* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Structure and Function
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
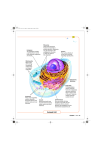
Cell Structure and Function Get out paper, pencil, any notes taken from book and class. Be prepared to take notes! Today we review and re-teach the parts of the cell. Use this to correct any misunderstanding you have about these parts! Cell Structure and Function KWL - The Cell What do you know? What do you want to know? What have you learned? Cell a usually microscopic structure containing nuclear and cytoplasmic material enclosed by a semipermeable membrane and, in plants, a cell wall the basic structural unit of all organisms. Cell Organelles Organelles Cells contain special parts called organelles. Each organelle has a specific job to do to keep the cell functioning properly, much like an organ in our body does. This is why they are called organelles. organelle nucleus cell organelle endoplasmic reticulum Next > Organelles There are many different types of organelles. nucleus cell Not all the different types are present in all cells. The types of organelles present in a cell depend on the job the cell does. endoplasmic reticulum Next > Animal and Plant Cells Some organelles are found in both plant and animal cells. These include: cell membrane nucleus cytoplasm endoplasmic reticulum plant cell animal cell mitochondria Next > Plant Cells Other organelles are present in plant cells but not in animal cells. These include: cell wall large central vacuole chloroplast plant cell Next > Question 1 Which of the following statements about cells is true? A) All cells in an organism contain the same organelles. B) Not all living organisms are made up of cells. C) Plant cells have organelles that are not found in animal cells. D) Plants and animals contain all the same organelles. Next > Question 1 Which of the following statements about cells is true? A) All cells in an organism contain the same organelles. B) Not all living organisms are made up of cells. C) Plant cells have organelles that are not found in animal cells. D) Plants and animals contain all the same organelles. Next > Cell Membrane Cell Membrane Function: Regulates what enters and leaves the cell Provides protection and support Structure: Double membrane Flexible structure that forms a strong barrier between the cell and its surroundings Cell Membrane Function: Regulates what enters and leaves the cell Provides protection and support Structure: Double membrane Flexible structure that forms a strong barrier between the cell and its surroundings Cell Wall Cell Wall Function: Provides support and protection for the cell Structure: Lies outside the cell membrane Found in plants, algae, fungi and many bacteria NOT FOUND IN ANIMAL CELLS! Cell Wall Function: Provides support and protection for the cell Structure: Lies outside the cell membrane Found in plants, algae, fungi and many bacteria NOT FOUND IN ANIMAL CELLS! Cytoplasm Cytoplasm is a watery substance inside a cell. Chemicals needed by the cell are dissolved in the cytoplasm. cytoplasm Next > Nucleus Nucleus-The control center Function: Contains almost all of the cell’s DNA DNA is found on chromosomes which contain genetic information. Nucleus-The control center Structure: Surrounded by a double membrane called a nuclear envelope (Nuclear Membrane). It is dotted with many pores (holes) to allow materials in and out of the nucleus. Nucleus-The control center Structure: Surrounded by a double membrane called a nuclear envelope (Nuclear Membrane). It is dotted with many pores (holes) to allow materials in and out of the nucleus. You have 3 minutes to compare your notes with a neighbor. Be sure to ask questions and fill in any blanks you may have in your notes at this time. Vacuoles - Storage Vacuoles - Storage Function: Stores water, salts, proteins and carbohydrates Structure: Sac-like Plant cells have one large central vacuole Animal cells have many small vacuoles Vacuoles - Storage Function: Stores water, salts, proteins and carbohydrates Structure: Sac-like Plant cells have one large central vacuole Animal cells have many small vacuoles Vacuoles - Storage Function: Stores water, salts, proteins and carbohydrates Structure: Sac-like Plant cells have one large central vacuole Animal cells have many small vacuoles Chloroplasts – Energy in Plants Function: Captures energy from the sun (solar energy) and changes it into food (chemical energy) for plants (photosynthesis) Structure: Contains green pigment called chlorophyll Not found in animal cells! Mitochondria - Energy Function: Convert chemical energy in food into materials easier for the cell to use. Structure: Enclosed by two membranes with the inner membrane folded up. Contains it’s own DNA (unlike other organelles) that is identical to your mother’s! Endoplasmic Reticulum Endoplasmic reticulum is the transport system of a cell. endoplasmic reticulum endoplasmic reticulum It takes proteins and lipids (fats) to other parts of the cell. Next > Endoplasmic Reticulum Endoplasmic reticulum can be ‘smooth’ or ‘rough’. Rough endoplasmic reticulum has structures on it called ribosomes that make it look rough. Ribosomes make the proteins that are carried by the endoplasmic reticulum. endoplasmic reticulum ribosomes Next > You have 3 minutes to compare your notes with a neighbor. Be sure to ask questions and fill in any blanks you may have in your notes at this time. Golgi Bodies The Golgi bodies receive materials and other proteins from the endoplasmic reticulum, package them, and send them to other parts of the cell. Sometimes called the cell’s ‘Mailroom’ Next > Individually, create a Venn Diagram for plant and animal cells. Plant Cell Animal Cell KWL - The Cell: Your ticket out the door What do you know? What do you want to know? What have you learned? 1. Circle information that you heard in today’s notes 2. Asterik (*) next to questions you had answered today 3. Add new information learned