* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Landscapes
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
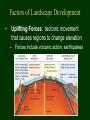
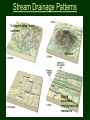
Landscapes Earth Science Mr. Cloud Zion National Park, Utah What is a landscape? • A landscape, or topography, are features of Earth’s surface at the interfaces between the atmosphere, or hydrosphere, and the top of the lithosphere. Types of Landscapes • Mountains • Plateaus • Plains Mountains • An area of high elevation with regions of steep gradient • Peaks are usually thousands of feet higher than their base • Internal Structure: • Distorted rock including faults, folds, and volcanic rock Plateaus • Area of high elevation with a more level slope or gradient than mountains • Internal Structure: • Undistorted, horizontal rock strata Greenland Plateau Plains • Low elevation, generally level surface with little change in gradient • Regions dominated by leveling forces • Composed primarily of sedimentary rocks Atlantic Coastal Plain Landscape Regions • Landscape characteristics such as elevation, bedrock structure, stream drainage, soil characteristics, and gradient occur in combination to form identifiable areas called landscape regions. Factors of Landscape Development • Uplifting Forces: tectonic movement that causes regions to change elevation – Forces include volcanic action, earthquakes Factors of Landscape Development • Leveling forces: lower and level out land surfaces by weathering and erosion Ice Wedging Weathering and Erosion at Niagara Falls • When both forces are present, the landscape will be uplifted or lowered, depending on which force is dominant. What other factors can affect landscape development? • Arid v. Humid • Bedrock Structure Sharp, unforgiving characteristics Arid Landscape Rolling, smooth, forgiving gradient Humid Landscape Bedrock Structure • The composition and structural features of bedrock are major factors in the rate of development and the features of landscapes. • Different rock types have varying degrees of resistance to weathering and erosion • If differing rocks are exposed to weathering and erosion, the landscape will change at varying rates. Stream Drainage Patterns V-shaped valley: most common Volcanic Faulting Folded mountains: varying bedrock resistance