* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Structures and Their Functions
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
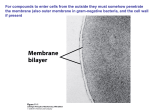
Cell Structures and Their Functions Things Common To All Cells Cell Membrane – Cytoplasm – Genetic Material – Ribosomes – Cell Types Prokaryotic – Eukaryotic – Structures Found in All Eukaryotic Cells Nucleus – Mitochondria – Endoplasmic Reticulum – Golgi Complex – Vesicles and Vacuoles – Lysosomes – Cytoskeleton – Structures Found in Plant Cells Cell Wall – Chloroplasts – Structures Found in Animal Cells Centrioles – Transport Through Cell Membranes Membrane Structure – Passive Transport – Active Transport – Unit III – Cells Learning Goal 2 Cell Structures and Their Functions Things Common to All Cells • Cell Membrane • Regulates materials entering and leaving the cell. • Cytoplasm • Fluid substance in which all cell structures are suspended. • Genetic Material • The nucleic acid DNA which holds instructions for all cell functions. • Ribosomes • Structures on which proteins are built. Cell Types Prokaryotic Cells • Lack a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. • All bacteria are prokaryotic. Eukaryotic Cells • Contain genetic material enclosed in a nucleus • All cells of protists, fungi, plants, and animals Structures Found in Eukaryotic Cells Nucleus – Controls all cell functions using DNA instructions. Mitochondria – Site of cellular respiration. Produces energy for cells in the form of ATP. Structures Cont. Endoplasmic Reticulum Manufactures and transports some cell molecules. Rough ER contains ribosomes. Golgi Apparatus – Prepares molecules for use in the cell or in other cells. Structures cont. • Vesicles and vacuoles • Function in storage of substances. • Lysosomes • Contain digestive enzymes that break down nutrients and old cell parts. Cytoskeleton – Network of fibers that help the cell maintain its shape and allow movement. Plant Cell Structures Cell Wall – Surrounds cell membrane in plant, fungi, and bacterial cells. Helps support and protect the cell. Chloroplasts – Found in plant cells. Site of photosynthesis where carbohydrates are produced. Animal Cell Structures Centrioles – Found only in animal cells. Play a role in cell division. Membrane Structure Details • The basic structure of cell membranes is a double layer of phospholipid molecules. • Various types of proteins are embedded in the membrane as well. Passive Transport Movement of molecules through the membrane using no energy • Diffusion Movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration until equilibrium is reached. Facilitated Diffusion • Diffusion through cell membranes with the help of channel proteins. • Necessary for molecules that are too large (like glucose) or too strongly charged to diffuse through the bilayer. Osmosis • Diffusion of water molecules through cell membranes. • Results in changes in osmotic pressure (water pressure). • Hypotonic: More water outside of cell so water moves in. • Isotonic: Same amount of water outside and in. • Hypertonic: Less water outside of cell so water moves out. Active Transport • Movement of molecules through cell membranes that requires energy. Molecular Transport • Small molecules and ions (charged atoms) are carried across membranes by proteins in the membrane that act like energy-requiring pumps. • Needed to move molecules from areas outside of the cell where they are less concentrated than inside. Endocytosis • Endocytosis is the process of taking material into the cell by means of infoldings, or pockets of the cell membrane. • Needed for extremely large molecules or large quantities of molecules. Exocytosis • The membrane of a vesicle, containing material that needs to exit the cell, fuses with the cell membrane, forcing the contents out of the cell.