* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Network Protocols
Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet wikipedia , lookup
Remote Desktop Services wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
Wireless security wikipedia , lookup
Extensible Authentication Protocol wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Server Message Block wikipedia , lookup
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
TCP congestion control wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
UniPro protocol stack wikipedia , lookup
Zero-configuration networking wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
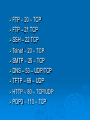
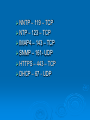
Network Protocols Why Protocols? Rules and procedures to govern communication Some for transferring data Some for route discovery TCP/IP Suite of Protocols to define communication Application – client functionality Transport - moving data Network – tasks for moving data Steps –Sending Protocol responsible for breaking data into smaller parts called packets Network address is attached to packet Data prepared for transmission and sent through NIC Steps - Receiving Data received, taken off network through NIC Address information stripped Data packets are resembles Packets are then sent to application for use. Common Protocols TCP FTP UDP TCP/IP DHCP TFTP DNS HTTP ARP SIP RTP SSH POP3 NTP IMAP4 TELNET SMTP SNMP ICMP IGMP TLS TCP Transmission Control Protocol Connection oriented – establishes a manually acknowledged session between two hosts. Provides reliability to IP Flow control, sequencing, and error detection and correction. Transport layer TCP Connection Sends SYN to target host Target opens connection and sends ACK Originated host sends ACK ready to transfer data Called three-way handshake UDP User Datagram Protocol No guarantee delivery “fire and forget” Uses IP Transport layer Lower overhead – low bandwidth FTP File Transfer Protocol Uploading and downloading of files Uses TCP as a transport protocol Used to transfer files over the LAN Popular to distribute files over the internet Application layer Common FTP commands know SSH Secure Shell Alternative to telnet Provides security and encryption Allows sessions to be opened on a remote host SFTP Secure File Transfer Protocol Authentication between sender and receiver Encryption – if packets copied remain hidden Implemented though client and server software Allows for securely uploading and downloading files to and from remote host TFTP Trivial File Transfer Protocol File transfer Not the same file security and functionality as FTP Simple downloads – firmware No directory navigation Uses UDP Application layer SMTP Simple Mail Transfer Protocol How mail is sent/transported through the network TCP Can be used to send and receive mail authentication HTTP Hypertext Transfer Protocol Uses TCP Allows text, graphics, multimedia and other material to be downloaded Requests sent in clear text HTTPS Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure SSL – encrypts Both the client and server must support POP3/IMAP4 Post Office Protocol 3/ Internet Message Access Protocol Can download email but not send Passwords transferred in clear text Telnet Virtual terminal protocol Allows session to be opened and commands executed Used to access routers and other network devices Not secure ICMP Internet Control Message Protocol Works with the IP layer to provide error checking and reporting Tools to provide best-delivery PING Used for error reporting, flow control, and route testing ARP Address Resolution Protocol Resolving IP addresses to MAC addresses RARP Reverse ARP Resolves MAC to IP addresses Reveres lookups in DNS Network Time Protocol NTP Facilitates the communication of time between systems Important for email and directory services Network News Transfer Protocol NNTP Posting and retrieval of messages Application layer Secure Copy Protocol SCP Secure means of copying files Encrypts data More secure then RCP Lightweight Directory Access Protocol LDAP Access and query directory services NDS and ADS Internet Group Management Protocol IGMP Manages multicast Used to register and discover devices Routers and videoconferencing clients Domain Name Service DNS Resolves host names to IP addresses Used to use txt file hosts WINS On windows allows NetBIOS names to be resolved to IP addresses. If no WINS server use LMHOSTS file Simple Network Management Protocol SNMP Network management of devices Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol DHCP Automatically assigns IP addresses Allows a range of IP addresses to be defined Clients ask the server for and address Lease - scope Transport Layer Security TLS Ensure privacy between client/server apps Session Initiation Protocol SIP VOIP Establish and maintain multimedia sessions Internet telephone calls Uses TCP or UDP Application layer Real Time Transport Protocol RTP Transport of real-time data Does not guarantee delivery Transport Layer Ports Each protocol needs a port to access and leave the system Ports TCP/IP has 65,535 ports Well known – 0-1023 Registered ports – 1024-49151 Used by apps or services Dynamic or private – 49152 – 65353 Can be used for any service or app – 20 – TCP FTP – 21 TCP SSH – 22 TCP Telnet – 23 – TCP SMTP – 25 – TCP DNS – 53 – UDP/TCP TFTP – 69 – UDP HTTP – 80 – TCP/UDP POP3 – 110 – TCP FTP – 119 – TCP NTP – 123 – TCP IMAP4 – 143 – TCP SNMP – 161- UDP HTTPS – 443 – TCP DHCP – 67 - UDP NNTP IP Address Consists of a series of 32 binary bits Grouped into four 8-bit bytes Called and octet Presented in decimal value Composed of two parts First part – network Second part - host Example 192.168.18.57 First three octets are network • 192.168.18 Last octet identifies the host • 57 Address Ranges Class Address Range A 10.0.0.0-10.255.255.255 255.0.0.0 B 172.16.0.0-172.31.255.255 255.255.0.0 C 192.168.0.0-192.168.255.255 255.255.255.0 Default Subnet Mask Need to Know 169.254.0.0- no DHCP server to give address 127 loopback Class IP addresses are divided into 5 classes Class A – large networks Class B – medium sized networks – universities Class C – small networks – ISP’s for customers Class D – multicasting Class E - testing Subnet Mask Network portion of the address Hosts on a LAN use the same subnet mask Subnet Mask cont Class A – 255.0.0.0 Class B – 255.255.0.0 Class C – 255.255.255.0