* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Synapse Notes
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
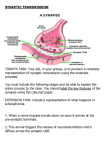
Synapse II. The synapse- junction between two communication neurons ie. Presynaptic neuron synaptic cleft post synaptic neuron Synaptic transmission A. Synaptic vesicles- membranes sacs in the synapse that contain neurotransmitters B. Neurotransmitters- 50 types produced in synaptic knobs 1. Acetylcholine- stimulate skeletal muscle 2. Monoamines- epinephrine, norepinephrine [very strong], dopamine etc. 3. Amino acids – anyone can act or be combined to act as neurotransmitters 4. Peptids 5. Monoamine oxidase [enzyme] C. Cholinesterase – decomposes some neurotransmitters D. Actions of neurotransmitters 1. Excitatory- increases pot synaptic membrane permeability to Na+ to trigger nerve impulses (acetylcholine and norepinephrine) 2. Inhibitory- decreases the membrane permeability to NA+ thus casing threshold to raise (dopamine and amino acids) 3. Combination of both – releases together. One in greater concentration has the effect E. Neuronal Pools- varying numbers of neurons in the CNS which receive and transmit impulses into branched systems consisting of hundreds of synapses 1. Facilitation – when one neuron in a neuronal pool becomes more excitable and triggers as a result of various neurotransmitters 2. Convergence- when two nerves in a pool transmit their impulse to one nerve in the pool 3. Divergence – when one nerve impulse leaves a nerve fiber and sends that impulse to 3 other nerves in the pool, this amplifies the impulse III. Types of neurons- classified by structure, size, shape and function A. Size 1. Multipolar- many nerve fibers only one is an axon the rest are dendrites (CNS nerves) 2. Bipolar- only 2 fibers 1 axon and 1 dendrite found in the eyes, nose and ears 3. Unipolar- one branched dendrite and one axon leading to CNS(spinal cord) 4. Ganglion- masses of unipolar nerve cells outside brain and spinal cord B. Function 1. Sensory – collect and carry sensory impulses o the brain receptors 2. Interneurons- transmit impulse to brain from one part to another. Direct impulses to proper locations. 3. Motor neurons- bring about muscle movement or glandular excretion