* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Equation sheet #1
Computational electromagnetics wikipedia , lookup
Electrical resistivity and conductivity wikipedia , lookup
Insulator (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Nanofluidic circuitry wikipedia , lookup
Multiferroics wikipedia , lookup
Hall effect wikipedia , lookup
Electrostatic generator wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic monopole wikipedia , lookup
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Electroactive polymers wikipedia , lookup
History of electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Electrical injury wikipedia , lookup
Electrocommunication wikipedia , lookup
Faraday paradox wikipedia , lookup
Maxwell's equations wikipedia , lookup
General Electric wikipedia , lookup
Mathematical descriptions of the electromagnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Static electricity wikipedia , lookup
Electric current wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Electromotive force wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Electricity wikipedia , lookup
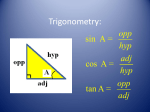
Physics122 Exam #1 September 29, 2004 12:10 to 1:10 pm Constants and equations for exam 1. You may detach this page if you wish. ________________________________________________________________________________ Coulumb’s Law constant k=8.99 x109 N m2/C2 Permittivity of free space 0=8.85 x10-12 C2/N m2 Charge of one electron -e=-1.60 x10-19 C ________________________________________________________________________________ Coulumb’s law Electric field Q1Q2 F qE - definition of E F k 2 r Q E k 2 - point charge r E V / d capacitor, constant field ________________________________________________________________________________ Electric Potential PE qV - potential energy of a charge in electric field V Edr Q V V V potential of a point charge Ex ; Ey ; Ez . r x y z Work done by a electric force: W=-PEfinal-PEinitial) Work done by external force to move a charge q in electric field: W=qVfinal-Vinitial) ________________________________________________________________________________ System of charges dQ E E1 E 2 E3 .... - sum of point - like charges E k 2 - continuous distributi on of charge r dQ V V1 V2 V3 ..... V k r ________________________________________________________________________________ Electric Flux, Gauss’s Law For unifrom field E E A - electric flux; A area vector, equal to area, pointing perpendicu lar to area Q E E dA E 0 outflux, E 0 influx, E , Q enclosed charge V k 0 ________________________________________________________________________________ Trigonometry review sin (opp) /( hyp), cos (adj ) /( hyp), tan (opp) /( adj ) Pythagorean theorem: (hyp) 2 (opp) 2 (adj ) 2 ________________________________________________________________________________ Vectors (A or A ) and Components (Ax, Ay) A + B Nose to tail – A points opposite A A – B means A + (–B) Component = (sign)(magnitude)(trig fn) C = A + B means C x Ax Bx and C y Ay B y Magnitude of C = |C| = C x2 C y2 Angle to nearest x-axis: tan 1 1 | Cy | | Cx | Specify axis!