* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 8.2 Major Endocrine Organs
History of catecholamine research wikipedia , lookup
Triclocarban wikipedia , lookup
Neuroendocrine tumor wikipedia , lookup
Xenoestrogen wikipedia , lookup
Menstrual cycle wikipedia , lookup
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency wikipedia , lookup
Bioidentical hormone replacement therapy wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (male-to-female) wikipedia , lookup
Breast development wikipedia , lookup
Hyperthyroidism wikipedia , lookup
Hyperandrogenism wikipedia , lookup
Endocrine disruptor wikipedia , lookup
Mammary gland wikipedia , lookup
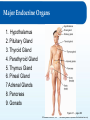
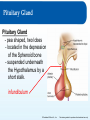
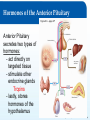
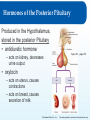
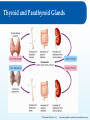
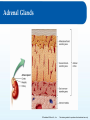
Chapter 8: The Endocrine System Lesson 8.2 Major Endocrine Organs Major Endocrine Organs 1. Hypothalamus 2. Pituitary Gland 3. Thyroid Gland 4. Parathyroid Gland 5. Thymus Gland 6. Pineal Gland 7 Adrenal Glands 8. Pancreas 9. Gonads Figure 8.1 - page 269 © Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only. The Hypothalamus The Endocrine System is run by the Hypothalamus - Buried deep within the brain (4 grams) - Collects information from each body system + integrate response with the NS + maintains homeostasis by regulating » metabolism » heart rate » energy level » body temperature » Thirst The Hypothalamus controls by releasing hormones to stimulate/inhibit Pituitary Hormones. © Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only. Pituitary Gland Pituitary Gland - pea shaped, two lobes - located in the depression of the Sphenoid bone - suspended underneath the Hypothalamus by a short stalk. infundibulum © Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only. Hormones of the Anterior Pituitary Figure 8.6 – page 277 Anterior Pituitary secretes two types of hormones: - act directly on targeted tissue - stimulate other endocrine glands Tropins - lastly, stores hormones of the hypothalamus © Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only. Hormones of the Anterior Pituitary • growth hormone (GH) - directly affect – growth of bone and muscles • prolactin (PRO) – directly affect – growth of mammary glands – milk production in a nursing mother • adrenocorticotropin hormone (ACTH) - Tropin – release of steroid hormones from adrenal cortex • thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) - Tropin – release of T4 and T3 from thyroid gland © Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only. Hormones of the Anterior Pituitary • follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) - Tropin – in females • estrogen production • egg production – in males • sperm production • luteinizing hormone (LH) - Tropin – in females • ovulation – in males • testosterone © Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only. Hormones of the Posterior Pituitary Produced in the Hypothalamus, stored in the posterior Pituitary • antidiuretic hormone – acts on kidney, decreases urine output Figure 8.7 – page 278 • oxytocin – acts on uterus, causes contractions – acts on breast, causes secretion of milk © Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only. Major Endocrine Glands - Thyroid • Thyroid gland - inferior to the larynx, two inches long, butterfly shaped, lies front and sides of the trachea – Secrete two hormones • Thyroid hormone (needs iodine) - thyroxine T4 and triiodothyronine T3 - controls rate of metabolism • Calcitonin - removes calcium from blood, puts into bones © Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only. Major Endocrine Glands - Parathyroid • Parathyroid gland – parathyroid hormone (PTH) – increases blood calcium levels Three ways: 1. removes calcium from bones (breakdown osteoclasts), puts into blood 2. Increase calcium absorption in intestines 3. Stimulate kidney reabsorption of calcium from urine © Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only. Major Endocrine Glands – Thymus & Pineal • Thymus gland – – – – Both part of endocrine and lymphatic system Lies under sternum and anterior to heart Large during childhood, shrinks with age Thymosin • development of immune system – T lymphocytes (white blood cells) aka T Cells • Pineal gland – Pine cone shaped in brain – unclear how it works – Melatonin • produces sleepiness © Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only. Thyroid and Parathyroid Glands © Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only. Adrenal Glands • adrenal medulla – epinephrine and norepinephrine • adrenaline rush • adrenal cortex – mineralocorticoids • aldosterone • sodium and water reabsorbed in kidneys – glucocorticoids • cortisone and cortisol • promote gluconeogenesis – sex hormones • estrogen and androgens • maintains sexual characteristics © Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only. Adrenal Glands © Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only. Pancreas • islets of Langerhans – alpha cells • glucagon • increase blood glucose level – beta cells • insulin • decrease blood glucose level © Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only. Gonads • testes – testosterone • sperm production • ovaries – estrogen • secondary sexual characteristics • progesterone • menstrual cycle © Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only. Review and Assessment Fill in the blanks with: ADH, thyroxine, thymosin, or adrenal cortex. 1. The thymus gland produces _______________. 2. The posterior pituitary gland produces oxytocin and _______________. 3. Mineralocorticoids are produced by the _______________. 4. T4 is also called _______________. © Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only.