* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Organic Chemistry
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
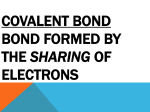
Organic Chemistry Organic Chemistry The chemistry of life The study of Carbon (C) More specifically, the study of the bonds formed between Carbon (C) and (mostly), Hydrogen (H), Oxygen (O) and Nitrogen (N). Valency Number of bonds formed determined by atomic structure Remember: A covalent bond is formed when two atoms share a pair of electrons! Covalent bonds of Carbon form basis of Org Chem Valency Sharing 1 pair of electron = single bond Sharing 2 pairs of electrons = double bond Sharing 3 pairs of electrons = triple bond Different atoms can form different amounts of bonds Why? Valency - H Look at atomic structure H is atom no. 1 No. of protons: 1 No. of electrons: 1 1 electron means it can form only 1 covalent bond (EVER!) Valency - H Look at atomic structure H is atom no. 1 No. of protons: 1 No. of electrons: 1 1 electron means it can form only 1 covalent bond (EVER!) Valency - C C : element number 6 => 6 protons and 6 electrons Electronic configuration: 1s2, 2s2, 2p2 1s electrons not involved in bonding so 4 valence electrons (v.e-.) Octet rule: C wants 8 electrons Must share all 4 electrons to get 8 Valency - C C must form 4 bonds to form stable compounds Can be any combination of single, double and triple bonds Can NEVER exceed 4 bonds around a C atom Valency - O Electronic structure: 1s2, 2s2, 2p4 6 valence electrons available Wants 8 so only needs 2 more O can form 2 bonds; valency = 2 This means 1 double bond or 2 single bonds Valency - O Electronic structure: 1s2, 2s2, 2p4 6 valence electrons available Wants 8 so only needs 2 more O can form 2 bonds; valency = 2 This means 1 double bond or 2 single bonds Valency - N Electronic structure: 1s2, 2s2, 2p3 5 valence electrons available Wants 8 so only needs 3 more N can form 3 bonds; valency = 3 This means 3 single bonds; 1 double bond and 1 single bond or 1 triple bond. Valency - N Drawing Organic Compounds Molecular Formula: tells exactly how many of each atom is present; Shorthand notation Tells nothing about how they are connected Structural Formula: Longhand; shows which atoms are connected to which. Drawing Organic Compounds Consider simplest organic molecule: Methane (natural gas) Molecular formula = CH4 Only 1 way they can be connected Methane is an Alkane, a compound which possesses only C and H single bonds Drawing Organic Compounds Next alkane is Ethane Molecular Formula: C2H6 Structural Formula: Drawing Organic Compounds Lets skip ahead a bit; Pentane: C5H12 Looks very messy (and this is still a very simple compound) Too complicated to draw all molecules like this Drawing Organic Compounds Easier method: Draw C-C bonds as lines. Whenever line ends (changes direction), that’s a C atom Don’t draw in H atoms. Can work out how many are present by subtracting number of bonds visible from 4. Implicit Hydrogens. Vs. Isomers Molecules can have the same molecular formula but different structural formulas Many possible ways to connect atoms 5 carbon alkane: C5H12 3 possible isomers Isomers Same molecular formula; different structural formula Can have very different properties and reactivity Chemically distinct molecules Naming Organic Molecules For alkanes its very easy Count how many C atoms in longest straight chain. Find corresponding prefix (next slide). Identify any side groups off major chain. Indicate their positions with lowest possible number. If all C-H single bonds then alkane. Suffix = ane Naming Organic Molecules No. of C atoms Name Formula Name of side group 1 Methane CH4 Methyl 2 Ethane CH3CH3 Ethyl 3 Propane CH3CH2CH3 Propyl 4 Butane CH3CH2CH2CH3 Butyl 5 Pentane CH3CH2CH2CH2CH3 Pentyl 6 Hexane CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH3 Hexyl 7 Heptane CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH3 Heptyl 8 Octane CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH3 Octyl 9 Nonane CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH3 Nonyl 10 Decane CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH3 Decyl If more than one side group present use di (2), tri (3) or tetra (4) to show how many Our isomers of C5H12 Longest chain = 5 C atoms No branching Pentane Our isomers of C5H12 Longest chain = 4 C atoms 4 = butane One branching group of 1 C unit = methyl group It’s on Carbon no. 2 so name is 2-methylbutane Numbers and letters are always separated by a hyphen (-) Our isomers of C5H12 Can we number any other way? Longest chain = 4 C atoms 4 = butane One branching group of 1 C unit = methyl group It’s on Carbon no. 3 so name is 3-methylbutane WRONG!! Must have lowest possible number for side chain Our isomers of C5H12 Longest chain = 3 C atoms 3 = propane Two branching groups of 1 C unit = 2 methyl groups Both on Carbon no. 2 so name is 2,2-dimethylpropane Multiple bonds Alkanes are saturated compounds, all single bonds If 1 or more double or triple bond present then molecule is unsaturated Molecules with a double bond are called alkenes Molecules with a triple bond are called alkynes More naming Similar to alkanes Select longest chain containing the multiple bond. Indicate location of multiple bond. Identify any side groups. More naming Similar to alkanes Select longest chain containing the multiple bond. Indicate location of multiple bond. Identify any side groups. 3-ethylpent-1-ene More naming Similar to alkanes Select longest chain containing the multiple bond. Indicate location of multiple bond. Identify any side groups. 3-ethylpent-1-ene 2-methyl-5-ethyloct-3-yne