* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
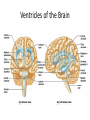
Download Basic Pattern of the Central Nervous System
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Binding problem wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Biology of depression wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience and intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Visual selective attention in dementia wikipedia , lookup
Broca's area wikipedia , lookup
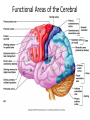
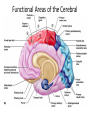
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Executive functions wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Dual consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Affective neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Orbitofrontal cortex wikipedia , lookup
Lateralization of brain function wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Eyeblink conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Emotional lateralization wikipedia , lookup
Anatomy of the cerebellum wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Cortical cooling wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy of memory wikipedia , lookup
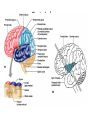
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Prefrontal cortex wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
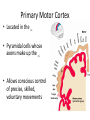
Motor cortex wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup