* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download step-up transformer
Wireless power transfer wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Power factor wikipedia , lookup
War of the currents wikipedia , lookup
Electric power system wikipedia , lookup
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Mercury-arc valve wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Spark-gap transmitter wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Earthing system wikipedia , lookup
Galvanometer wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Amtrak's 25 Hz traction power system wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Distribution management system wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic core wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Ignition system wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Single-wire earth return wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
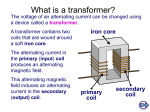
HASMUKH GOSWAMI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING TOPIC :- Transformer PREPARED BY, Radadiya Radhika L. 140240109506 Champaneri Shubham R.150243109501 Patel Jaimin S. 150243109014 Shrimali Chirag J. 150243109502 Tripathi Aman N. 150243109021 Guided by, Niketan Dobriya Electrical DEPARTMENT 1/80 A transformer is a device for increasing or decreasing an a.c. voltage. WHAT IS A TRANSFORMER? • TRANSFORMER IS A STATIC DEVICE WHICH TRANSFORMS A.C. ELECTRICAL POWER FROM ONE VOLTAGE TO ANOTHER VOLTAGE KEEPING THE FREQUENCY SAME BY ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION. TYPES OF TRANSFORMER BY APPLICATION • • • • • • • • • • • • • • 1. DISTRIBUTION TRANSFORMER 2.POWER TRANSFORMER 3.CURRENT TRANSFORMER 4.POTENTIAL TRANSFORMER 5.FURNACE TRANSFORMER 6.BOOSTER TRANSFORMER 7.RECTIFIER TRANSFORMER 8.LOCOMOTIVE TRANSFORMER 9.MINING TRANSFORMER 10.PHASE SHIFTING TRANSFORMER 11.WELDING TRANSFORMER 12.HIGH VOLTAGE TESTING/SC TESTING TRF. 13.GROUNDING TRANSFORMERS 14.CONVERTER TRANSFORMER Structure of Transformer PARTS OF TRANSFORMER • • • • • • • • • • • • • • MAIN TANK RADIATORS CONSERVATOR EXPLOSION VENT LIFTING LUGS AIR RELEASE PLUG OIL LEVEL INDICATOR TAP CHANGER WHEELS HV/LV BUSHINGS FILTER VALVES OIL FILLING PLUG DRAIN PLUG CABLE BOX Circuit Symbol for Transformer How Transformer works Laminated soft iron core Input voltage Output voltage (a.c.) (a.c.) Primary coil Secondary coil All transformers have three parts: 1. Primary coil – the incoming voltage Vp (voltage across primary coil) is connected across this coil. 2. Secondary coil – this provides the output voltage Vs (voltage across the secondary coil) to the external circuit. 3. Laminated iron core – this links the two coils magnetically. Notice that there is no electrical connection between the two coils, which are constructed using insulated wire. Two Types of Transformer A step-up transformer increases the voltage there are more turns on the secondary than on the primary. A step-down transformer decreases the voltage - there are fewer turns on the secondary than on the primary. To step up the voltage by a factor of 10, there must be 10 times as many turns on the secondary coil as on the primary. The turns ratio tells us the factor by which the voltage will Formula for Transformer voltage across the primary coil number of turns on primary voltage across the secondary coil number of turns on secondary Vp Vs Np Ns Where Vp = primary voltage Vs = secondary voltage Np= Number of turns in primary coil Ns = Number of turns in a secondary coil. Ideal Transformer Relationships Note that I2 and I2’ are in opposite directions Assume we have flux m in magnetic material. Then flux linking coil 1 having N1 turns is: 1 N1m , and similarly d m d 1 v1 d m dt dt v1 N1 N1 dt v2 N2 , v2 2 N 2m d 2 dt d m N2 dt V1 N1 a = turns ratio V2 N2 12 Worked example No. 1 The diagram shows a transformer. Calculate the voltage across the secondary coil of this transformer. Step-up transformer! Solution VP N P VS N S Substituting 12 180 VS 540 Crossmultiplying 180.VS 12 x 540 12 x 540 VS 180 VS 36 V Worked example No. 2 A transformer which has 1380 turns in its primary coil is to be used to convert the mains voltage of 230 V to operate a 6 V bulb. How many turns should the secondary coil of this transformer have? VP = 230 V VS = 6 V NP = 1380 NS = ? Obviously, a Step-down transformer!! Solution VP N P VS N S Substituting 230 1380 6 NS Crossmultiplying 2300.N S 6 x 13800 6 x 1380 NS 230 N S 36 turns MAIN FEATURES • OUTDOOR,OIL COOLED, 3 PHASE,50HZ • PRIMARY IS DELTA CONNECTED AND SECONDARY IS STAR CONNECTED. • NATURALY COOLED (ONAN TYPE). • AMONGST ALL THE TYPES OF TRANSFORMERS THIS IS THE MOST REQUIRED AND MOST USED TYPE. MAINTENANCE OF TRANSFORMER • Transformer is the heart of any power system. Hence preventive maintenance is always cost effective and time saving. Any failure to the transformer can extremely affect the whole functioning of the organization. PROTECTION OF TRANSFORMERS • The best way of protecting a transformer is to have good preventive maintenance schedule. • Oil Temperature Indicators. • Winding Temperature indicators. • Buchholz Relay. • Magnetic Oil level Gauge. • Explosion Vent. Transformer Losses and Efficiency •Transformer Losses •Core/Iron Loss =V12 / Rc1 •Copper Loss = I12 R1+ I22 R2 Definition of % efficiency V2 I 2Cos 2 *100 Losses V2 I 2Cos 2 V2 I 2Cos 2 V12 / Rc1 I12 R1 I 2 R2 V2 I 2Cos 2 2 V2 I 2Cos 2 V12 / Rc1 I 2 Req 2 V2 I 2Cos 2 2 Cos 2 *100 *100 = load power factor Transformer 20 Maximum Transformer Efficiency The efficiency varies as with respect to 2 independent quantities namely, current and power factor •Thus at any particular power factor, the efficiency is maximum if core loss = copper loss .This can be obtained by differentiating the expression of efficiency with respect to I2 assuming power factor, and all the voltages constant. •At any particular I2 maximum efficiency happens at unity power factor. This can be obtained by differentiating the expression of efficiency with respect to power factor, and assuming I2 and all the voltages constant. •Maximum efficiency happens when both these conditions are satisfied. Transformer 21 Maximum efficiency point 100 pf=1 pf= 0.8 pf= 0.6 At this load current core loss = copper loss 0 % full load current Transformer 22 23/80