FinalExamReview
... 1. What is an index? What is the maintenance cost of an index? 2. What is a primary index? What is a secondary index? 3. What is a dense index? What is a sparse index? 4. What is a B+ tree index? What are the main properties of B+ tree? 5. How to build a B+ tree given a sequence of search keys? 6. W ...
... 1. What is an index? What is the maintenance cost of an index? 2. What is a primary index? What is a secondary index? 3. What is a dense index? What is a sparse index? 4. What is a B+ tree index? What are the main properties of B+ tree? 5. How to build a B+ tree given a sequence of search keys? 6. W ...
Database Query Analysis - BASIS International Ltd.
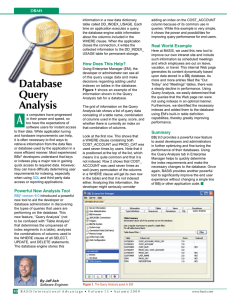
... indexes on tables in the database. Figure 1 shows an example of the information shown in the Query Analysis tab for a database. The grid of information on the Query Analysis tab shows a list of query data consisting of a table name, combination of columns used in the query, score, and whether there ...
... indexes on tables in the database. Figure 1 shows an example of the information shown in the Query Analysis tab for a database. The grid of information on the Query Analysis tab shows a list of query data consisting of a table name, combination of columns used in the query, score, and whether there ...
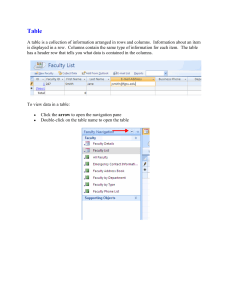
Chapter 17: Creating a Database Quiz Yourself Answers 1. A field is
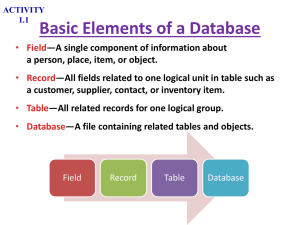
... 1. A field is a single characteristic of a person, place, object, event, or idea. 2. A record is all the fields about a single person, place, object, event, or idea collected in a row in a table. 3. Tables in a relational database are related through common fields. 4. The primary key, whose values u ...
... 1. A field is a single characteristic of a person, place, object, event, or idea. 2. A record is all the fields about a single person, place, object, event, or idea collected in a row in a table. 3. Tables in a relational database are related through common fields. 4. The primary key, whose values u ...
Database Management System
... Fields and Records • Fields are like columns in a spreadsheet • Records are like rows in a spreadsheet ...
... Fields and Records • Fields are like columns in a spreadsheet • Records are like rows in a spreadsheet ...
Unit 5 Study Guide
... 8. What is a relational database management system? 9. What does the query language do? 10. What is a query generator? 11. What is a record? 12. What is the purpose of the SHOW line? 13. What are some characters that CANNOT be used in a file name? ...
... 8. What is a relational database management system? 9. What does the query language do? 10. What is a query generator? 11. What is a record? 12. What is the purpose of the SHOW line? 13. What are some characters that CANNOT be used in a file name? ...
Indexes
... be found in the primary keys of tables, which have inherent indexes, additional columns may be referenced enough to consider the creation of an index to enhance performance. ...
... be found in the primary keys of tables, which have inherent indexes, additional columns may be referenced enough to consider the creation of an index to enhance performance. ...
Course Name
... Description The value stored at the intersection of each row and column must be a scalar value, and a table must not contain any repeating columns. Every non-key column must depend on the entire primary key. Every non-key column must depend only on the primary key. ...
... Description The value stored at the intersection of each row and column must be a scalar value, and a table must not contain any repeating columns. Every non-key column must depend on the entire primary key. Every non-key column must depend only on the primary key. ...
week5
... • Indexes greatly increase query response time • every index requires system resources to store and maintain • indexes can actually slow down the performance of UPDATES, INSERTS, and DELETES due to index maintenance So… don’t over index ...
... • Indexes greatly increase query response time • every index requires system resources to store and maintain • indexes can actually slow down the performance of UPDATES, INSERTS, and DELETES due to index maintenance So… don’t over index ...
Index Example
... What is an Index? • Let’s say relation R has an attribute A • An index on A is a data structure that allows quick access to tuples of R if you know the value of A • Implementation: hash table or similar data structure. ...
... What is an Index? • Let’s say relation R has an attribute A • An index on A is a data structure that allows quick access to tuples of R if you know the value of A • Implementation: hash table or similar data structure. ...
presentation source
... • rejects duplicates and returns an error • should only be created on a column that requires uniqueness eg. ssn, acct code • can be created as a composite or single column • helps in maintaining data integrity • boosts search performance ...
... • rejects duplicates and returns an error • should only be created on a column that requires uniqueness eg. ssn, acct code • can be created as a composite or single column • helps in maintaining data integrity • boosts search performance ...
Diapositive 1
... • Table, a set of columns that contain data. In the old days, a table was called a file. • Row, a set of columns from a table reflecting a record. • Index, an object that allows for fast retrieval of table rows. Every primary key and foreign key should have an index for retrieval speed. • Primary ke ...
... • Table, a set of columns that contain data. In the old days, a table was called a file. • Row, a set of columns from a table reflecting a record. • Index, an object that allows for fast retrieval of table rows. Every primary key and foreign key should have an index for retrieval speed. • Primary ke ...
week5
... Indexes greatly increase query response time every index requires system resources to store and maintain indexes can actually slow down the performance of UPDATES, INSERTS, and DELETES due to index maintenance So… don’t over index ...
... Indexes greatly increase query response time every index requires system resources to store and maintain indexes can actually slow down the performance of UPDATES, INSERTS, and DELETES due to index maintenance So… don’t over index ...
Data manipulation intro 1
... A query is used to extract specific information from a database. Like a question that gives you the correct answers ...
... A query is used to extract specific information from a database. Like a question that gives you the correct answers ...
BI Accelarator (BIA)
... • Redundant data store of a BI InfoCube on the BI accelerator server. • To improve the performance of BI queries when data is read from an InfoCube • Data of a BI InfoCube is made available as a BI accelerator index in a compressed but not aggregated form. • Consists of several, possibly split index ...
... • Redundant data store of a BI InfoCube on the BI accelerator server. • To improve the performance of BI queries when data is read from an InfoCube • Data of a BI InfoCube is made available as a BI accelerator index in a compressed but not aggregated form. • Consists of several, possibly split index ...