* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Potential Difference
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
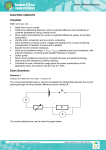
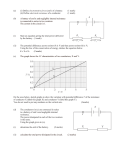
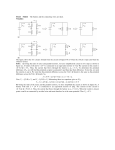
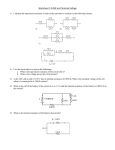
Potential Difference Electricity Lesson 2 Learning Objectives To know what is meant by potential difference. To define potential difference. To define the emf of a source. To calculate electrical power supplied to a device. Potential Difference The work done per unit charge is defined as the potential difference (pd) or voltage across the component. Potential difference is defined as the work done (or energy transfer) per unit charge. The unit of pd is the volt which is equal to 1 joule per coulomb. Potential Difference If work W is done when charge Q flows through the component, the pd across the component V is given by:- W V Q In words:- work done p.d. charge flow Example 1 If 30 J of work is done when 5 C of charge passes through a component, what is the pd across it? Example 1 If 30 J of work is done when 5 C of charge passes through a component, what is the pd across it? W 30 J V 6V Q 5C Example 2 If the pd across a component in a circuit is 12 V, how much energy is transferred from the battery to the component if 3 C of charge passes through it? Example 2 If the pd across a component in a circuit is 12 V, how much energy is transferred from the battery to the component if 3 C of charge passes through it? W QV 3 C 12 V 36 J The emf of a source The emf of a source of electricity is defined as the electrical energy produced per unit charge passing through the source. The unit of emf is the volt, the same as the unit of pd. For a source of emf, ε, in a circuit, the electrical energy produced when charge Q passes through the source = Qε transferred to other parts of the circuit. Electrical Power Q It W QV IVt Consider a component The symbol Δ is delta, a Greek capital letter Δ, meaning “change in”. power current p.d. P IV Current For a current I, the charge flow ΔQ in a time Δt is given by:- Q I t