* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Integumentary system
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
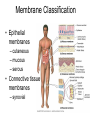
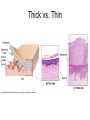
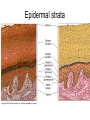
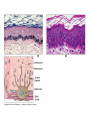
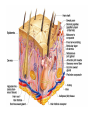
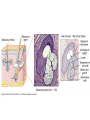
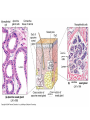
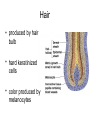
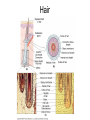
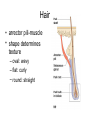
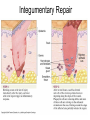
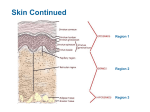
Integumentary System Membrane Classification • Epithelial membranes – cutaneous – mucous – serous • Connective tissue membranes – synovial Cutaneous Membrane - skin Functions? • • • • • • Protection Excretion Maintenance of body temperature Synthesis Storage Detection of sensation Thick vs. Thin Skin Structure • Epidermis – outer layer – Stratified squamous epithelium – Often keratinized (hardened by keratin) • Dermis – Dense connective tissue Epidermal strata Epidermal strata • Stratum basale (germinativum) – cells dividing – next to dermis – melanocytes - umbrella for DNA Epidermal strata • Stratum spinosum – spiny layer • Stratum granulosum – grainy layer – still living – produce keratin • Stratum lucidum – thick skin – dead Epidermal strata • Stratum corneum – keratinized “shinglelike” cells – water resistant – 20-30 cell layers thick – 25-45 days What happens to the epidermis when… • You have a blister? • You take a bath? What factors contribute to skin color? • Carotene • Blood flow/hemoglobin • Melanin Dermis consists of connective tissue Dermis has 2 layers – Papillary layer • Projections called dermal papillae • Pain receptors • Capillary loops – Reticular layer • Blood vessels • Glands • Nerve receptors Dermal papillae Hypodermis • Consists of areolar and adipose tissue • Not really part of the integumentary system • Target site for subcutaneous injection Glands in the skin • Sebaceous glands – Produce oil (sebum) • Lubricant for skin/hair • Kills bacteria – Most with ducts that empty into hair follicles – Glands are activated at puberty Sweat (sudoriferous) glands • Apocrine sweat glands – Armpits – Produce a stick, cloudy, and odorous secretion – Begin secreting at puberty Eccrine sweat glands • Eccrine – Found all over body – Open via duct to pore on skin surface – Not odorous, inhibit bacterial growth eccrine eccrine eccrine Sweat • Composition – Mostly water – Some metabolic waste – Fatty acids and proteins (apocrine only) • Function – Helps dissipate excess heat – Excretes waste products – Acidic nature inhibits bacteria growth • Odor is from associated bacteria Hair • produced by hair bulb • hard keratinized cells • color produced by melanocytes Hair Hair • arrector pili-muscle • shape determines texture – oval: wavy – flat: curly – round: straight Integumentary Repair Burns • Tissue damage and cell death – heat – electricity – UV radiation – chemicals • Associated dangers – dehydration – electrolyte imbalance – circulatory shock Burns • First-degree burns – Only epidermis is damaged – Skin is red and swollen • Second degree burns – Epidermis and upper dermis are damaged – Skin is red with blisters • Third-degree burns – Destroys entire skin layer – Burn is gray-white or black