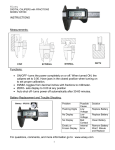
* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Proposal for Battery Facilities Technical and Operating Requirements Work Group Session
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Telecommunications engineering wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Proposal for Battery Facilities Technical and Operating Requirements Work Group Session November 20th, 2013 Battery Facilities – Work Group – Nov 20th, 2013 Agenda • Introductions • Background • Purpose – Q&A on AESO Paper “Proposal for Battery Facilities Technical and Operating Requirements” – Review each section to ensure market participant understanding of the proposals contained within the paper • Discussion of Technical Requirements • Additional Questions and Comments on Technical Requirements • Next Steps 2 Battery Facilities – Work Group – Nov 20th, 2013 Background • 2011 – AESO & Alberta Innovates Technology Futures conduct a study on using ES to support dispatch of WAGFs • FERC issues direction to allow non-generating resources to participate in energy and OR markets • 2012 – interest in integrating ES facilities into the Alberta Market increased – driven by the funding initiative of CCEMC – currently three ES projects with SASR’s, two of which are batteries • 2013 – NERC approves new BAL-002-WECC-1 which allows nongenerating resources to participate in energy and OR markets – Awaiting FERC approval before being adopted in Alberta 3 Battery Facilities – Work Group – Nov 20th, 2013 Purpose • Two projects with SASR’s for battery facilities – All facilities must connect to the transmission system with requirements that promote the safe and reliable operation on the transmission system – The requirements must be fair and efficient for all market participants – The current rules/standards for generating units and WAGF’s are not a good fit for batteries due to the unique technical and operational characteristics of batteries • The proposed rules 502.13 and 502.14 will address the issues for the interconnection and operation of the battery facilities 4 Battery Facilities – Work Group – Nov 20th, 2013 Purpose • As required, other rules will be created or updated to address: – other ES technologies such as: • pumped storage hydro; • compressed air energy storage; • flywheels; and • super-conducting magnetic energy storage – markets-related issues; – operating reserve (OR) technical requirements or procurement practices; and – ISO tariff 5 Battery Facilities – Work Group – Nov 20th, 2013 Technical Requirements - General • AESO proposal: Battery facility technical requirements will be generally in alignment with the requirements for synchronous generating units. • AESO proposal: Performance-based and not equipmentbased requirements. • AESO proposal: Refer to the batteries as a source and sink resource. – More accurately describes the behaviour of batteries than: • generation and load • positive and negative generator 6 Battery Facilities – Work Group – Nov 20th, 2013 Technical Requirements - General • AESO proposal: Create two rules: – 502.13 for the connection of a battery facility which would incorporate the engineering, design and construction requirements. – 502.14 for the operation of a battery facility which would incorporate the ongoing operation and testing requirements. • Similar to the layout of the proposed generator rules (proposed sections 502.5 and 502.6 of the ISO rules). The format of these rules was well received by participants during the consultation period on these rules. 7 Battery Facilities – Work Group – Nov 20th, 2013 Technical Requirements - General • For interconnection and operation the impact on other existing ISO rules may need to be reviewed and have incidental amendments: – Section 502.4 Automated Dispatch and Messaging System and Voice Communication System Requirements; – Section 502.3 Protection Technical Requirements; and – Section 502.8 SCADA Technical Requirements 8 Battery Facilities – Work Group – Nov 20th, 2013 Technical Requirements - General • AESO proposal: The technical requirements will be applicable to all transmission connected battery facilities regardless of size. – This is consistent with both synchronous generating units and WAGFs. – It is the AESO’s view that small battery facilities are more likely to be distribution connected and the legal owner of an electric distribution system (DFO) will have its own technical and operating requirements, which are outside the scope of this proposal. 9 Battery Facilities – Work Group – Nov 20th, 2013 Technical Requirements Energy Storage - Battery Facility Single Line Diagram 10 Battery Facilities – Work Group – Nov 20th, 2013 Technical Requirements Maximum Authorized Real Power (MARP) • AESO proposal: Review the current definition of MARP to determine if it needs to be revised. – Should MARP be applied to the full range of the battery capability or only to the sourcing capability? • • The workgroup may need to consider battery facilities that do not have symmetrical sourcing and sinking capabilities. AESO proposal: The market participant will declare the MARP that is alignment with other aspects of the rule. – This aligns with technical requirements for WAGF’s and synchronous generating units. 11 Battery Facilities – Work Group – Nov 20th, 2013 Technical Requirements Maximum Authorized Real Power (MARP) - Example • The facility has a 15 MWhr battery – – The facility could be designed to source: • 5 MW for three hours; or • 15 MW for one hour In either case the facility could be designed to sink: • 5 MW for three hours; or • 15 MW for one hour – If only sourcing capability is considered the possible MARP’s are 5 or 15 MW. – If only sourcing and sinking capabilities are considered the range of possible MARP’s are 10 through to 30 MW. – A key issue will be transformer sizing. 12 Battery Facilities – Work Group – Nov 20th, 2013 Technical Requirements Operating Voltage Requirements • AESO proposal: The market participant provides the AESO with the values for the high side voltage of the inverter transformer and the high side voltage of the transmission system step-up transformer. – The high side voltage of the inverter transformer to be used to assess/confirm compliance to the reactive power and the voltage regulation capabilities of the facility; and – The high side voltage of the transmission system step-up transformer to be used to assess/confirm compliance to the voltage ride through capabilities. – This aligns with technical requirements for WAGF’s and synchronous generating units. 13 Battery Facilities – Work Group – Nov 20th, 2013 Technical Requirements Voltage Ride-Through Requirements • AESO proposal: The battery facility meets the requirements of the NERC reliability standard PRC-024-1 – This requirement would be applicable when the battery facility is operating as a source or a sink. – Note when the AESO adopts PRC-024-1 the AESO will remove this from the rule. 14 Battery Facilities – Work Group – Nov 20th, 2013 Technical Requirements Voltage Ride-Through Requirements 15 Battery Facilities – Work Group – Nov 20th, 2013 Technical Requirements Voltage Regulation • AESO Proposal: The battery facility has a voltage regulating system (VRS) that is in-service and controlling voltage whether the facility is operating as a source or sink. – Power flow can be ramped very quickly from source to sink and back again. – Turning the VRS on and off as the battery facility ramps from sink to source and back may cause the transmission system voltage to fluctuate at unacceptable levels. – If this occurs several times in an hour it may result in unacceptable flicker on the transmission system. – The point of control must not be the transmission system. 16 Battery Facilities – Work Group – Nov 20th, 2013 Technical Requirements Voltage Regulation • AESO Proposal: For battery facilities located within other generating facilities such as WAGFs the participant may use the existing VRS to control the battery facilities. – The VRS must be in service when the battery facility is in service regardless of the state of the WAGF. 17 Battery Facilities – Work Group – Nov 20th, 2013 Technical Requirements Reactive Power Capability • AESO Proposal: The battery facilities have a full dynamic reactive power capability whether the facility is operating as a source or sink. – This proposal is in alignment with the proposal for voltage regulation. – Battery facilities located within other generating facilities such as WAGF’s the participant may use that facility’s reactive power resources in place of using the battery facility. – The reactive power obligations of the facility must be in alignment with the MARP associated with the entire facility. 18 Battery Facilities – Work Group – Nov 20th, 2013 Technical Requirements Reactive Power Capability 19 Battery Facilities – Work Group – Nov 20th, 2013 Technical Requirements Reactive Power Capability 20 Battery Facilities – Work Group – Nov 20th, 2013 Technical Requirements Transmission System Step-up Transformer • AESO Proposal: The capability of the transformer must allow for the vector sum of the real power capability and the reactive power obligations of the battery facility. – This is in alignment with the requirements for WAGFs and synchronous generating units. • A favorable circuit to block the transmission of harmonic currents; • Isolation of transmission system side ground fault current contributions; and • An effectively grounded wye connection on the high voltage side of the transmission system step up transformer. 21 Battery Facilities – Work Group – Nov 20th, 2013 Technical Requirements Off Nominal Frequency • AESO proposal: The battery facility meets the requirements of the NERC reliability standard PRC-024-1 – This requirement would be applicable when the battery facility is operating as a source or a sink – Note when the AESO adopts PRC-024-1 the AESO will remove this from the rule Frequency (Hz) >61.7 Hz 61.6 Hz to 61.7 Hz 60.6 Hz to <61.6 Hz >59.4 Hz to <60.6 Hz >58.4 Hz to 59.4 Hz >57.8 Hz to 58.4 Hz >57.3 Hz to 57.8 Hz >57.0 Hz to 57.3 Hz ≤57.0 Hz Minimum Time Delay 0 seconds 30 seconds 3 minutes Continuous Operation 3 minutes 30 seconds 7.5 seconds 45 cycles 0 seconds 22 Battery Facilities – Work Group – Nov 20th, 2013 Technical Requirements Off Nominal Frequency – Tripping must not take place inside the red and blue boundaries – Tripping may take place outside the red and blue boundaries 62.5 62 Instantaneous tripping is permitted at 61.7 Hz and above. < 61.7 and > 61.6 Hz @ 30 s 61.5 61 < 61.6 and > 60.6 Hz @ 180 s 60.5 Frequency (Hertz) 60 > 59.4and < 61.6Hz = continuous operation 59.5 59 > 58.4 and < 59.4 Hz @ 180 s 58.5 > 57.8 and < 58.4 Hz @ 30 s 58 57.5 > 57.3 and < 57.8 Hz @ 7.5 s 57 > 57 and < 57.3 Hz @ 0.75 s Instantaneous tripping is permitted at 57.0 Hz and below. 56.5 56 -50 0 50 100 150 Time (seconds) Under Frequency Requirement 200 250 300 Over Frequency Requirement 23 Battery Facilities – Work Group – Nov 20th, 2013 Technical Requirements Frequency Responsive Control System • AESO proposal: The battery facility has frequency responsive control system requirements when sourcing or sinking real power. – respond to both over and under frequency events. – The response characteristics would be similar to that of generating units in terms of droop, dead band, etc. 24 Battery Facilities – Work Group – Nov 20th, 2013 Technical Requirements Real Power and Ramp Rate Control • AESO proposal: The battery facility has real power and ramp rate control systems in service whether sourcing or sinking real power. – Battery facilities can ramp from full charge to full discharge in a few cycles, and depending on the size and location of the facility this behavior could appear as a system disturbance rather than assistance to transmission system. – There are similar issues with WAGF’s and the AESO uses a default setting of 10% of the facility rating per minute. • There maybe advantages of a higher ramp rate for battery facilities. • The exact number may have to be developed on a project by project basis. 25 Battery Facilities – Work Group – Nov 20th, 2013 Technical Requirements Power Quality • AESO proposal: The battery facility has power quality requirements that are applicable to the battery energy storage facility when sourcing or sinking real power. • The key parameters will be similar to WAGF’s and synchronous generating units including: – voltage flicker; – harmonic control; – resonance; and – voltage unbalance. 26 Battery Facilities – Work Group – Nov 20th, 2013 Technical Requirements WECC Stability Control • AESO proposal: The battery facility will have no requirements for stability control systems at this time but if in the future either the WECC or the AESO require such systems that battery facilities have this capability. – At this time there are no requirements from WECC to have stability control systems similar to power system stabilizers. – It is the AESO’s understanding that battery facilities will not contribute to either intra- or inter-area oscillations but may have the ability to assist in decreasing the oscillations. 27 Battery Facilities – Work Group – Nov 20th, 2013 Technical Requirements Synchrophasor Measurement • AESO proposal: Synchrophasor measurement systems be installed at the battery facility’s the high voltage side of both the inverter transformer and transmission system step up transformer. – The AESO believes that such a system will provide valuable information to both the participant and the AESO regarding the performance of the battery facility. – Modern protective relays have this capability built in. 28 Battery Facilities – Work Group – Nov 20th, 2013 Technical Requirements Facilities Testing Post Connection • AESO proposal: The voltage regulation and power conversion models be validated during commissioning. • AESO proposal: The models be revalidated every five years. • AESO proposal: The reactive capability of the battery facility will also be verified at the same intervals. – The proposals are in alignment with the synchronous generating unit’s rules and upcoming NERC reliability standards. 29 Battery Facilities – Work Group – Nov 20th, 2013 Next Steps • AESO proposal: The following matters will be implemented in alignment with the requirements for WAGF’s and synchronous generators. • facilities disconnection • isolating devices • fault interrupting devices • operator availability • grounding • lightning surge protection • requirements to operate and maintain a battery facility in accordance with ISO rules • requirements for operation at maximum authorized real power • operating data requests 30 Additional Questions and Comments on the Technical Requirements • Are there any other comments on the battery facility technical requirements? 31 Battery Facilities – Work Group – Nov 20th, 2013 Technical Requirements • The AESO invites stakeholders to provide comments on this paper by December 11, 2013 on the proposals for the technical requirements for battery facilities brought forward in the paper. • The AESO will respond to the comments in Q1 2014. • After a review of the comments the AESO will determine the need for additional work group sessions. 32 Thank you