* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ics8543.pdf
Time-to-digital converter wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Transmission line loudspeaker wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Linear time-invariant theory wikipedia , lookup
Control system wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Scattering parameters wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Immunity-aware programming wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Analog-to-digital converter wikipedia , lookup
Integrating ADC wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Flip-flop (electronics) wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
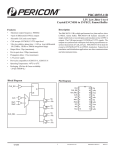
ICS8543 Integrated Circuit Systems, Inc. LOW SKEW, 1-TO-4 DIFFERENTIAL-TO-LVDS FANOUT BUFFER GENERAL DESCRIPTION FEATURES The ICS8543 is a low skew, high performance 1-to-4 Differential-to-LVDS Clock Fanout Buffer HiPerClockS™ and a member of the HiPerClockS™ family of High Performance Clock Solutions from ICS. Utilizing Low Voltage Differential Signaling (LVDS) the ICS8543 provides a low power, low noise, solution for distributing clock signals over controlled impedances of 100Ω. The ICS8543 has two selectable clock inputs. The CLK, nCLK pair can accept most standard differential input levels. The PCLK, nPCLK pair can accept LVPECL, CML, or SSTL input levels. The clock enable is internally synchronized to eliminate runt pulses on the outputs during asynchronous assertion/deassertion of the clock enable pin. • 4 differential LVDS outputs Guaranteed output and part-to-part skew characteristics make the ICS8543 ideal for those applications demanding well defined performance and repeatability. • Part-to-part skew: 500ps (maximum) ICS • Selectable differential CLK, nCLK or LVPECL clock inputs • CLK, nCLK pair can accept the following differential input levels: LVPECL, LVDS, LVHSTL, SSTL, HCSL • PCLK, nPCLK supports the following input types: LVPECL, CML, SSTL • Maximum output frequency: 800MHz • Translates any single ended input signal to LVDS levels with resistor bias on nCLK input • Output skew: 40ps (maximum) • Propagation delay: 2.6ns (maximum) • 3.3V operating supply • 0°C to 70°C ambient operating temperature • Lead-Free package available • Industrial temperature information available upon request BLOCK DIAGRAM PIN ASSIGNMENT GND CLK_EN CLK_SEL CLK nCLK PCLK nPCLK OE GND VDD D CLK_EN Q LE CLK nCLK PCLK nPCLK CLK_SEL 0 1 Q0 nQ0 Q1 nQ1 Q2 nQ2 20 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 Q0 nQ0 VDD Q1 nQ1 Q2 nQ2 GND Q3 nQ3 ICS8543 Q3 nQ3 20-Lead TSSOP 4.4mm x 6.5mm x 0.92mm body package G Package Top View OE 8543BG 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 www.icst.com/products/hiperclocks.html 1 REV. D JUNE 16, 2004 ICS8543 Integrated Circuit Systems, Inc. LOW SKEW, 1-TO-4 DIFFERENTIAL-TO-LVDS FANOUT BUFFER TABLE 1. PIN DESCRIPTIONS Number Name 1, 9, 13 GND Power Type Description 2 CLK_EN Input Pullup 3 CLK_SEL Input Pulldown 4 CLK Input Pulldown 5 nCLK Input Pullup 6 PCLK Input Pulldown 7 nPCLK Input Pullup 8 OE Input Pullup Power supply ground. Synchronizing clock enable. When HIGH, clock outputs follows clock input. When LOW, Q outputs are forced low, nQ outputs are forced high. LVCMOS / LVTTL interface levels. Clock select input. When HIGH, selects PCLK, nPCLK inputs. When LOW selects CLK, nCLK inputs. LVCMOS / LVTTL interface levels. Non-inver ting differential clock input. Inver ting differential clock input. Non-inver ting differential LVPECL clock input. 10, 18 VDD Power Inver ting differential LVPECL clock input. Output enable. Controls enabling and disabling of outputs Q0, nQ0 through Q3, nQ3. When logic HIGH, the outputs are active. When logic LOW, the outputs are in high impedance state. LVCMOS/ LVTTL interface levels. Positive supply pins. 11, 12 nQ3, Q3 Output Differential output pair. LVDS interface levels. 14, 15 nQ2, Q2 Output Differential output pair. LVDS interface levels. 16, 17 nQ1, Q1 Output Differential output pair. LVDS interface levels. 19, 20 nQ0, Q0 Output Differential output pair. LVDS interface levels. NOTE: Pullup and Pulldown refer to internal input resistors. See Table 2, Pin Characteristics, for typical values. TABLE 2. PIN CHARACTERISTICS Symbol Parameter CIN Input Capacitance Test Conditions Minimum Typical 4 Maximum Units pF RPULLUP Input Pullup Resistor 51 KΩ RPULLDOWN Input Pulldown Resistor 51 KΩ 8543BG www.icst.com/products/hiperclocks.html 2 REV. D JUNE 16, 2004 ICS8543 Integrated Circuit Systems, Inc. LOW SKEW, 1-TO-4 DIFFERENTIAL-TO-LVDS FANOUT BUFFER TABLE 3A. CONTROL INPUT FUNCTION TABLE Inputs Outputs OE CLK_EN CLK_SEL Selected Source Q0:Q3 nQ0:nQ3 0 X X Hi Z Hi Z 1 0 0 CLK, nCLK Disabled; Low Disabled; High 1 0 1 PCLK, nPCLK Disabled; Low Disabled; High 1 1 0 CLK, nCLK Enabled Enabled 1 1 1 PCLK, nPCLK Enabled Enabled After CLK_EN switches, the clock outputs are disabled or enabled following a rising and falling input clock edge as shown in Figure 1. In the active mode, the state of the outputs are a function of the CLK, nCLK and PCLK, nPCLK inputs as described in Table 3B. Enabled Disabled nCLK, nPCLK CLK, PCLK CLK_EN nQ0:nQ3 Q0:Q3 FIGURE 1. CLK_EN TIMING DIAGRAM TABLE 3B. CLOCK INPUT FUNCTION TABLE Inputs Outputs CLK, PCLK nCLK, nPCLK Q0:Q3 nQ0:nQ3 0 1 LOW HIGH Input to Output Mode Polarity Differential to Differential Non Inver ting 1 0 HIGH LOW Differential to Differential Non Inver ting 0 Biased; NOTE 1 LOW HIGH Single Ended to Differential Non Inver ting 1 Biased; NOTE 1 HIGH LOW Single Ended to Differential Non Inver ting Biased; NOTE 1 0 HIGH LOW Single Ended to Differential Inver ting Biased; NOTE 1 1 LOW HIGH Single Ended to Differential Inver ting NOTE 1: Please refer to the Application Information section "Wiring the Differential Input to Accept Single Ended Levels". 8543BG www.icst.com/products/hiperclocks.html 3 REV. D JUNE 16, 2004 ICS8543 Integrated Circuit Systems, Inc. LOW SKEW, 1-TO-4 DIFFERENTIAL-TO-LVDS FANOUT BUFFER ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS Supply Voltage, VDD 4.6V Inputs, VI -0.5V to VDD + 0.5V Outputs, IO Continuous Current Surge Current 10mA 15mA Package Thermal Impedance, θJA 73.2°C/W (0 lfpm) Storage Temperature, TSTG -65°C to 150°C NOTE: Stresses beyond those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. These ratings are stress specifications only. Functional operation of product at these conditions or any conditions beyond those listed in the DC Characteristics or AC Characteristics is not implied. Exposure to absolute maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect product reliability. TABLE 4A. POWER SUPPLY DC CHARACTERISTICS, VDD = 3.3V±5%, TA=0°C TO 70°C Symbol Parameter VDD Positive Supply Voltage Test Conditions IDD Power Supply Current Minimum Typical Maximum Units 3.135 3.3 3.465 V 50 mA Maximum Units 3.765 V 0.8 V 5 µA TABLE 4B. LVCMOS / LVTTL DC CHARACTERISTICS, VDD = 3.3V±5%, TA=0°C TO 70°C Symbol Parameter Test Conditions VIH Input High Voltage CLK_EN, CLK_SEL, OE VIL Input Low Voltage CLK_EN, CLK_SEL, OE IIH Input High Current IIL Input Low Current Minimum Typical 2 CLK_EN, OE CLK_SEL 150 CLK_EN, OE CLK_SEL µA -150 µA -5 µA TABLE 4C. DIFFERENTIAL DC CHARACTERISTICS, VDD = 3.3V±5%, TA=0°C TO 70°C Symbol Parameter IIH Input High Current Test Conditions CLK Minimum VDD = VIN = 3.465V nCLK VDD = VIN = 3.465V CLK VDD = 3.465V, VIN = 0V -5 nCLK VDD = 3.465V, VIN = 0V -150 IIL Input Low Current V PP Peak-to-Peak Input Voltage Typical 0.15 www.icst.com/products/hiperclocks.html 4 Units 150 µA 5 Common Mode Input Voltage; NOTE 1, 2 0.5 VCMR NOTE 1: Common mode voltage is defined as VIH. NOTE 2: For single ended applications, the maximum input voltage for CLK, nCLK is VDD + 0.3V. 8543BG Maximum µA µA µA 1.3 V VDD - 0.85 V REV. D JUNE 16, 2004 ICS8543 Integrated Circuit Systems, Inc. LOW SKEW, 1-TO-4 DIFFERENTIAL-TO-LVDS FANOUT BUFFER TABLE 4D. LVPECL DC CHARACTERISTICS, VDD = 3.3V±5%, TA=0°C TO 70°C Symbol IIH Parameter Input High Current Test Conditions PCLK Minimum Typical VDD = VIN = 3.465V Maximum Units 150 µA nPCLK VDD = VIN = 3.465V PCLK VDD = 3.465V, VIN = 0V -5 µA nPCLK VDD = 3.465V, VIN = 0V -150 µA IIL Input Low Current V PP Peak-to-Peak Input Voltage 5 0.3 VCMR Common Mode Input Voltage; NOTE 1, 2 1.5 NOTE 1: Common mode voltage is defined as VIH. NOTE 2: For single ended applications, the maximum input voltage for PCLK and nPCLK is VDD + 0.3V. µA 1 V VDD V TABLE 4E. LVDS DC CHARACTERISTICS, VDD = 3.3V±5%, TA=0°C TO 70°C Symbol Parameter VOD Differential Output Voltage ∆ VOD VOD Magnitude Change VOS Offset Voltage ∆ VOS VOS Magnitude Change Test Conditions Minimum Typical Maximum Units 200 280 360 mV 0 40 mV 1.25 1.375 V 5 25 mV +10 µA ±1 +20 µA -3.5 -5 mA 1.125 IOZ High Impedance Leakage Current -10 IOFF Power Off Leakage -20 IOSD Differential Output Shor t Circuit Current IOS Output Shor t Circuit Current -3.5 -5 mA VOH VOL Output Voltage High Output Voltage Low 1.6 0.9 1.34 1.06 V V Test Conditions Minimum Typical f ≤ 800MHz 1.7 TABLE 5. AC CHARACTERISTICS, VDD = 3.3V±5%, TA=0°C TO 70°C Symbol Parameter Maximum Units 800 MHz 2.6 ns 40 ps fMAX Output Frequency t PD Propagation Delay; NOTE 1 tsk(o) Output Skew; NOTE 2, 4 tsk(pp) Par t-to-Par t Skew; NOTE 3, 4 500 ps tR Output Rise Time 20% to 80% @ 50MHz 150 350 ps tF Output Fall Time 20% to 80% @ 50MHz 150 350 ps 55 % odc Output Duty Cycle 45 50 All parameters measured at 500MHz. NOTE 1: Measured from the differential input crossing point to the differential output crossing point. NOTE 2: Defined as skew between outputs at the same supply voltage and with equal load conditions. Measured the output differential cross points. NOTE 3: Defined as skew between outputs on different devices operating at the same supply voltages and with equal load conditions. Using the same type of inputs on each device, the outputs are measured at the differential cross points. NOTE 4: This parameter is defined in accordance with JEDEC Standard 65. 8543BG www.icst.com/products/hiperclocks.html 5 REV. D JUNE 16, 2004 ICS8543 Integrated Circuit Systems, Inc. LOW SKEW, 1-TO-4 DIFFERENTIAL-TO-LVDS FANOUT BUFFER PARAMETER MEASUREMENT INFORMATION VDD 3.3V SCOPE nCLK, nPCLK Qx 3.3V±5% Power Supply Float GND + - V LVDS V Cross Points PP CMR CLK, PCLK nQx GND 3.3V OUTPUT LOAD AC TEST CIRCUIT DIFFERENTIAL INPUT LEVEL VDD nQx Qx nQ0:nQ3 nQy V Cross Points OD Qy Q0:Q3 t sk(o) V OS GND DIFFERENTIAL OUTPUT LEVEL OUTPUT SKEW nQx 80% PART 1 Qx 80% VOD Clock Outputs nQy PART 2 Qy 20% 20% tR tF t sk(pp) PART-TO-PART SKEW OUTPUT RISE/FALL TIME nQ0:nQ3 nCLK, nPCLK Q0:Q3 CLK, PCLK Pulse Width t odc = nQ0:nQ3 PERIOD Q0:Q3 t PW tPD t PERIOD OUTPUT DUTY CYCLE/PULSE WIDTH/PERIOD 8543BG PROPAGATION DELAY www.icst.com/products/hiperclocks.html 6 REV. D JUNE 16, 2004 ICS8543 Integrated Circuit Systems, Inc. LOW SKEW, 1-TO-4 DIFFERENTIAL-TO-LVDS FANOUT BUFFER VDD VDD out LVDS ➤ out ➤ ➤ DC Input ➤ out LVDS 100 VOD/∆ VOD VOS/∆ VOS out ➤ DC Input ➤ OFFSET VOLTAGE SETUP DIFFERENTIAL OUTPUT VOLTAGE SETUP VDD out 3.3V±5% POWER SUPPLY + Float GND _ IOZ DC Input out ➤ LVDS DC Input IOZ ➤ ➤ LVDS IOSD out out HIGH IMPEDANCE LEAKAGE CURRENT SETUP DIFFERENTIAL OUTPUT SHORT CIRCUIT SETUP VDD out DC Input ➤ IOS LVDS ➤ LVDS ➤ IOSB out VDD IOFF OUTPUT SHORT CIRCUIT CURRENT SETUP 8543BG POWER OFF LEAKAGE SETUP www.icst.com/products/hiperclocks.html 7 REV. D JUNE 16, 2004 ICS8543 Integrated Circuit Systems, Inc. LOW SKEW, 1-TO-4 DIFFERENTIAL-TO-LVDS FANOUT BUFFER APPLICATION INFORMATION WIRING THE DIFFERENTIAL INPUT TO ACCEPT SINGLE ENDED LEVELS Figure 2 shows how the differential input can be wired to accept single ended levels. The reference voltage V_REF = VDD/2 is generated by the bias resistors R1, R2 and C1. This bias circuit should be located as close as possible to the input pin. The ratio of R1 and R2 might need to be adjusted to position the V_REF in the center of the input voltage swing. For example, if the input clock swing is only 2.5V and VDD = 3.3V, V_REF should be 1.25V and R2/R1 = 0.609. VDD R1 1K CLK_IN + V_REF C1 0.1uF R2 1K FIGURE 2. SINGLE ENDED SIGNAL DRIVING DIFFERENTIAL INPUT 8543BG www.icst.com/products/hiperclocks.html 8 REV. D JUNE 16, 2004 ICS8543 Integrated Circuit Systems, Inc. LOW SKEW, 1-TO-4 DIFFERENTIAL-TO-LVDS FANOUT BUFFER DIFFERENTIAL CLOCK INPUT INTERFACE The CLK /nCLK accepts LVDS, LVPECL, LVHSTL, SSTL, HCSL and other differential signals. Both VSWING and VOH must meet the VPP and VCMR input requirements. Figures 3A to 3E show interface examples for the HiPerClockS CLK/nCLK input driven by the most common driver types. The input interfaces suggested here are examples only. Please consult with the vendor of the driver component to confirm the driver termination requirements. For example in Figure 3A, the input termination applies for ICS HiPerClockS LVHSTL drivers. If you are using an LVHSTL driver from another vendor, use their termination recommendation. 3.3V 3.3V 3.3V 1.8V Zo = 50 Ohm CLK Zo = 50 Ohm CLK Zo = 50 Ohm nCLK Zo = 50 Ohm LVPECL nCLK HiPerClockS Input LVHSTL ICS HiPerClockS LVHSTL Driver R1 50 R1 50 HiPerClockS Input R2 50 R2 50 R3 50 FIGURE 3A. HIPERCLOCKS CLK/nCLK INPUT DRIVEN ICS HIPERCLOCKS LVHSTL DRIVER FIGURE 3B. HIPERCLOCKS CLK/nCLK INPUT DRIVEN 3.3V LVPECL DRIVER BY 3.3V 3.3V 3.3V 3.3V 3.3V R3 125 BY R4 125 Zo = 50 Ohm LVDS_Driv er Zo = 50 Ohm CLK CLK R1 100 Zo = 50 Ohm nCLK LVPECL R1 84 HiPerClockS Input nCLK Receiv er Zo = 50 Ohm R2 84 FIGURE 3C. HIPERCLOCKS CLK/nCLK INPUT DRIVEN 3.3V LVPECL DRIVER FIGURE 3D. HIPERCLOCKS CLK/nCLK INPUT DRIVEN 3.3V LVDS DRIVER BY BY 3.3V 3.3V 3.3V LVPECL Zo = 50 Ohm C1 Zo = 50 Ohm C2 R3 125 R4 125 CLK nCLK R5 100 - 200 R6 100 - 200 R1 84 HiPerClockS Input R2 84 R5,R6 locate near the driver pin. FIGURE 3E. HIPERCLOCKS CLK/NCLK INPUT DRIVEN 3.3V LVPECL DRIVER WITH AC COUPLE 8543BG BY www.icst.com/products/hiperclocks.html 9 REV. D JUNE 16, 2004 ICS8543 Integrated Circuit Systems, Inc. LOW SKEW, 1-TO-4 DIFFERENTIAL-TO-LVDS FANOUT BUFFER LVPECL CLOCK INPUT INTERFACE here are examples only. If the driver is from another vendor, use their termination recommendation. Please consult with the vendor of the driver component to confirm the driver termination requirements. The PCLK /nPCLK accepts LVPECL, CML, SSTL and other differential signals. Both VSWING and VOH must meet the VPP and VCMR input requirements. Figures 4A to 4F show interface examples for the HiPerClockS PCLK/nPCLK input driven by the most common driver types. The input interfaces suggested 3.3V 3.3V 3.3V 3.3V 3.3V R1 50 CML Zo = 50 Ohm R2 50 Zo = 50 Ohm PCLK PCLK R1 100 Zo = 50 Ohm nPCLK nPCLK Zo = 50 Ohm HiPerClockS PCLK/nPCLK HiPerClockS PCLK/nPCLK CML Built-In Pullup FIGURE 4A. HIPERCLOCKS PCLK/nPCLK INPUT DRIVEN BY AN OPEN COLLECTOR CML DRIVER FIGURE 4B. HIPERCLOCKS PCLK/nPCLK INPUT DRIVEN BY A BUILT-IN PULLUP CML DRIVER 3.3V 3.3V 3.3V 3.3V 3.3V R3 125 3.3V R4 125 Zo = 50 Ohm 3.3V LVPECL Zo = 50 Ohm C1 Zo = 50 Ohm C2 R3 84 R4 84 PCLK PCLK Zo = 50 Ohm nPCLK LVPECL R1 84 nPCLK HiPerClockS Input R5 100 - 200 R2 84 FIGURE 4C. HIPERCLOCKS PCLK/nPCLK INPUT DRIVEN BY A 3.3V LVPECL DRIVER R6 100 - 200 R1 125 FIGURE 4D. HIPERCLOCKS PCLK/nPCLK INPUT DRIVEN BY A 3.3V LVPECL DRIVER WITH AC COUPLE 3.3V 2.5V 3.3V 3.3V 3.3V 2.5V R3 120 SSTL Zo = 50 Ohm R4 120 C1 LVDS Zo = 60 Ohm R3 1K R4 1K PCLK PCLK R5 100 Zo = 60 Ohm nPCLK R1 120 C2 nPCLK Zo = 50 Ohm HiPerClockS PCLK/nPCLK R1 1K R2 120 FIGURE 4E. HIPERCLOCKS PCLK/nPCLK INPUT DRIVEN BY AN SSTL DRIVER 8543BG HiPerClockS PCLK/nPCLK R2 125 FIGURE 4F. HIPERCLOCKS PCLK/nPCLK INPUT DRIVEN BY A 3.3V LVDS DRIVER www.icst.com/products/hiperclocks.html 10 HiPerClockS PCL K/n PC LK R2 1K REV. D JUNE 16, 2004 ICS8543 Integrated Circuit Systems, Inc. LOW SKEW, 1-TO-4 DIFFERENTIAL-TO-LVDS FANOUT BUFFER 3.3V LVDS DRIVER TERMINATION A general LVDS interface is shown in Figure 4. In a 100Ω differential transmission line environment, LVDS drivers require a matched load termination of 100Ω across near the receiver in- put. For a multiple LVDS outputs buffer, if only partial outputs are used, it is recommended to terminate the un-used outputs. 3.3V 3.3V LVDS_Driv er + R1 100 - Ω 100Ω Differential Transmission Line 100 Ohm Differiential Transmission Line FIGURE 5. TYPICAL LVDS DRIVER TERMINATION RELIABILITY INFORMATION TABLE 6. θJAVS. AIR FLOW TABLE FOR 20 LEAD TSSOP θJA by Velocity (Linear Feet per Minute) 0 Single-Layer PCB, JEDEC Standard Test Boards Multi-Layer PCB, JEDEC Standard Test Boards 114.5°C/W 73.2°C/W 200 98.0°C/W 66.6°C/W 500 88.0°C/W 63.5°C/W NOTE: Most modern PCB designs use multi-layered boards. The data in the second row pertains to most designs. TRANSISTOR COUNT The transistor count for ICS8543 is: 636 8543BG www.icst.com/products/hiperclocks.html 11 REV. D JUNE 16, 2004 ICS8543 Integrated Circuit Systems, Inc. PACKAGE OUTLINE - G SUFFIX FOR LOW SKEW, 1-TO-4 DIFFERENTIAL-TO-LVDS FANOUT BUFFER 20 LEAD TSSOP TABLE 7. PACKAGE DIMENSIONS Millimeters Symbol Minimum N Maximum 20 A -- 1.20 A1 0.05 0.15 A2 0.80 1.05 b 0.19 0.30 c 0.09 0.20 D 6.40 6.60 E E1 6.40 BASIC 4.30 e 4.50 0.65 BASIC L 0.45 0.75 α 0° 8° aaa -- 0.10 Reference Document: JEDEC Publication 95, MO-153 8543BG www.icst.com/products/hiperclocks.html 12 REV. D JUNE 16, 2004 ICS8543 Integrated Circuit Systems, Inc. LOW SKEW, 1-TO-4 DIFFERENTIAL-TO-LVDS FANOUT BUFFER TABLE 8. ORDERING INFORMATION Part/Order Number Marking Package Count Temperature ICS8543BG ICS8543BG 20 lead TSSOP 72 per tube 0°C to 70°C ICS8543BGT ICS8543BG 20 lead TSSOP on Tape and Reel 2500 0°C to 70°C ICS8543BGLF ICS8543BGLF 20 lead "Lead Free" TSSOP 72 per tube 0°C to 70°C ICS8543BGLFT ICS8543BGLF 20 lead "Lead Free" TSSOP on Tape and Reel 2500 0°C to 70°C The aforementioned trademark, HiPerClockS™ is a trademark of Integrated Circuit Systems, Inc. or its subsidiaries in the United States and/or other countries. While the information presented herein has been checked for both accuracy and reliability, Integrated Circuit Systems, Incorporated (ICS) assumes no responsibility for either its use or for infringement of any patents or other rights of third parties, which would result from its use. No other circuits, patents, or licenses are implied. This product is intended for use in normal commercial applications. Any other applications such as those requiring extended temperature range, high reliability, or other extraordinary environmental requirements are not recommended without additional processing by ICS. ICS reserves the right to change any circuitry or specifications without notice. ICS does not authorize or warrant any ICS product for use in life support devices or critical medical instruments. 8543BG www.icst.com/products/hiperclocks.html 13 REV. D JUNE 16, 2004 ICS8543 Integrated Circuit Systems, Inc. LOW SKEW, 1-TO-4 DIFFERENTIAL-TO-LVDS FANOUT BUFFER REVISION HISTORY SHEET Rev Table Page A T4E 5 A 3 A 3 1 6-10 5 1 A B T5 C T4E T2 D D D 8543BG T1 T8 5 2 4 9 10 11 2 10 13 Description of Change In the VOL row, 1.06 has been moved to the Typical column from the maximum column. Updated Figure 1, CLK_EN Timing Diagram. Updated Figure 1, CLK_EN Timing Diagram. Features section, Bullet 6 to read 3.3V LVDS levels instead of LVPECL. Udated Parameter Measurment Information figures. AC Characteristics table - revised Output Frequency from 650MHz to 800MHz. Features - deleted bullet "Designed to meet or exceed the requirements of ANSI TIA/EIA-644". LVDS Table - changed VOD typical value from 350mV to 280mV. Pin Characteristics - changed CIN 4pF max. to 4pF typical. Absolute Maximum Ratings - changed Output rating. Added Differential Clock Input Interface section. Added LVPECL Clock Input Interface section. Added LVDS Driver Termination section. Updated format throughout data sheet. Pin Description table - added function description to the OE pin. Updated LVPECL CLock Input Interface section. Added Lead Free par t number to Ordering Information table. www.icst.com/products/hiperclocks.html 14 Date 9/18/01 10/17/01 11/2/01 5/6/02 6/5/02 9/19/02 12/31/03 4/7/04 6/16/04 REV. D JUNE 16, 2004