2a -( ) ( 2 ) - 4( 2( ) )( ) Worksheet 35 (7.4) ) 4 +( ) 2 -2 x= 2 -2 2 x= 2 2( ) x= 2 The solution set is ____________. x= x= ( 163 b) 2y(y + 3) = - 17 2 y + y= y= y= y= = 0 ; a = ____, b = ____, c = ____ y+ - b b2 - 4ac 2a ) ( -( ( 2 ) - 4( 2( ) ) ( )-( )( ) ) 4 -6 4 -6 ( y= 4 2( y= 4 y= ) ) The solution set is ____________. Worksheet 41 (7.4) c) 6 n2 - 5n - 25 = 0 ; a = ____, b = ____, c = ____ n= n= n= -b -( 2 b - 4ac 2a ) ( 5 ( ( 2 ) - 4( 2( ) )+( ) )( ) ) 5 12 5 ( ) n= 12 5 +( ) 5 -( ) n= or n = 12 12 or n = n= n= The solution set is __________. Note: 6n2 - 5n - 25 = 0 can also be solved by factoring 6n2 - 5n - 25. Try it. 164 Problems - Solve using the quadratic formula: 1. x2 + 7 = 3x 2. 2x2 + 5x = 3 3. 4x2 - 20x + 25 = 0 Worksheet 41 (7.4) The root of an equation is another name for solution. Summary 2: 165 The discriminant is the number which appears under the radical sign (radicand) in the quadratic formula: b2 - 4ac. The discriminant indicates the kind of roots a quadratic equation will have. It allows for looking ahead to tell the type of solution that can be expected. Nature of roots for ax2 + bx + c = 0: 1. If b2 - 4ac < 0, then the equation has two nonreal complex solutions. 2. If b2 - 4ac = 0, then the equation has one real solution with multiplicity of two. 3. If b2 - 4ac > 0, then the equation has two real solutions. Evaluating the discriminant to determine the nature of the roots for a quadratic equation: 1. Rewrite equation in standard form: ax2 + bx + c = 0 2. Identify a, b, and c from the standard form. 3. Recall the expression for the discriminant: b2 - 4ac 4. Substitute a, b, and c and evaluate the expression. 5. Use this value to compare to 0, see list above, and determine the type of solution that will be obtained. Note: The equation can be solved to verify the conclusions made using the discriminant. 166 Warm-up 2. Use the discriminant to determine the nature of the roots: a) x2 + 5x - 24 = 0 ; a = ____, b = ____, c = ____ b2 - 4ac = ( )2 - 4( )( = 25 + ( ) = _____ ) Circle the true statement: 121 < 0 ; two nonreal complex solutions 121 = 0 ; one real solution with a multiplicity of two 121 > 0 ; two real solutions Therefore, x2 + 5x - 24 = 0 has _______________ solutions. Worksheet 41 (7.4) b) 2y2 + 17 = 6y ____________________ = 0 ; a = ____, b = ____, c = ____ b2 - 4ac = ( )2 - 4( )( = _____ - 136 = _____ ) Circle the true statement: -100 < 0 ; two nonreal complex solutions -100 = 0 ; one real solution with multiplicity of two -100 > 0 ; two real solutions Therefore, 2y2 + 17 = 6y has ______________________ solutions. Problems - Use the discriminant to determine the nature of the roots: 4. 9x2 - 12x = 60 5. x2 + 12x + 36 = 0 167 Summary 3: All quadratic equations have two roots, x1 and x2. Note: When b2 - 4ac = 0, there is one real solution with a multiplicity of two. This means that the two roots are equal. Given ax2 + bx + c = 0 with roots x1 and x2, the two following relationships hold true: b 1. Sum of the Roots: x1 + x2 = a c 2. Product of the Roots: (x1)(x2) = a Both of these relationships can be tested. If both test true, then the values are in the solution set. The sum and product of the roots can be used to replace traditional checking which may be cumbersome with irrational or complex roots. Worksheet 41 (7.4) Warm-up 3. Use the sum and product of the roots to check the previously solved equations: a) y2 - 10y + 28 = 0 (See warm-up 2(a) in section 6.3.) Solution Set = 5 + i 3 , 5 - i 3 x1 + x2 = - Sum of the Roots: ( 168 )+( )= -( ( b a ) ) 10 = 10 Product of the Roots: ( x1 )( x 2 ) = ( ( ) ( ) ) = 28 28 = 28 )= )( ( c a )+( Problems - Use the sum and product of the roots to check the previously solved equations: 6. 6n2 - 5n - 25 = 0 (See warm-up 1(c) in this section.) Solution Set = 156 , - 53 7. x2 + 2x = 2 (See warm-up 1(a) in this section.) Solution Set = - 1 + 3 , - 1 - 3 Worksheet 42 (7.5) 7.5 More Quadratic Equations and Applications Key Factors to Consider when Solving Quadratic Equations Summary 1: 169 1. The factoring method works only when the polynomial, written in standard form is factorable. 2. Completing the square works for any quadratic equation. It can often lead to cumbersome fractions and is usually used only when the directions specifically request this method. It is considered an important skill because it is used in other situations in algebra. 3. The quadratic formula works for any quadratic equation. It is used when it has been determined that the polynomial in the standard form equation is not factorable or appears to be difficult to factor. Warm-up 1. Set up and write an algebraic equation, then solve using any appropriate method: a) Find two consecutive even whole numbers such that the sum of their squares is 1252. Let x = first of two consecutive even whole numbers _____ = second of two consecutive even whole numbers ( )2 + ( )2 x + _____ + 4x + _____ _____ + 4x + 4 2x2 + 4x - _____ 2( ) 2 x + 2x - 624 x2 + 2x 2 x + 2x + _____ 2 170 = 1252 = 1252 = 1252 =0 =0 =0 = 624 = 624 + _____ (x + 1)2 = _____ x + 1= 625 x = -1 ± 25 x = _____ x + 2 = _____ or x = _____ The two consecutive even whole numbers are _____ and _____. Worksheet 42 (7.5) b) The length of a rectangular plot of ground is three more than twice its width. It is surrounded by a sidewalk of uniform width of 3 meters. Find the dimensions of the plot of ground if the area including the sidewalk is 819 square meters. Let x = width of rectangular plot of ground _______ = length of rectangular plot of ground _______ = width of rectangle including sidewalk _______ = length of rectangle including sidewalk Note: Drawing a figure is helpful in this word problem. ( 2 2 x +( )( ) )+( ) = 819 = 819 2 x2 + 21x - 765 x= x= -b -( =0 2 b - 4ac 2a ) ( )2 - 4( 2( ) )( ) - 21 4 - 21 81 x= 4 102 60 x= or x = 4 4 x = _____ ; 2x + 3 = _____ The dimensions are ________ by ________. x= 171 Worksheet 42 (7.5) Problems - Set up and write an algebraic equation, then solve: n(n - 3) yields the number of diagonals, D, in a polygon of n 2 sides. Find the number of sides of a polygon that has 35 diagonals. 1. The formula D = 2. At a point 8 yards from the base of a tower, the distance to the top of the tower is 2 yards more than the height of the tower. Find the height of the tower. 172 Worksheet 43 (7.6) 7.6 Quadratic Inequalities Summary 1: Quadratic inequalities in one variable are expressed in one of the following forms: 173 1. ax2 + bx + c > 0 2. ax2 + bx + c 0 3. ax2 + bx + c < 0 4. ax2 + bx + c 0 A critical number in a quadratic inequality is a number that makes the given polynomial equal to zero. It is used to help determine those values that make the inequality true. Finding the critical numbers on a number line for a quadratic inequality: 1. Set ax2 + bx + c = 0 and solve for x by factoring. 2. The critical numbers are located on a number line to prepare for graphing. Finding the solution of a quadratic inequality using a number line analysis: 1. Express the inequality in standard form. 2. Determine the critical numbers. 3. Organize a chart to determine appropriate intervals found by locating critical numbers on a number line. 4. Choose one test number from within each interval and see how it affects the sign of each factor. Use multiplication sign rules to determine whether or not the standard form inequality tests true. Note: A positive product is always > 0. A negative product is always < 0. 5. Shade intervals that test true. 6. Use ( or ) for those critical numbers that are excluded from the solution: ax2 + bx + c > 0 or ax2 + bx + c < 0. Use [ or ] for those critical numbers that are included in the solution: ax2 + bx + c 0 or ax2 + bx + c 0. 7. Use set builder notation and/or interval notation to express the solution. Worksheet 43 (7.6) Warm-up 1. Solve: a) x2 - x - 12 > 0 (x - 4)(x + 3) > 0 174 Determine critical numbers: (x - 4)(x + 3) = 0 x = ______ or x = ______ Organize a chart for number line analysis: (x - 4)(x + 3)=0 (x - 4)(x + 3)=0 | | -4 | 0 | 5 | | <--------------(-3)--------------(4)---------------> (x - 4) is (-) | (x - 4) is (-) | (x - 4) is (+) (x + 3) is (-) | (x + 3) is (+) | (x + 3) is (+) | | Their product | Their product | Their product is positive. is negative. ( > 0) test values number line sign of product is positive. ( < 0) ( > 0) Graph results on a number line: x2 - x - 12 > 0 (x - 4)(x + 3) > 0 <--------------------------------> -3 4 Set builder notation:_______________ b) y2 - 6y + 5 0 (y - 5)(y - 1) 0 Determine critical numbers: (y - 5)(y - 1) = 0 y = ______ or y = ______ Worksheet 43 (7.6) Organize a chart for number line analysis: (y - 5)(y - 1)=0 (y - 5)(y - 1)=0 | | 175 Interval notation:__________ 0 | 2 | 6 | | <---------------(1)--------------(5)---------------> (y - 5) is (-) | (y - 5) is (-) | (y - 5) is (+) (y - 1) is (-) | (y - 1) is (+) | (y - 1) is (+) | | Their product | Their product | Their product is positive. ( > 0) is negative. test values number line sign of product is positive. ( < 0) ( > 0) Graph results on a number line: y2 - 6y + 5 0 (y - 5)(y - 1) 0 <--------------------------------> 1 5 Set builder notation:_______________ Interval notation:__________ Problems - Solve: 1. x2 + x - 12 0 2. y2 + 6y + 5 < 0 Worksheet 43 (7.6) Summary 2: 176 Rational inequalities in one variable can be 1. xx ++ ba > 0 that are indicated 2. xx ++ ba quotients 0 solved3.using x + a a number line analysis 4. xx ++ ba 0when expressed in one of the x+b < 0 following forms: The inequalities in one of the above forms have critical numbers which are determined in each of the following ways: 1. Critical numbers determined by setting the numerator equal to zero. These are numbers that make the quotient = 0. 2. Critical numbers determined by setting the denominator equal to zero. These are numbers that make the quotient undefined. Finding the solution of a rational inequality using a number line analysis: 1. Express the inequality in one of the above forms. Note: Use LCD to add or subtract rational expressions as one indicated quotient. 2. Determine the critical numbers. 3. Organize a chart to determine appropriate intervals found by locating the critical numbers on a number line graph. 4. Choose a test number in each interval and see how it affects the sign of the factor in the numerator and the sign of the factor in the denominator. Use division sign rules to determine whether or not the indicated quotient in one of the above forms tests true. Note: A positive quotient is always > 0. A negative quotient is always < 0. 5. Shade intervals that test true. 6. Use ( or ) for those critical numbers that are excluded from the solution: xx ++ ba > 0 , xx ++ ba < 0 ,and critical numbers that make the quotient undefined. Use [ or ] for those critical numbers that are included in the solution: x+a x+a x + b 0 or x + b 0 7. Use set builder notation and/or interval notation to express the solution when directed to do so. Worksheet 43 (7.6) Warm-up 2. Solve: 177 a) x -1 <0 x+5 Determine critical numbers x-1=0 x+5=0 x = ______ x = ______ Organize a chart for number line analysis x -1 x+5 undefined =0 | | | 0 | 2 | | <--------------(-5)--------------(1)---------------> (x - 1) is (-) | (x - 1) is (-) | (x - 1) is (+) (x + 5) is (-) | (x + 5) is (+) | (x + 5) is (+) | | The quotient | The quotient | The quotient -6 is positive. is negative. ( > 0) test values number line sign of quotient is positive. ( < 0) ( > 0) Graph results on a number line x -1 <0 x+5 <--------------------------------> -5 1 Set builder notation:_____________ Interval notation:_________ 2x + 10 1 x+4 2x + 10 -1 x+4 b) Worksheet 43 (7.6) 2x + 10 ( x+4 ( 2x + 10 - ( ) - ( x+4 ) 0 ) ) 0 ( ) x+4 0 178 Determine critical numbers x+6=0 x+4=0 x = ______ x = ______ Organize a chart for number line analysis x+6 x+4 undefined =0 | | -7 | -5 | 0 | | <--------------(-6)-------------(-4)---------------> (x + 6) is (-) | (x + 6) is (+) | (x + 6) is (+) (x + 4) is (-) | (x + 4) is (-) | (x + 4) is (+) | | The quotient | The quotient | The quotient is positive. ( > 0) is negative. test values number line sign of quotient is positive. ( < 0) ( > 0) Graph results on a number line 2x + 10 1 x+4 x+6 0 x+4 <--------------------------------> -6 -4 Set builder notation:_____________ Interval notation:_________ Worksheet 43 (7.6) Problems - Solve: 3. x+3 0 x-2 179 4. x -1 + 1< 0 x-2 180