* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Mitosis ppt
Microtubule wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Kinetochore wikipedia , lookup
Spindle checkpoint wikipedia , lookup
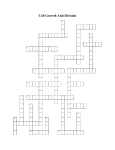
Cell Division & Mitosis RUSSELL BIOLOGY RHODES AP BIO Multicellular organisms are made of cells and cell products Multicellular organisms have divided from a single cell Most cells are specialized Regeneration is a limited property Cells must form 3-D organism with specialized tissues in specific locations Zebra fish (Danio rerio) grows new fin when attacked by Knifefish (Notopterus notopterus) 10.1 Overview: The Cycle of Cell Growth and Division STEPS Cell growth and everyday activity like making proteins from accessible DNA regions called genes and making of new organelles and structures DNA replication DNA (chromosomes) segregated into equal parts; even distribution DNA moved into two new nuclear regions Cytoplasm divided; fairly even distribution 2 new cells; genetically identical to each other and the parent PURPOSES Growth Maintenance Repair Reproduce Concepts DNA is chemical that stores information Genes are regions of chromosomes that code for proteins A-T, C-G (Purines and pyrimidines) Double helix Chromosomes are individual and linear Replication Chromosomes that have replicated are called sister chromatids and are joined at kinetochores by centromeres, forming arms Cell division is used for Growth = larger organisms Replacement = due to wear and tear Repair = to fix wounds Reproduction of single celled eukaryotes Duplicates Chromosomes are replicated Cells produced are identical genetically to each other AND to the cell produced In meiosis cells generated have potential to be genetically different and contain ½ the DNA of the parent cell = gametes Partitioning of Chromosomes 2 copies of each chromosome = Diploid; These are homologous meaning they have the same genes in the same positions and sequences 1 copy of each chromosome = haploid “ploidy “ refers to chromosome sets Chromosomes replicate into sister chromatids ( for a phase there are 4 of each) Sister chromatids move apart in Segregation Each cell gets one of each set of chromatids; pairs of homologous chromosomes creating CLONES 10.2 Overview: The Mitotic Cell Cycle Cell Cycle = Interphase + Mitosis + Cytokinesis Interphase Between NUCLEAR divisions Phases of Mitosis Prophase Prometaphase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase Cytokinesis Animal cells “furrow” with a band of microfilaments pinching the cell into two Plant cells deposit material for new cell wall starting at midpoint Concepts Chromatid Kinetochore Spindle Centrosome centriole Microtubules Metaphase plate (plane) Segregation Page 207 Interphase = between divisions G1 = chromosomes as chromatin, dark nucleus, everyday protein synthesis; cell growth S= synthesis or REPLICATION of DNA; chromosomes are sister chromatids G2 = cohesions; centrosomes have replicated; new organelles G0 = sometimes cells are suspended and won’t divide again (not the typical scenario) Mitosis= division of eukaryotic nucleus Prophase= chromosomes visible (chromatids); nucleus disintegrating; centrosomes moving and creation of spindle occurring Prometaphase= nucleus gone, spindle formed; kinetochores attached to spindle; tugging starts to move chromosomes to metaphase plane Metaphase= chromosomes aligned at spindle midpoint Anaphase= kinetochores separate and chromatids/ now chromosomes move toward poles along the spindle microtubules; cohesions are cut Telophase= two separate nuclei (piles of chromosomes at the poles) now begin to uncoil and become chromatin, nuclei are rebuilt; cytokinesis has started; clones will be created Cytokinesis= physical division of cytoplasm Animal = cleavage furrow Plant= cell plate 10.3 Overview: Formation and Action of the Spindle Plant cells No centrosomes – spindle forms around nucleus Animal cells Centrosomes divide and two parts move apart Microtubules form creating the spindle Kinetochore microtubules Pole to kinetochore of chromosome Motor proteins of kinetochore WALK chromosome along microtubule Motor proteins at poles pull kinetochore microtubules Movement is species and cell-type specific Anaphase Non-kinetochore microtubules Pole to overlap region at metaphase plane without chromosomes Overlap region is reduced and cell lengthens 10.4 Overview: Cell Cycle Regulation Check points for starting critical phases Internal check points Cyclin and cyclin dependent protein kinases (Cdk) Cyclin + phosphate (phosphorylation) = Cdk Initiate or regulate 4 key events External check points Surface receptors and binding sites for proteins G1, G1/S, S and M Growth hormones, peptide hormones, surface groups, matrix Speed/ slow/ stop Contact inhibition Cancer Control of cell cycle is lost, continuous and uncontrolled growth of cells = mass oncogenes SEE PAGE 217 Control proteins called Cyclins regulate function of many checkpoints Cyclins are proteins (work based on concentration) and Cdk are enzymes (function when phosphorylated and connected to cyclin) and cause action to occur 1. G1/S checkpoint Cell is stopped ; waiting for extracellular signals, checking for DNA damage; needs growth factor to procede. MAIN check point; once past G1/ S committed to mitosis 2. G2/M checkpoint Stopped before Mitosis if DNA didn’t replicate Insure identical daughter cells 3. Mitotic Spindle checkpoint Check at metaphase to see if chromosomes and kinetochores attached to spindle; insures even distribution of DNA MPF Maturation Promoting Factor 10.5 Overview: Cell Division in Prokaryotes Replication of DNA caused by enzymes Two circles of DNA migrate to opposite ends of cell Move as they are attached to CM and cell is elongating CW grows inward to create two cells “ Theta replication” “Binary fission”