* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Temporal Bone
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
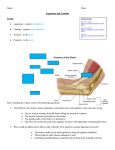
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Focus on the Skull Review Anatomical Terms Anterior/Posterior Dorsal/Ventral Medial/Lateral Superior/Inferior Bone Markings - Review Projections for attachment of muscles, ligaments and tendons (Process, trochanter, tuberosity, tubercle, crest, line, spine) Processes for articulation with other bones (Head, neck, condyle, trochlea, facet) Openings = holes or spaces in bone for nerves and vessels to pass (Foramen, canal, meatus, fissure, sinus) Depressions = indentations (Fossa, sulcus) Axial Skeleton Includes bones of the skull, vertebral column and thoracic cage Creates a framework of support and protection for internal organs Provides sites of attachment of muscles The Skull Protects the brain and supports delicate sense organs Bones that form the skull include 8 cranial bones 14 facial bones 6 auditory ossicles (tiny bones in the ears) Hyoid bone (the only freely moveable bone) Bones are joined by sutures Bones of the Cranium Frontal bone (1)- forms the forehead and roof of the ocular orbits Parietal Bone (2) – posterior to the frontal bone; forms the sides and roof of skull Occiptal Bone (1) – most posterior part of the cranium foramen magnum = large opening for spine Temporal Bone (2) – form the sides and base of the skull; a number of distinct anatomical landmarks Sutures of the Cranium Sagittal Suture – midline suture; between parietal bones Coronal Suture – between frontal bone and parietal bones Lambdoid Suture – between occipital and parietal bones Squamous Suture– between the temporal bones and the parietal bones Bones and Sutures of the Cranium Lateral View Coronal Suture Parietal Bone Temporal Bone Lambdoid Suture Squamous Suture Occipital Bone Frontal Bone Bones and Sutures of the Cranium Frontal View Coronal Suture Parietal Bone Frontal Bone Temporal Bone Bones and Sutures of the Cranium Inferior View Temporal Bone Parietal Bone Occipital Bone Bones and Sutures of the Cranium Horizontal View Frontal Bone Temporal Bone Parietal Bone Occipital Bone REVIEW The skull at birth The skull at birth Bones of the Cranium continued Sphenoid Bone– irregular bat-shaped bone forms part of the cranial floor Ethmoid Bone –stabilizes the brain; forms the roof and sides of the nasal cavity Vomer – nasal septum Palatine Bone – posterior hard palate (“roof of mouth”) Bones of the Cranium – Lateral View Coronal Suture Frontal Bone Parietal Bone Sphenoid Bone Temporal Bone Ethmoid Bone Lambdoid Suture Squamous Suture Occipital Bone Bones of the Cranium - Frontal Coronal Suture Parietal Bone Frontal Bone Sphenoid Bone Ethmoid Bone Temporal Bone Vomer Bones of the Cranium – Inferior View Palatine Bone Sphenoid Bone Vomer Temporal Bone Parietal Bone Occipital Bone Bones of the Cranium–Horizontal View Frontal Bone Sphenoid Bone Temporal Bone Parietal Bone Occipital Bone Ethmoid Bone Facial Bones Maxilla (2) – anterior part of hard palate; upper jaw; articulates with all other facial bones except the mandible Zygomatic Bones (2) – “cheek bones” Nasal Bones– bridge of nose Lacrimal Bones– tiny bones bearing tear ducts Mandible – lower jaw Bones of the Face – Lateral View Coronal Suture Frontal Bone Parietal Bone Sphenoid Bone Temporal Bone Ethmoid Bone Lambdoid Suture Squamous Suture Occipital Bone Lacrimal Bone Nasal Bone Zygomatic Bone Maxilla Mandible Bones of the Face - Frontal Coronal Suture Parietal Bone Frontal Bone Nasal Bone Sphenoid Bone Ethmoid Bone Lacrimal Bone Zygomatic Bone Temporal Bone Maxilla Mandible Vomer Bones of the Face – Inferior View Maxilla Palatine Bone Zygomatic Bone Vomer Temporal Bone Parietal Bone Occipital Bone Maxilla Sphenoid Bone Teeth (32) Incisors Canines Pre-molars Molars Pre-molars Canines Incisors Processes Any elevation or projection Can be part of a joint or a site of attachment for muscles, ligaments and tendons Processes of the cranium PROCESS Protrusion for attachment of tendons and ligaments Styloid process (temporal bone) Mastoid process (temporal bone) Zygomatic process (temporal bone) Occipital condyle (occipital bone) External occipital protuberance (occipital bone) Coronoid process (mandible) Condylar process (mandible) Mandibular process (mandible) Pterygoid process (sphenoid) Hamulus of the pterygoid process (sphenoid) Styloid Process Pointed piece of bone that extends down from the temporal bone just below the ear Attaches to ligaments that support the hyoid bone muscles that control the tongue and pharynx Mastoid Process Built up area of the lower temporal bone where important neck muscles attach Muscle that rotate and elevate the head and clavicle attach here Zygomatic Process of the Temporal Bone Connects temporal bone to facial bones (zygomatic bone) Occipital Condyle The site on the occipital bone where skull meets vertebrae Atlas = the first vertebrae in the spinal column External Occipital Protuberance Medial protrusion of the occipital bone Muscles that keep the head upright and allow the head to tilt backward attach here Coronoid Process (coronation day) “like a crown” Attachment point for muscle that closes the jaw Condylar Process Forms a hinge with the temporal bone Mandibular Process Smooth surface of the condylar process The Sphenoid Bone Pterygoid Process and the hamulus of the pterygoid process Process of the Skull – Lateral View Coronal Suture Parietal Bone Frontal Bone Sphenoid Bone Temporal Bone Ethmoid Bone Lambdoid Suture Lacrimal Bone Squamous Suture Occipital Bone Nasal Bone Zygomatic Process Zygomatic Bone Maxilla Mastoid Process Styloid Process Mandible Process of the Skull - Frontal Coronal Suture Parietal Bone Frontal Bone Nasal Bone Sphenoid Bone Ethmoid Bone Lacrimal Bone Zygomatic Bone Temporal Bone Ethmoid Bone Maxilla Mandible Vomer Process of the Skull– Inferior View Maxilla Palatine Bone Zygomatic Bone Zygomatic Process Maxilla Sphenoid Bone Vomer Styloid Process Mastoid Process Temporal Bone Parietal Bone Occipital Bone Occipital Condyle Processes of the Skull – Horizontal View Frontal Bone Sphenoid Bone Temporal Bone Parietal Bone Occipital Bone Ethmoid Bone Name the Process Name the Process Foramina and Other Structures General terms to describe openings include Foramen, canal, meatus, fissure sinus Foramina and Other Structures Supraorbital foramen (frontal) Infraorbital foramen (maxilla) Mental foramen (mandible) Foramen magnum (occipital) Jugular foramen (temporal) Carotid canal (temporal) External acoustic meatus (temporal) Mandibular foramen (mandible) Palatine foramen (palatine) Foramen lacerum (temporal) Foramen ovale (sphenoid) Foramen spinosum (sphenoid) Foramen rotundum (sphenoid) Stylomastoid foramen (temporal) FORAMEN, MEATUS, FISSURE, CANAL: Terms to describe openings for passage of nerves and blood vessels Supraorbital foramen** “above” the orbit blood vessels and nerves that innervate the eyebrows and eyelids Infraorbital foramen** “below the orbit” Facial nerves Mental foramen** Distal/lateral opening for the mental nerve and vessels that innervate the lip Mandibular foramen Proximal/medial opening for the mental nerve and vessels that innervate the lip and teeth Palatine foramen Nerves that innervate the palate External Auditory meatus** Opening that leads to the eardrum (tympanum) Foramen magnum** Spinal cord Jugular foramen** Jugular vein Carotid Canal** Carotid artery Foramen ovale** Trigeminal nerve – mandibular branch Foramen spinosum Nerves that innervate the meninges enter the brain Foramen lacerum Fills with cartilage after birth Foramen rotundum Trigeminal nerve: maxillary branch Stylomastoid foramen Facial nerves exit skull Foramina of the Skull – Lateral View Coronal Suture Frontal Bone Parietal Bone Sphenoid Bone Temporal Bone Ethmoid Bone Lambdoid Suture Lacrimal Bone Squamous Suture Occipital Bone Nasal Bone Zygomatic Bone Maxilla Zygomatic Process External Auditory Meatus Mastoid Process Styloid Process Mandible Mandible Mental Foramen Foramina of the Skull - Frontal Coronal Suture Parietal Bone Frontal Bone Supraorbital Foramen Nasal Bone Sphenoid Bone Ethmoid Bone Lacrimal Bone Zygomatic Bone Superior Orbital Fissure Optic Canal Temporal Bone Infraaorbital Foramen Ethmoid Bone Maxilla Mandible Vomer Foramina of the Skull– Inferior View Maxilla Palatine Bone Zygomatic Bone Zygomatic Process Vomer Styloid Process Mastoid Process Temporal Bone Parietal Bone Occipital Bone Maxilla Sphenoid Bone Foramen Ovale Carotid Canal Jugular Foramen Occipital Condyle Foramen Magnum Foramina of the Skull – Horizontal View Frontal Bone Sphenoid Bone Ethmoid Bone Optic Canal Foramen Ovale Temporal Bone Jugular Foramen Carotid Canal Parietal Bone Occipital Bone Foramen Magnum Other Features Superior Nuchal Line Inferior Nuchal Line Mandibular foss THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Continue with the vertebrae Vertebral Column Consists of 26 bones 24 vertebrae Sacrum Coccyx Vertebrae separated by cartilage (intervertebral discs) Subdivided based on vertebral structure Vertebrae Anatomy - general Vertebral body – massive weight bearing portion Vertebral foramen – the opening through which the spinal cord passes Articular processes – extensions of the vertebrae that articulate with other bones or provide attachment for muscles Transverse processes Superior articular processes Inferior articular processes Vertebrae Anatomy - General Vertebrae Anatomy by region Cervical Region Seven cervical vertebrae (C1 to C7) The first cervical vertebrae (C1; atlas) articulates with the occipital condyle Cervical region Anatomical Features oval concave body large vertebral foramen Stumpy spinous process with a notched tip Transverse foramina within the transverse processes Protect blood vessels supplying the brain Cervical Vertebrae Anatomy Cervical region Spinous Process Vertebral Arch Lamina Vertebral Foramen Superior Articular Processes Superior Articular Facet Pedicle Transverse Foramen Transverse Process Body Cervical region The first two cervical vertebrae have unique characteristics C1 = ATLAS (‘yes) Articulation of atlas with skull allows you to nod your head C2 = AXIS (“no”) Articulation of atlas and axis allows you to rotate your head The Atlas and Axis Dens (odontoid process) Ligament Articulates with occipital condyles Atlas (C1) Articulates with atlas Axis (C2) Thoracic Region Twelve cervical vertebrae (T1 to T12) Each thoracic vertebrae articulates with one or more pairs of ribs Thoracic region Vertebrae Anatomy Heart shaped body More massive than cervical vertebrae Large, slender spinous processes that point inferiorly Costal facets – for articulating with one or more pairs of ribs Vertebral Anatomy – thoracic region Spinous Process Transverse Process Lamina Articular facets Vertebral Arch Pedicle Articular facets Pedicle Vertebral Foramen Body Lumbar Region Five lumbar vertebrae (L1 to L5) The fifth lumbar vertebrae articulates with the sacrum Lumbar region Vertebrae Anatomy Vertebral body is thick and more oval than thoracic Massive, stumpy spinous process that projects posteriorly Bladelike transverse processes; no articulation for ribs Most massive, least mobile Vertebral Anatomy – lumbar region Spinous Process Vertebral Foramen Lamina Articular facets Transverse Process Pedicle Body Sacrum Region sacrum Single bone formed by the fusion of 5 embryonic vertebrae Sacrum Protects reproductive, digestive and excretory organs Attaches the axial skeleton to the appendicular skeleton Broad surface – attachment of leg muscles Bones fuse shortly after puberty Prominent bulge (sacral promontory) is an important landmark in females during labor and delivery Coccyx Coccyx Series of small fused vertebrae Coccyx Attachment site for muscle that closes that anal opening Fusion of the bone is not complete until late in adulthood May eventually fuse with the sacrum Normal Spinal Curvature Four spinal curves (seen in lateral view) Primary curves Thoracic and sacral curves Appear late in fetal development Secondary curves Cervical curve as baby holds head up Lumbar curve as baby learns to stand Normal Spinal Curvature Spinal curvature development Cervical curvature develops as a baby learns to hold its head Spinal curvature development Lumbar curvature develops as a baby learns to stand Abnormal spinal curvature Several abnormal conditions can arise during childhood and adolescence Kyphosis – exaggerated thoracic curvature Lordosis – exaggerated lumbar curvature Scoliosis – abnormal lateral curvature Kyphosis Lordosis Scoliosis THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Continue with the Thoracic Cage Thoracic Cage Consists of the thoracic vertebrae, the ribs and the sternum Ribs + sternum = rib cage Provides bony support for the walls of the thoracic cavity Protects heart and lungs Serves as base for muscles involved in respiration Ribs AKA costal bones Elongated flattened bones 12 pairs Ribs 1-7 = true ribs attach to the sternum by separate cartilage extensions Ribs 8-10 = false ribs; do not attach directly to the sternum; cartilages fuse before attachment Ribs 11-12 = floating ribs; do not connect to sternum at all Sternum AKA breastbone 3 parts Manubrium = Broad triangular part articulates with clavicle Elongated body articulates with ribs Ziphoid process 1. 2. 3. Damage to this process can puncture the liver CPR training places special emphasis on location of this part of the sternum to reduce damage during compressions Thoracic vertebrae Manubrium True Ribs Body Sternum Ziphoid Process Ribs False Ribs Costal Cartilage Floating Ribs