* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 1.1 Linear Equations
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
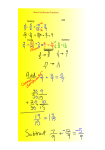
1.1 Linear Equations A linear equation in one variable is equivalent to an equation of the form To solve an equation means to find all the solutions of the equation. ax b 0 where a and b are real numbers and a 0. Equivalent Equations Two or more Examples of equations that have equivalent precisely the same equations: solutions are called 3 x and x 3 equivalent ( x 2) 6 2 x ( x 1) and equations. x 8 3x 1 3x 5 4 and (3x 5) 5 4 5 Solving a Linear Equation Solve the equation: 3x 5 4 (3 x 5) 5 4 5 3x 9 3x 9 3 3 x3 We replace the original equation by succession of equivalent equations. Add 5 to both sides. Simplify. Divide both sides by 3. Simplify. Solving a Linear Equation Involving Fractions Solve the equation: x 1 x 5 2 6 x x 1 30 30 6 5 2 x 1 x 30 30 30 5 2 6 6 x 15 5 x 6 x 5 x 15 5 x 5 x x 15 0 x 15 15 0 15 x 15 Multiply both sides by the least common denominator 30. Be sure to multiply all terms by 30. Divide out common factors. Subtract 5x to get the x-terms on the left. Simplify. Solve an Equation Involving Rational Expressions Solve: 4 9 7x 4 x 5 5x 4 9 7x 4 x 5 5x 4 9 7x 4 5x 5x x 5x 5 4 9 7x 4 5x 5x 5x x 5 5x 20 9 x (7 x 4) 20 9 x 7 x 4 20 2 x 4 20 4 2 x 4 4 16 2 x 16 2 x 2 2 8 x This is the given equation. Multiply both sides by 5x (LCD). Be sure to multiply all terms by 5x. Divide out the common factors. Simplify. Subtract 4 from both sides. Divide both sides by 2.