* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Membrane
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
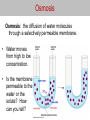
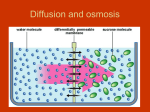
Osmosis Osmosis: the diffusion of water molecules through a selectively permeable membrane. • Water moves from high to low concentration. • Is the membrane permeable to the water or the solute? How can you tell? Osmosis Tonicity: Determines the direction of water movement due to osmosis. • Hypertonic: the solution with a greater concentration of the solute. – A cell would lose water and shrink if it is placed in a hypertonic solution. – Plasmolysis: when the cell membrane of a plant cell pulls away from the cell wall. – Causes the plant to wilt due to a lack of osmotic pressure. Osmosis Tonicity: Determines the direction of water movement due to osmosis. • Hypertonic: the solution with a greater concentration of the solute. – A cell would lose water and shrink if it is placed in a hypertonic solution. – Plasmolysis: when the cell membrane of a plant cell pulls away from the cell wall. – Causes the plant to wilt due to a lack of osmotic pressure. Osmosis • Hypotonic: the solution with the lesser concentration of the solute. – A cell would gain water and swell if it is placed in a hypertonic solution. – Cytolysis: when a cell bursts because of osmotic pressure. – Turgor Pressure: the pressure created when the cell membrane pushes against a cell wall. Osmosis • Isotonic: concentration of the solute is the same on both sides of the membrane (equilibrium). – Cells will stay the same size in a isotonic solution, there is no net movement of water molecules. http://www.glencoe.com/sites/common_ass ets/science/virtual_labs/LS03/LS03.html 10% NaCL 90% H2O CELL 20% NaCL 80% H2O What is the direction of water movement? Cell in Hypertonic Solution 15% NaCL 85% H2O ENVIRONMENT CELL 5% NaCL 95% H2O What is the direction of water movement?