* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download DNA Notes
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
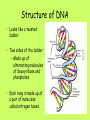
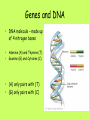
The DNA Connection DNA • Deoxyribonucleic acid • Genetic material that carries information about an organism and is passed from parent to offspring. • 1953: Watson and Crick figure out the structure of DNA (double helix). The Genetic Code • Genes control the production of proteins. • Proteins determine: – – – – Size Shape Color Many other traits of an organism Structure of DNA • Looks like a twisted ladder • Two sides of the ladder: – Made up of alternating molecules of deoxyribose and phosphates • Each rung is made up of a pair of molecules called nitrogen bases. Genes and DNA • DNA molecule – made up of 4 nitrogen bases • Adenine (A) and Thymine (T) • Guanine (G) and Cytosine (C) • (A) only pairs with (T) • (G) only pairs with (C) Mutations • Any change in a gene or chromosome • Mutation – Latin word that means “change” What happens when a mutation occurs? • Organism’s trait, or phenotype, may be different from what it normally would have been. Three Types of Mutations • Substitution – One base pair is substituted for another • Deletion – One base pair is removed • Addition – One base pair is added Effects of Mutations • A mutation is harmful if it reduces the organism’s chance for survival and reproduction. Example: white lemurs Effects of Mutations • Helpful mutations improve an organism’s chances for survival and reproduction. • Example: Antibiotic resistance in bacteria. Think about it! • We can use DNA to catch criminals. Should Americans be forced to give DNA samples so everyone is on file to make it easier to catch criminals?