* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File - respiratorytherapyfiles.net
Saturated fat and cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
History of invasive and interventional cardiology wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
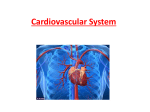
Cardiovascular System Chapter 5 Cardiovascular System (CV) • Composed of the heart and blood vessels • Arteries • Capillaries • Veins Internal structures of the heart 3 BLOOD VESSELS Heart Intro • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v= X9ZZ6tcxArI Pericardium – Surrounding the heart • Membrane that surrounds the heart as the pericardial sac and secretes pericardial fluid. • Heart is located within the pericardial sac Internal structures of the heart Pericardium, outermost layer • Pericardial cavity contains serous fluid, which reduces friction between the pericardial membranes as the heart moves What is being done here? CV System - Function • Right Side for circulating blood to lungs for oxygenation (pulmonary circulation) • Left Side for circulating blood to all body systems (systemic circulation) CV System - Function • Disposes of waste products • Aids lymphatic system in circulating substances Valves of the Heart •Tricuspid valve between right atrium and right ventricle •Pulmonary valve: between right ventricle and pulmonary artery Valves of the Heart • Mitral valve: between left atrium and the left ventricle • Aortic valve: between left atrium and aorta Pathway of blood through the heart 15 17 Heartbeat – two phases • Diastole: relaxation • Systole: contraction – The diastole-systole cardiac cycle occurs between 70-80 times per minute (100,000 times per day). – The heart pumps 3 ounces of blood with each contraction. This means that about 5 quarts are pumped per minute (75 gallons an hour and about 2000 gallons a day). Heart sounds Closure of valves associated with sounds “lubb-dubb, lubb-dubb” • lubb: closure of the tricuspid and mitral valves at the beginning of systole • dubb: closure of the aortic and pulmonary valves at the end of systole • Murmor: abnormal heart sound caused by improper valve closure Quick Quiz 1. What is the main function of the heart? 2. What heart structures control blood flow through the heart? Quick Quiz 1. What is the main function of the heart? Pump blood through blood vessels to all the cells of the body 2. What heart structures control blood flow to and from the heart? Heart valves Define Combining Forms – page 157 1. angi/o: vessel (ex: angiogram) 2. aneurysm/o: widening (blood vessel) 3. aort/o: aorta 4. arteri/o: artery Define Combining Forms – page 157 5. arteriol/o: arteriole 6. ather/o: fatty plaque (ex: atherosclerosis) 7. atri/o: atrium 8. cardi/o, coron/o: heart Define Combining Forms – page 157 9. phleb/o, ven/o: (Ex: phlebotomy) vein 10. thromb/o: blood clot (thrombi/thrombus) (traveling clot = emboli) Define Combining Forms – page 158 11. varic/o: Varicose veins dilated vein 12. vas/o: vessel 13. vascul/o: vessel 14. ventricul/o: ventricle What do these terms mean? • Vasoconstriction: • Vasodilation: What would these conditions do to blood pressure? Define Suffixes – page 158 13. -cardia: heart condition 14. -gram: record, writing 15. -graph: instrument for recording What do these terms mean? • Tachycardia • Bradycardia Define Suffixes 16. -megaly: enlargement 17. -graphy: process of recording 18. -oma: tumor or mass 19. -stenosis: narrowing/stricture 20. -ectasis: expansion/dilation Normal Heart and Cardiomegaly 32 Build Medical Words rapid heart rate: tachy/ suture of a widened blood vessel: aneurysm/o/ inflammation of an arteriole: /itis Build Medical Words 1. rapid heart rate: tachy/cardia 2. suture of a widened blood vessel: aneurysm/o/rrhaphy 3. inflammation of an arteriole: arteriol/itis Build Medical Words pertaining to the atrium and ventricle: /o/ventricul/ abnormal condition of fatty plaque hardening: ather/o/ /osis destruction or loosening of a thrombus: /o/ Build Medical Words pertaining to the atrium and ventricle: atri/o/ventricul/ar abnormal condition of fatty plaque hardening: ather/o/scler/osis destruction or loosening of a thrombus: thromb/o/lysis Build Medical Words narrowing or stricture of an artery: medical specialist in heart (disease): Build Medical Terms narrowing or stricture of an artery: arteri/o/stenosis medical specialist in the heart (disease): cardi/o/logist Build Medical Words enlargement of the heart: process of recording electrical activity of the heart: excision of an embolus: Build Medical Terms enlargement of the heart: cardi/o/megaly process of recording electrical activity of the heart: electr/o/cardi/o/graphy excision of an embolus: thromb/ectomy 41 CONDUCTION SYSTEM OF THE HEART • The pacemaker or SA Node begins wave of excitation again. • EKG or ECG (electrocardiogram): The record used to detect electrical changes in heart muscle as the heart beats. 42 CONDUCTION SYSTEM OF THE HEART 43 Electrocardiogram • P wave = spread of excitation wave over the atria just before contraction; • QRS wave = spread of excitation wave over the ventricles as the ventricles contract; • • T wave = electrical recovery and relaxation of ventricles. Myocardial Infarction, MI A heart attack - _______A heart attack Can be recognized by elevation in the S-T segment of the ECG. segment of the ECG. 45 Electrocardiogram 46 Electrocardiogram Pathology of the CV System DVT • Formation of a thrombus, usually in calf or thigh muscle • Part or complete block of blood flow • May cause pain, but often asymptomatic Deep vein thrombosis Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) - Treatment Anticoagulants: Prevent future thrombi formation Thrombolytics: Also called Fibrinolytics Dissolve blood clots Anti-Platelet 5 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Clinically Related Exercise 1. Mr. X is a postsurgical patient who complains of soreness in his right calf muscle. The doctor assesses the right calf and finds it to be warm and red. What is the likely diagnosis for Mr. X? 5 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Clinically Related Exercise 1. The physician prescribes medication for Mr. X to dissolve his DVT. This type of medication is called a ____________________ Pathology: Blood Vessels Coronary Artery Disease - CAD – Atherosclerosis • thrombotic occlusion (occlusive/mural) • ischemia • necrosis • infarction – Acute Coronary Syndromes (ACS) • unstable angina • myocardial infarction (MI) 53 Atherosclerosis Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) Signs and Symptoms • Angina • Shortness of breath (SOB) Common locations of anginal pain, which may vary in combination and intensity. Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) • Accumulation of plaque in arterial walls causing them to harden. • Complete blockage of arterial wall caused by blood clot formation or ruptured plaque. • Pieces of plaque break free, travel to the brain, and block blood vessels that supply blood to the brain. Atherosclerosis of internal carotid artery. Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) • Risk factors – – – – – – – Smoking Hypertension, stress Physical inactivity Family history Diabetes Obesity High cholesterol Drug therapies for CAD • nitrates (nitroglycerin) • Aspirin • beta-blockers • ACE inhibitors • calcium channel blockers • statins 58 59 Surgical therapies for CAD • coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG)________________ • percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI)_____________ • percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty_________ Aneurysm Signs and Symptoms • Local dilation of an artery or chamber of the heart due to weakening of its walls. • May cause thrombus formation, hemorrhage from rupture, or ischemia. Aneurysm - Types •Fusiform – dilation of entire circumference •Saccular – shaped like a sac, bulging on only one side •Dissecting – inner layer tear causes a cavity to form that fills with blood with each heartbeat) AneAneurysms Aneurysm • Three common types: abdominal thoracic peripheral artery aneurysms. • May be asymptomatic • Symptoms may include mild to severe weakness, sweating, tachycardia, and hypotension. Aneurysm - Treatment • Depends on the size, location, and the likelihood of its rupturing, as well as the general physical status of the individual. • Most are treated surgically. 5 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Clinically Related Exercise 1. An aneurysm may cause weakness, sweating, tachycardia, and low blood pressure, also known as (hypotension, hypertension, hypothymia). 2. During a physical examination, the doctor palpates and feels an abnormal dilation of a blood vessel. This may be diagnosed as a/an (aneurysm, carcinoma, tumor). Varicose Vein • Defective or incompetent valves in veins prevent blood from flowing freely toward the heart. – Buildup of pressure in superficial veins causes varicosities. Valve function in competent and incompetent valves 5 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Varicose Veins Signs and Symptoms (continued) • Could be due to inherited defect or to venous diseases. • May occur from conditions, such as pregnancy or jobs requiring prolonged standing or heavy lifting. • Person may be asymptomatic even though the varicose vein condition is severe. Varicose Veins • Swollen, tortuous, and knotted veins, usually occur in the lower legs. • As the condition progresses, veins thicken and feel hard to the touch. • Develop gradually, with a feeling of fatigue in the legs followed by a dull ache. Varicose veins More vocabulary for CV system 1. arrhythmia: 2. bruit: 1. arrhythmia: irregularity or loss of rhythm of the heartbeat; also called dysrhythmia 2. bruit: soft blowing sound heard on auscultation caused by turbulent blood flow 5 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Vocabulary Challenge Exercise 3. heart block: 4. heart failure (HF): heart block: interference with normal transmission of electrical impulses through the conducting system of the heart 4. heart failure (HF): inability of the heart to pump blood effectively enough to meet the body’s metabolic needs Vocabulary 5. hypertension: 6. ischemia: hypertension: consistently elevated blood pressure that is higher than 140/90 causing damage to the blood vessels and ultimately the heart ischemia: inadequate supply of oxygenated blood to a body part due to an interruption of blood flow Diagnostic Procedures • Cardiac Catheterization: • Catheter is guided into the heart via a vein or artery. Catheter insertion in femoral vein or artery Diagnostic Procedures Cardiac enzymes • Test to measure levels of enzymes released into the blood during an MI. • CK, CPK, Troponin Holter Monitoring • Records ECG readings, usually 24 hours, on a portable tape recorder to document arrhythmias and link them to activities or to symptoms, such as chest pain. Stress test •Exercise tolerance test to determine the heart’s response to physical exertion (stress). •ECG is recorded under controlled exercise stress conditions using a treadmill. •Nuclear stress test uses a radioisotope to evaluate coronary blood flow. Doppler Ultrasonography (US) • US used to assess blood flow through blood vessels and the heart. • Handheld US transducer emits sound waves as it is placed on the carotid artery to produce images of blood flow. Diagnostic Procedures Troponin I • Blood test that measures levels of proteins released into the blood when myocardial cells die (damaged heart muscle). ___________________________ • Recording of electrical activity of the heart. Vocabulary 1. record of electrical (activity) of the heart: 2. separation or destruction of a blood clot: Voacabulary record of electrical (activity) of the heart: electrocardiogram 4. separation or destruction of a blood clot: thrombolysis Vocabulary 3. abnormal condition of arterial (walls) hardening: 4. process of recording (radiography) vessels after injection of a contrast dye: Vocabulary abnormal condition of arterial (walls) hardening: arteriosclerosis process of recording (radiography) vessels (after injection of a contrast dye): angiography Medical and Surgical Procedures Automatic implantable cardioverterdefibrillator (AICD) • Device implanted in a patient who is at high risk for developing a serious arrhythmia Automatic implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (AICD) Angioplasty • Any endovascular procedure that reopens narrowed blood vessels. – Restores blood flow, usually using balloon dilation. Coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) Medical and Surgical Procedures Coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) • Vein taken from leg or other part of the body is grafted onto the heart to circumvent an obstruction in a coronary artery. Coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) Pharmacology Beta blockers • Decrease heart rate and dilate arteries by blocking beta receptors. Nitrates • Treat angina pectoris and hypertension. Pharmacology Nitrates • Treat angina pectoris. • Dilate veins, which decreases the amount of work the heart must do. • Dilate arteries to decrease blood pressure. Pharmacology Statins • Lower cholesterol levels in the blood. • Reduce cholesterol production in the liver. – Block the enzyme that produces cholesterol. Pharmacology Thrombolytics • Lyse (break apart) blood clots. • Used in acute management of myocardial infarction (MI). • Used to treat ischemic stroke. 5 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Clinically Related Exercise 1. Mrs. T is diagnosed with deep vein thrombosis in her lower leg. She is prescribed a drug that dissolves a blood clot. It is known as a (beta blocker, nitrate, thrombolytic). 2. Mr. B is diagnosed with hypercholesterolemia and advised to follow a low-fat diet. He is prescribed a drug that reduces cholesterol levels and is known as a (beta blocker, nitrate, statin).