* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The structure and function of Xylem and phloem tissue
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
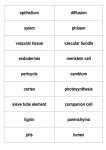
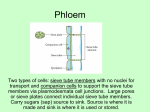
The structure and function of Xylem and phloem tissue Objectives To understand and be able to describe the structure of xylem and phloem as seen under a microscope The structure and function of Xylem and phloem tissue • Xylem tissue transports water, inorganic ions and a few small organic molecules from the roots upwards • Phloem tissue transports organic substances made by the plant, such as sucrose, from where they are made to the rest of the plant, such as leaves to storage organs • Xylem and phloem usually are held close together in a vascular bundle Xylem • Made from dead vessel elements (cells) aligned end to end to form a continuous tube called a xylem vessel • Thick walls impregnated with lignin - waterproofs the cells and and is strong to provide structural support. • End walls and cell contents decay as xylem develops. • Lignin is laid down in various patterns. • Pits in lignin allow communication between adjacent cells. Why is the flow of water not impeded? Xylem Images Xylem Structure Made from dead cells aligned end to end in a continuous column Function Xylem tubes are narrow Lignified walls Pits in lignified walls Lignin first laid down in spiral/reticulate format Phloem Structure Reduced cytoplasm and no nucleus Companion cells have numerous mitochondria Plasmodesmata link the cytoplasm of the sieve tube cell and the companion cell Function The structure and function of xylem and phloem • Consists of sieve tube elements and companion cells. • Sieve tube elements have very little cytoplasm and no nucleus but they are living cells. • They line up end to end, and are connected by a sieve plate. • Sieve tube elements have thin walls and are usually 5 or 6 sided. • Each sieve tube element lies closely to a Companion cell. • These are small cells with a large nucleus, dense cytoplasm and numerous mitochondria to produce ATP for the active loading of sucrose into the sieve tube elements. • Cytoplasm of the companion cell is linked to the sieve tube element by gaps in the cell walls called plasmodesmata. Phloem Phloem Images