* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Directed Reading A Section: The Organization of Living Things
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
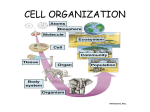
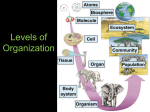
Name Class Date Skills Worksheet Directed Reading A Section: The Organization of Living Things (pp. 128–133) Write the letter of the correct answer in the space provided. ______ 1. What is anything that can perform life processes by itself called? a. a cell b. a tissue c. an organ d. an organism ______ 2. What are the two types of organisms called? a. old organisms and new organisms b. large organisms and small organisms c. living organisms and nonliving organisms d. unicellular organisms and multicellular organisms UNICELLULAR ORGANISMS ______ 3. What are organisms that are made of one cell called? a. unicellular organisms b. multicellular organisms c. inorganic organisms d. nonreproducing organisms ______ 4. What kind of organism does NOT need many resources to stay alive? a. unicellular organisms b. multicellular organisms c. inorganic organisms d. nonreproducing organisms MULTICELLULAR ORGANISMS ______ 5. What are organisms that are made of many cells called? a. unicellular organisms b. multicellular organisms c. inorganic organisms d. nonreproducing organisms ______ 6. How does a multicellular organism start out? a. as a single cell b. as a clump of cells c. as a collection of yeasts d. as a piece of another organism Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved. Holt California Life Science 61 Cells: The Basic Units of Life Name Class Date Directed Reading A continued ______ 7. In multicellular organisms, what happens as a single cell becomes many cells? a. Cells become disorganized. b. Cells become larger. c. Cells become smaller. d. Cells become differentiated. ______ 8. What does it mean when cells become differentiated? a. Cells can do everything. b. Cells cannot do anything. c. Cells do only one thing. d. Cells grow and divide. The Characteristics of Being Multicellular ______ 9. How do multicellular organisms become larger? a. by making their cells larger b. by making more small cells c. by connecting to other organisms d. by living in a larger group ______ 10. What happens to a unicellular organism if its cell dies? a. The organism dies. b. The organism lives. c. The organism grows. d. The organism shrinks. ______ 11. What happens to a multicellular organism if one cell dies? a. The organism dies. b. The organism lives. c. The organism grows. d. The organism shrinks. ______ 12. Why is a multicellular organism more efficient than a unicellular organism? a. Each cell is specialized. b. Each cell does everything. c. Each cell does two things. d. Each cell lives forever. ______ 13. How is having specialized cells like having an assembly line in a factory? a. Each job takes a long time. b. No job takes very long. c. More things are done in less time. d. Nothing is done on time. Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved. Holt California Life Science 62 Cells: The Basic Units of Life Name Class Date Directed Reading A continued FROM CELLS TO ORGANISMS ______ 14. What are the four levels of organization for a multicellular organism? a. cells, tissues, organs, bodies b. cells, organs, organ systems, bodies c. cells, tissues, organ systems, bodies d. cells, tissues, organs, organ systems Cells: The First Level of Organization ______ 15. What is the job that a cell does called? a. function b. structure c. specialty d. normality ______ 16. What is the way a cell is put together called? a. function b. structure c. specialty d. normality ______ 17. What sausage-shaped plant cells control openings for carbon dioxide and oxygen? a. guard cells b. oxygen cells c. bacterial cells d. mitochondrial cells Tissues: The Second Level of Organization ______ 18. What is a group of cells that work together called? a. cell group b. tissue c. organ d. body system ______ 19. What are the four kinds of tissues that animals have? a. transport, protective, ground, nerve b. nerve, muscle, connective, protective c. cardiac, digestive, brain, respiratory d. cell, tissue, organ, organ system Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved. Holt California Life Science 63 Cells: The Basic Units of Life Name Class Date Directed Reading A continued Match the correct description with the correct term. Write the letter in the space provided. ______ 20. tissue that moves water and food through a plant a. protective b. transport ______ 21. tissue that covers and protects a plant c. ground ______ 22. tissue where photosynthesis takes place in a plant Organs: The Third Level of Organization Write the letter of the correct answer in the space provided. ______ 23. What is made up of two or more tissues working together? a. cell b. connective tissue c. organ d. tissue system ______ 24. What organ is made of cardiac, nerve, and blood vessel tissues? a. heart b. stomach c. brain d. skin ______ 25. What plant organ has tissue that traps sunlight energy to make food? a. root b. leaf c. stem d. flower Organ Systems: The Fourth Level of Organization ______ 26. What is a group of organs that work together called? a. connective organs b. organism c. organ system d. tissue ______ 27. What organ system works together to move blood through the body? a. digestive system b. respiratory system c. stem system d. cardiovascular system Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved. Holt California Life Science 64 Cells: The Basic Units of Life Name Class Date Directed Reading A continued ______ 28. What are three organ systems in plants? a. leaf, root, stem b. respiratory, cardiovascular, digestive c. transport, protective, ground d. membrane, chloroplast, lysosome ORGANISMS Use the terms from the following list to complete the sentences below. tissue cell organ organ system organism 29. The first level of organization in a multicellular organism is a(n) . 30. A group of cells that do a special job is called a(n) . 31. A group of tissues forms a(n) . 32. A group of organs forms a(n) . 33. Organ systems form a(n) . UNICELLULAR ORGANIZATION Write the letter of the correct answer in the space provided. ______ 34. How does a unicellular organism live? a. Many cells do many things. b. Many cells do one thing. c. One cell does everything. d. One cell does one thing. Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved. Holt California Life Science 65 Cells: The Basic Units of Life