* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cardiovascular System
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
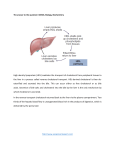
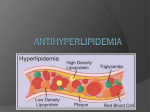
Cardiovascular System ANTILIPEMICS LILLEY, READING & WORKBOOK: CHAP 28 Antilipemics Drugs used to lower lipid levels Triglycerides and Cholesterol Two primary forms of lipids in the blood Water-insoluble fats that must be bound to apolipoproteins, specialized lipid-carrying proteins Lipoprotein is the combination of triglyceride or cholesterol with a polipoprotein Lipoproteins Very-low-density lipoprotein (VLDL) Produced by the liver Transports endogenous lipids to the cells Low-density lipoprotein (LDL) High-density lipoprotein (HDL) Responsible for “recycling” of cholesterol Also known as “good cholesterol” Coronary Heart Disease The risk of CHD in patients with cholesterol levels of 300 mg/dL is three to four times greater than that in patients with levels less than 200 mg/dL Coronary Heart Disease Positive Risk Factors Age Male 45 years or older Female 55 years or older, or women with premature menopause not on estrogen replacement therapy Family history: history of premature CHD Current cigarette smoker Hypertension BP 140/90 or higher, or on antihypertensive medication Low HDL levels: less than 35 mg/dL Diabetes mellitus Treatment Guidelines Antilipemic drugs are used as an adjunct to diet therapy Drug choice based on the specific lipid profile of the patient All reasonable non-drug means of controlling blood cholesterol levels (e.g., diet, exercise) should be tried for at least 6 months and found to fail before drug therapy is considered Antilipemics HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors (HMGs, or statins) Bile acid sequestrants Niacin (nicotinic acid) Fibric acid derivatives Cholesterol absorption inhibitor Combination drugs Antilipemics: HMG-CoA Reductase Inhibitors (HMGs, or statins) Most potent LDL reducers lovastatin (Mevacor) pravastatin (Pravachol) simvastatin (Zocor) atorvastatin (Lipitor) fluvastatin (Lescol) HMG-CoA Reductase Inhibitors (statins) Indications First-line drug therapy for hypercholesterolemia Treatment of types IIa and IIb hyperlipidemias Reduce LDL levels by 30% to 40% Increase HDL levels by 2% to 15% Reduce triglycerides by 10% to 30% HMG-CoA Reductase Inhibitors (statins) Adverse effects Mild, transient GI disturbances Rash Headache Myopathy (muscle pain), possibly leading to the serious condition rhabdomyolysis Elevations in liver enzymes or liver disease Bile Acid Sequestrants cholestyramine (Questran) colestipol hydrochloride (Colestid) colesevelam (tablet form) Also called bile acid–binding resins and ion-exchange resins Bile Acid Sequestrants Mechanism of action Prevent resorption of bile acids from small intestine Bile acids are necessary for absorption of cholesterol Indications Type II hyperlipoproteinemia Relief of pruritus associated with partial biliary obstruction (cholestyramine) May be used along with statins Bile Acid Sequestrants Adverse effects Constipation Heartburn, nausea, belching, bloating These adverse effects tend to disappear over time Niacin (Nicotinic Acid) Vitamin B3 Lipid-lowering properties require much higher doses than when used as a vitamin Effective, inexpensive, often used in combination with other lipid-lowering drugs Niacin (Nicotinic Acid) Mechanism of action Increases activity of lipase, which breaks down lipids Reduces the metabolism of cholesterol and triglycerides Indications Effective in lowering triglyceride, total serum cholesterol, and LDL levels Increases HDL levels Effective in the treatment of types IIa, IIb, III, IV, and V hyperlipidemias Niacin (Nicotinic Acid) Adverse effects Flushing (due to histamine release) Pruritus GI distress Fibric Acid Derivatives Also known as fibrates gemfibrozil (Lopid) fenofibrate (Tricor) Fibric Acid Derivatives Mechanism of action Activate lipase, which breaks down cholesterol Suppress release of free fatty acid from the adipose tissue, inhibit synthesis of triglycerides in the liver, and increase the secretion of cholesterol in the bile Indications Treatment of types III, IV, and V hyperlipidemias Drug Effects Decrease the triglyceride levels Increase HDL by as much as 25% Fibric Acid Derivatives Adverse effects Abdominal discomfort, diarrhea, nausea Blurred vision, headache Increased risk of gallstones Prolonged prothrombin time Liver studies may show increased function Cholesterol Absorption Inhibitor ezetimibe (Zetia) Inhibits absorption of cholesterol and related sterols from the small intestine Results in reduced total cholesterol, LDL, triglylceride levels Also increases HDL levels Works well when taken with a statin drug Nursing Implications Patient Education Before beginning therapy, obtain a thorough health and medication history Assess dietary patterns, exercise level, weight, height, VS, tobacco and alcohol use, family history Assess for contraindications, conditions that require cautious use, and drug interactions Nursing Implications Patient Education Contraindications include biliary obstruction, liver dysfunction, active liver disease Obtain baseline liver function studies Patients on long-term therapy may need supplemental fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, K) Take with meals to decrease GI upset Nursing Implications Patient Education Patient must be counseled concerning diet and nutrition on an ongoing basis Instruct on proper procedure for taking the medications Powder forms must be taken with a liquid, mixed thoroughly but not stirred, and NEVER taken dry Nursing Implications Patient Education Other medications should be taken 1 hour before or 4 to 6 hours after meals to avoid interference with absorption Clofibrate often causes constipation; instruct patients to increase fiber and fluid intake to offset this effect Nursing Implications Patient Education To minimize adverse effects of niacin, start on low initial dose and gradually increase it, and take with meals Small doses of aspirin or NSAIDs may be taken 30 minutes before niacin to minimize cutaneous flushing Inform patients that these drugs may take several weeks to show effectiveness Nursing Implications Patient Education Instruct patients to report persistent GI upset, constipation, abnormal or unusual bleeding, and yellow discoloration of the skin Monitor for adverse effects, including increased liver enzyme studies Monitor for therapeutic effects Reduced cholesterol and triglyceride levels Review In addition to drug therapy, the patient should be encouraged to do which of the following to treat hyperlipidemia? (Select all that apply.) 1. Reduce cholesterol and fats in diet. 2. Reduce weight. 3. Decrease exercise. 4. Increase use of polyunsaturated and monounsaturated fats. Review Before initiating a statin drug, the premedication assessment should include: 1. complete blood count (CBC). 2. liver function studies. 3. bleeding time. 4. gastrointestinal (GI) series. Review Ezetimibe (Zetia) acts by: 1. an unknown mechanism of action. 2. binding bile acids in the intestines. 3. removing fat-soluble vitamins. 4. blocking absorption of cholesterol by the small intestines.