* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Anatomy
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
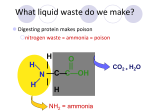
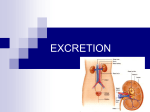
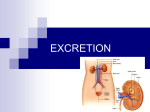
URINARY SYSTEM MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY Chapter Six HIT #141 Anatomy • Kidneys = bean-shaped organs, located on each side of the spinal column, removal of waste from the blood. – Nephron = microscopic located in the kidney, urine producing . – Glomerulus = process begins here, clusters of capillaries at the entrance of the nephron . – Renal pelvis = funnel shaped reservoir & passes it to the urter. – Hilum = indentation in kidney, ureter leaves. • Ureters = tubes, carry urine to the bladder. 1 Anatomy • Urinary bladder = hollow organ that temporarily holds the urine. • Urethra = tube, from bladder to the outside of the body, longer in the male. – Urinary meatus = opening through which the urine passes to the outside. • Urine = pale yellow liquid waste product, 95% water and 5% nitrogenous waste. Word Parts • • • • • • • • • Cyst/o vesic/o = bladder, sac. Glomerul/o = Glomerulus. Meat/o = meatus (opening). Nephr/o ren/o = kidney. Pyel/o = kidney. Ureter/o = ureter. Urethr/o = urethra. Albumin/o = albumin Azot/o = urea, nitrogen 2 Combining Forms • • • • • • • • • • Blast/o = developing cell. Glyc/o = sugar. Hydr/o = water. Lith/o = stone, calculus. Noct/i = night. Olig/o = scanty, few. Son/o = sound. Tom/o = cut, section. Urin/o = urine. Ven/o = vein. Suffixes • • • • • • • • -iasis esis = condition -lysis = loosening, dissolution, separating -megaly = enlargement -orrhaphy = suturing, repairing -ptosis = drooping, sagging, prolapse -tripsy = surgical crushing -uria = urine, urination -trophy = nourishment, development 3 Disease & Disorder Terms • • • • • • • • Cystitis = inflammation of the bladder. Cystocele = protrusion of the bladder. Cystolith = stone in the bladder. Hydronephrosis = abnormal condition of water in the kidney, from an obstruction. Nephroblastoma = kidney tumor, developing cell, (Wilms’ tumor). Nephrolithiasis = stones in the kidney. Nephroma = tumor of the kidney. Nephromegaly = enlargement of the kidney. Disease & Disorder Terms • • • • • • Nephroptosis = drooping kidney. Pyelitis = inflammation of the renal pelvis. Uremia = urine in the blood, toxic condition. Ureterocele = protrusion of a ureter. Ureterostenosis = narrowing of the ureter. Urethrocystitis = inflammation of the urethra and the bladder. • Polycystic kidney = kidney contains many cysts and is enlarged. • Renal calculi = stones in the kidney. 4 Disease & Disorder Terms #3 • Renal hypertension = elevated blood pressure, resulting from kidney disease. • Urinary retention = accumulation of urine in the bladder. Inability to urinate. • Urinary suppression = sudden stoppage of urine formation. • Urinary tract infection (UTI) = infection of one or more of the urinary tract. Surgical Terms • Cystectomy = excision of the bladder. • Cystolithotomy = incision of the bladder to remove a stone. • Cystoplasty = surgical repair of the bladder. • Cystostomy = creating an artificial opening into the bladder. • Lithotripsy = surgical crushing of a stone. • Nephrectomy = excision of a kidney. • Nephropexy = surgical fixation of the kidney. 5 Surgical Terms take two • Pyelolithotomy = incision of the renal pelvis to remove a stone. • Ureterectomy = excision of a ureter. • Urethroplasty = surgical repair of the urethra. • Urethrotomy = incision in the urethra. • Fulguration = destruction of living tissue with an electric spark, to remove growths. • Renal transplant = implantation of a donor kidney. • Lithotrite = instrument used to crush a stone. Procedural Terms • Cystogram = x-ray film of the bladder. • Cystography = x-ray filming the bladder. • Cystopyelgram = x-ray film of the bladder and the renal pelvis. • Intravenous pyelogram (IVP) = x-ray film of the renal pelvis with contrast medium injected intravenously. • Nephrogram = x-ray film of the kidney. • Nephrosonography = recording the kidney with sound. Ultrasound test. 6 Procedural Terms • Renogram = graphic record of the kidney. • Retrograde pyelogram = x-ray of the renal pelvis, opposite from normal direction with contrast medium injected through the urethra. • Cystoscope = instrument for visual examination of bladder. • Cystoscopy = visual examination of the bladder. • Nephroscopy = visual examination of kidney. • Urethroscope = used to visualize the urethra. Procedural Terms • KUB = an x-ray of the abdomen, kindey, ureter & bladder. • BUN = measure the amount of urea in the blood. Determines kidney function. Increase indicates renal dysfunction. • Specific gravity = test on urine specimen to measure the concentration or diluting ability of the kidneys. • Urinalysis (UA) = multiple routine test done on a urine specimen. 7 Complementary Terms • Albuminuria = albumin in the urine, indicates kidney problems. • Anuria = absence of urine. • Dysuria = difficulty of painful urination. • Glycosuria - sugar (glucose) in the urine. • Hematuria = blood in the urine. • Nocturia = night urination. • Oliguria = scanty urination. • Polyuria = excessive urine. Complementary Terms • Pyuria = pus in the urine. • Urologist = physician who specializes in the diagnosis and treatment of the urinary system. • Urology = study of the urinary system. The the reproductive system of the male. • Catheter = flexible, tube-like device for withdrawing or instilling fluids. • Distended = stretched out. • Diuretic = agent that increases the amount of urine. 8 Complementary Terms • Enuresis = involuntary urination (bed wetting). • Hemodialysis = procedure of removing impurities from the blood, because kidney can’t. • Incontinence = inability to control the bladder and/or bowels. • Micturate = to urinate of void. • Stricture = abnormal narrowing, urethral stricture. • Void = to empty or evacuate waste material. Abbreviations • • • • • • • • • BUN = blood urea nitrogen cath = catheterization ESWL = extracorporeal shock wave Lithotripsy HD = hemodialysis KUB = kidney, ureter, and bladder SG = specific gravity UA = urinalysis UTI = urinary tract infection VCUG = voiding cystourethrogram 9 Micturation Break The end of chapter 6 10