* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Anatomical Directions and Major Body Regions
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
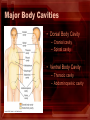
Anatomical Directions and Major Body Regions Anatomical Position and Bilateral Symmetry • In the anatomical position, the body is in an erect, or standing, posture with the arms at the sides and palms forward. The head and feet are also pointing forward. • Bilateral Symmetry – the left and right sides are mirror images of each other, and only one plane can divide the body into left and right sides. Anatomical Position and Bilateral Symmetry • Ipsilateral – on the same side • Contralateral – on the opposite side Major Body Cavities • Dorsal Body Cavity – Cranial cavity – Spinal cavity • Ventral Body Cavity – Thoracic cavity – Abdominopelvic cavity Body Regions • Axial – consists of the head, neck and torso • Appendicular – consists of the upper and lower extremities and their connections to the axial portion Directional Terms • Superior – toward the head • Inferior – toward the feet • Anterior – front or in front of • Posterior – back or in back of • Ventral – toward the belly • Dorsal – toward the back • Medial – toward the midline of the body • Lateral – toward the side of the body, or away from its midline • Proximal – toward the nearest the trunk of the body, or nearest point of origin • Distal – away from or farthest from the trunk or point of origin of a body part • Superficial – nearer the surface • Deep – farther away from the body surface Body Planes • Sagittal – A lengthwise plane running from front to back that divides the body into right and left sides. • Coronal – A lengthwise plane running from side to side. Divides the body or any of its parts into anterior and posterior. Also called a frontal plane. • Transverse – A crosswise plane; divides the body or any of its parts into upper and lower parts. Also called a horizontal plane.