* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plant Structure and Function Notes Outline
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
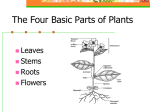
Name __________________________ Date:_________ Period ____ Plant Structure and Function Notes Outline Tissues A plant’s body is made of _____________ that form _____________. A waxy __________, which prevents ___________ loss, __________ the epidermis of the __________ and _____________. Often the ________ of the _______________ have ________-like extensions or other ___________________. In ________________ plants, there are _________________ of the _______________ cells on __________ and ________ types of _________ systems. _____________ often help to ________ water _______. _______________ Tissue System Forms the protective ___________ layer of a plant. ________________ Tissue System Makes up much of the _________ of the nonwoody parts of a plant, including _________, __________, and ___________. ________________ Tissue System ________________ of the epidermal _______ on ________ tips help ________________ water ________________. The ____________ tissue on woody ________ and ____________ consists of several layers of ____________ cells that are referred to as ____________. ____________ cells contain a ___________________ chemical and are _____ covered by a waxy _____________. Forms strands that conduct _________, ____________ and In addition to ________________, _____________ tissue also functions in _______________ compounds throughout a __________ plant. ________ exchange and in the ______________ of mineral ________________. Dermal Tissue System Ground Tissue System ____________ tissue covers the _______________ tissue makes up much of the ____________ of most plants. ______________ of a plant’s body. Most __________ tissue consists of ______-walled ________ that remain In the _________________ parts of a __________ and keep their ____________ after they ______________. plant, dermal tissue forms a “________” Some ______________ tissue contains some __________-walled cells. called the _____________________.! ____________ tissue has different ______________, depending on where it is The __________________ of most plants is made up of a _____________ layer _________________ in a plant. of flat __________. The ground tissue in _____________, which is packed with ________________, is specialized for _________________________. Vascular Tissue System Plants have _______ kinds of _________________ tissue. The ground tissue in __________ and _________ functions mainly in the _____________ and ______________. ____________ of ________, __________, and _________. Both _____________ and _______________ contain strands of ________ that Throughout the _________ of a plant, __________ tissue also _____________ are _____________ end to end and act like tiny __________. and _________________ the third kind of plant tissue – ______________ tissue. These _______________ of cells act as a ______________ system, carrying ______________ and dissolved _________________ throughout a plant’s body. Xylem ___________ has ________-walled ________ that conduct _________ and _______________ nutrients from a plant’s ____________ through its _________ to its _____________. The conducting cells in ___________ must ________ their cell _____________, _______________, and _________________ before they can conduct _______. At ____________, all that is left of these ______ is their cell ____________. _________ in the walls ______________ neighboring ________-tube cells One type of __________ cell found in all vascular plants is called a __________. connect the _________________ and allow _____________ to pass freely from ______________ are ____________, elongated, and ___________ at each end. ________ to __________. ___________ flows from one ____________ to the next through _______, which Beside the _________ tubes are rows of ______________________ cells, which are _____ areas in the cell _________. contain _________________. Gnetophytes and flowering plants also have a second type of __________ cell, _________________ cells carry out cellular _____________, protein which makes up ______________ strands called _____________. ______________, and other _____________ functions for the ______-tube cells. The _______________ cells are _________ than _______________ and have large ______________________ in their ends. The _____________________ allow ____________ to flow more _________ between _______________ cells. Phloem _______________ contains cells that conduct ___________ and other ______________ throughout a plant’s body. The conducting _____________ of phloem have a cell _________, a cell Plant Cells and Tissues ________________, and _____________________. These _________ either _________ organelles or have _______________ organelles. Plant Tissue _____________ Tissue The __________________ strands in _____________ are called __________ ____________. _____________ Tissue _____________ Tissue Cell Types Roots Most ___________ are ________________ to Roots are covered by __________ tissue.! An ________________ covers all of a the spot where they _________ by _________, _________ except for the root ______. which also ___________ water and mineral The _____________ cells just behind a _________________. root _______ often produce root In many plants, _________ also function in the _________, which are slender ______________ of organic nutrients, such as _______________ of the cell __________________. ________ and ____________. Root ___________ greatly increase the surface ___________ of a root and its Many _________, such as ___________ and ___________ to absorb __________ and mineral _______________. ___________, have a large ___________ root from which much ___________ A mass of ________ called the root ______ covers and ____________ the roots _________. actively ________________ root tip. This type of ________ system is called a ________________ system. A layer of ________ replaces the ______________ in the _________ sections of Most ____________ such as ___________, have a highly ____________, a root. _____________ root system. Many plants have __________ that become __________ as they get ________. Some plants have _________ that grow from ____________________ stems or Layers of ___________ replace the ___________ tissue in ___________ roots. ______________. These roots are called _____________________ roots. Stems The ______________ of most plants consist of ___________ and The _________ roots of corn and the ________ roots of orchids are ______________. examples of ____________________ roots. _____________ support the __________ and house the _________________ A _________ has a central _________ of ___________________ tissue that is tissue, which ________________ substances between the _________ and the surrounded by ______________ tissue. ____________. The _____________ tissue surrounding the ____________ tissue is called the Many plants have __________ that are __________________ for other __________. ________________. Stems of _______________ store _________. Cactus ___________ are specialized for ____________ and __________ _____________ are stems that are specialized for _____________ storage conservation, while garden-pea _________ are specialized for _________. and for __________________ reproduction. A _______ is a mass of _____________ tissue and _____________ tissue covered by ______________. Leaves ________________ are the primary A _____________ coats the ___________ and __________ epidermis. ____________________ organs of plants. Both _____________ and ____________ are found in the __________ of a leaf. Most __________ have a flattened portion, ____________ are _________________ of vascular ______________ that run called the __________, that is often from the tips of ___________ to the edges of _____________. ________________ to a __________ by a In _____________, the ground tissue is called ______________________. _________ called the _____________. _______________ cells are packed with _________________, where A leaf __________ may be divided into _______ or more ___________ called ___________________________ occurs. ______________. The ___________________ in ________________ makes leaves look _______. _____________ with an ________________ blade are called _____________ leaves. Leaves with ________ or more ___________ are called _______________ leaves. ______________ reduce the ______________ area of a leaf ___________. Many plants have highly _______________ leaves that are _______________ for particular ________________. The ___________ of a __________ and the __________ of a garden __________ are ______________ leaves. Leaves Most ________ have leaves with _____ layers of _______________. The _______________ of water _____________ causes water molecules that are being _________ by a plant to _______ on the water _____________ still in One or more ______ of closely packed _______________ cells make up the the __________. ______________ layer, which lies just _________ the upper _______________. This _______ extends through the ___________ in the ____________. A layer of _________ packed, ___________ cells, called the _________ layer, _________ is drawn ____________ in the same way __________ is drawn lies ______________ the ____________ layer and the lower ______________. through a ______________. The ___________ layer has many ______ spaces through which _________ can As long as the _____________ of water in the __________ does not _________, travel. __________ will keep moving ___________ as ___________________ occurs. ____________, the tiny _________ in the _____________, connect the ______ _____________ take in ___________ from the _________ by ______________. spaces to the ___________ air. This _____________ enters the ___________ and _____________ the water Movement of Water in Plants ____________ through ___________________. _________ and __________ nutrients move up from a plant’s _________ to its Guard Cells and Transpiration ____________ through ____________. A _________ is surrounded by a ________ of ___________ cells that are __________ is pulled ______ through a plant as it ______________ from the __________ like two cupped hands. plants ____________. ____________ in water ___________ within the __________ cells cause the The __________ of ____________ are coved with many tiny __________, the __________ to _________ or __________. ____________. When the __________ cells take in __________, they ___________. When the __________ are ________, water _______ diffuses ______ of a leaf. Extra _____________ strands in their cell _________ permit the ________ This ______ of water ________ from a plant is called __________________. to ______________ in length but not in _____________.! In most _____________, more than _____% of the ________ taken in by the As a result, ___________ cells that take in ____________ bend _________ from ___________ is ultimately ________ through _________________. each other, _____________ the __________ and The ____________ contains a _____________ of water that extends from the allowing _______________ to proceed. __________ to the ___________. When ___________ leaves the ___________ cells, they ____________ and Translocation move ___________ to each other, ____________ the The ________________ of organic _______________ in a plant is more stoma and ______________ transpiration. __________ than the movement of ___________ for three reasons. The _______ of water from ___________ cells (for 1. _________ flows ___________ through empty ___________ cells, but any reason) causes ________________ to _________, _______________ ______________ compounds must ______ through the further water ________. _________________ of ___________ phloem _________. This is an example of ________________________. Movement of Organic Compounds in Plants _______________ compounds move throughout a plant within the _________. ____________ use the term __________ to refer to a part of a plant that _____________ organic compounds for _______ parts of the ________. 2. ____________ only moves _____ in _______, while _____________ compounds move in ____ directions in __________. 3. __________ can ___________ through cell ________________ but ____________ compounds _____________. The ______________ botanist Ernst ___________ proposed a model of A _________ is a __________ because it makes __________ during ___________________ in _________. In this _____________ –_______ ____________________. ________________: A ________ that stores _________ is also a ___________. ___________ from a __________ enters _____________ cells by ___________ use the term __________ to refer to a part of a _________ that ______________ __________________. organic compounds are ________________ to. When the ___________ concentration in the phloem _________________, ____________ growing _________, such as root ______ and developing ____________ enters the __________ tubes in ___________ from _________, are examples of ________. ___________ by ______________. The _____________ of organic compounds ____________ a plant from a _______________ builds up ___________ the __________-tube __________ to a _________ is called ____________________. ________ and ____________ sugar through the ___________ tubes. __________ moves from _____________ cells into a _________ by _______________ ____________________.