* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Approach to myopathy
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
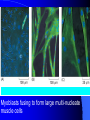
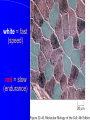
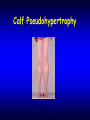
Approach to myopathy Dr omid yaghini MUSCLES DISORDERS Definition: Diseases involving the muscle fibers (myogenic) Unlike: neuronopathies: secondary to LMN Heterogenous etiology, genotype, phenotype… No specific treatment for most of them Myoblasts fusing to form large multi-nucleate muscle cells white = fast (speed) red = slow (endurance) ETIOLOGY / CLASSIFICATION Inherited myopathies – Muscular dystrophies – Congenital myopathies – Inherited channelopathies – Periodic paralysis – Inherited metabolic myopathies Disorders of glycolysis Disorders of oxidative metabolism Lipid myopathies Mitochondrial myopathies Acquired myopathies Inflammatory myopathies Acquired metabolic myopathies Toxic myopathies Weakness Constant Longlife Progressive Dystrophy fluctuation acquired MG periodic P metabolic static congenital muscular dystrophy are inherited myopathy characterized by progressive muscles weakness °eneration &subsequent replacement by fibrous & fatty connective tissue Historically were categorized by their: Age onset /distribution of weakness& pattern of inheritance The genetic mutation &abnormal gene product were defined for many of them disease inheritance duchenne X linked age protein 2y dystrophin beckers MD X linked Emery-dreifuss X linked LGD AD/AR Cong/CNS AR Cong/noCNS AR Distal MD AD/AR bethlen AD FSH AD oculodystrophy AD 5th dec Myotonic type1 AD 2th,3th decade 5-15 .. childh emerin sacroglycan birth .. merosin Child& adult Myotonic type 2 AD myofibrillar AD desmmin Congenital myopathy Are distinguished from dystrophy in three respect: Characteristic morphologic alteration At birth Non progressive However there are exception to all these generalization Inheritance: are variable c/p: hypotonia with subsequent developmental delay Reduce muscles bulk, slender body build &long narrow face Skeletal abnormalities: high arched palate ,pectus exacavitum, kyphscliosis, dislocated hip, pes cavus) Absent or reduced muscle stretch reflex Weakness: limb girdle mostly, but distal weakness exist CK &EMG may be normal Muscle biopsy: the diagnostic method Metabolic myopathy Glucose/glycogen metabolism Fattay acid metabolism mitochondrial Calf Pseudohypertrophy Gowers' Sign “Climbing up himself” Gowers’ sign always denotes proximal muscle weakness Common Features: Clinical: Muscle weakness: main feature Gower’s sign (proximaly dominating deficit) Contractures +/- severe: advanced stages Pain: in inflamm. Disorders only Atrophy (+/- pseudohypertrophy in X-linked) Deformity: advanced disease DTR: normal, diminished or absent Tone: slightly or normal Other systems may be involved Common Features: Laboratory Investigations: CBC, LFT.. Normal ESR: high in inflammatory only U&E: abnormalities in some endocrinopathies and periodic paralysis C.K & aldolase: generaly: raised (normal in few sittings: metabolic, endocrine…) Lactic acid Genetic study: location & type of chromozomal abnormalities: Common Features: Neurophysiology NCS: normal EMG: – Spontaneous activities +/- in inflammatory disorders – Interferential tracing – MUPs: small A Short D polyphsics