* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Trophic Levels - davis.k12.ut.us
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
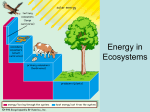
Trophic Levels Notes #10 Trophic Level (notes) • A trophic level is the “level” an organism occupies in a food chain or food web based on how far away it is from the original source of energy Trophic Levels (not notes) • This concept is easier to see than it is to explain • First: where does the food chain start? • Second: how many steps does it take to get from the beginning to the organism? Trophic Level Terms (notes) In order of increasing trophic level, the terms are: • Primary producer • Primary consumer • Secondary consumer • Tertiary consumer • Quaternary consumer … • Apex predator (trophic number changes, but nothing consumes it) (Not notes) Carnivore Top/Apex Predator Hawk Carnivore/Omnivore Tertiary Consumer Snake Carnivore/Omnivore Secondary Consumer Lizard Herbivore/Omnivore Primary Consumer Harvester Ant Primary Producer Seed-producing plant Names of levels Example food chain Consumers Producer (Sun) Trophic Practice (not notes) Which level does each of the species represent on the food chain? • Plant • Grasshopper • Bird • Snake • Owl Trophic Practice (not notes) Which level does each of the species represent on the food chain? • Plant Primary producer • Grasshopper Primary consumer • Bird Secondary consumer • Snake Tertiary consumer • Owl Quaternary consumer (apex predator) What About Food Webs? (not notes) • What about food webs where it is possible for an organism to have more than one trophic level? • In these cases scientists calculate a “fractional trophic level.” This is based on the trophic levels of the species’ prey as compared to their overall diet 10% Rule (notes) • Review: whenever energy is transformed some is lost as waste heat • On average, only 10% of the energy from each level is transferred to the next • This limits how many organisms an ecosystem can support, and is why there are always more prey than predators (Not notes) Apex predator Tertiary Consumer Secondary Consumer Primary Consumer Primary Producer As you go up in trophic level, the mass of each level decreases because of the limited amount of energy available. Example Problem (not notes) • If there are 100 grams of minnows in a population, about how many grams of tuna could they support? Example Problem (not notes) • If there are 100 grams of minnows in a population, about how many grams of tuna could they support? About 10 grams (or 10% of the mass of the minnows) Example Problem (not notes) • If there are 100 grams of minnows in a population, about how many grams of tuna could they support? About 10 grams (or 10% of the mass of the minnows) • About how many grams of shark could be supported by this ecosystem? Example Problem (not notes) • If there are 100 grams of minnows in a population, about how many grams of tuna could they support? About 10 grams (or 10% of the mass of the minnows) • About how many grams of shark could be supported by this ecosystem? About 1 gram (10% the mass of the tuna, or 1% the mass of the minnows) Woodlands Food Web Continued • Reminder: neatness is key! Plan before you glue things down • In addition to what you began yesterday, label each of the organisms on your web with their trophic level (including apex predators). • If an organism has multiple levels list all that apply.