Here is a very brief outline of the development of string theory, the
... oscillating strings. Originally String Theory was formulated to explain the strong force. But it predicted a massless spin–2 particle (the graviton), which did not fit into the standard picture as of that time. Later it was found that Quantum Chromo Dynamics (QCD) could describe strong interactions ...
... oscillating strings. Originally String Theory was formulated to explain the strong force. But it predicted a massless spin–2 particle (the graviton), which did not fit into the standard picture as of that time. Later it was found that Quantum Chromo Dynamics (QCD) could describe strong interactions ...
entanglement properties of quantum many
... Our study of the entanglement properties of correlated wave functions for spin lattices was motivated by the work of Osterloh et al. [26] and more especially that of Osborne and Nielsen (ON) [27]. These authors were the rst to explore possible connections between quantum phase transitions and entan ...
... Our study of the entanglement properties of correlated wave functions for spin lattices was motivated by the work of Osterloh et al. [26] and more especially that of Osborne and Nielsen (ON) [27]. These authors were the rst to explore possible connections between quantum phase transitions and entan ...
gauge-like variables for ordered media containing defects - HAL
... of defects (the two-defect problem). Recently, I. Dzyaloshinskii and G. Volovik [1] have put forward an approach to the many-defect problem based on gauge theory concepts, which contains both a reappraisal of ancient ad hoc theories for the hydrodynamics of superfluid helium 4 containing vortices [2 ...
... of defects (the two-defect problem). Recently, I. Dzyaloshinskii and G. Volovik [1] have put forward an approach to the many-defect problem based on gauge theory concepts, which contains both a reappraisal of ancient ad hoc theories for the hydrodynamics of superfluid helium 4 containing vortices [2 ...
The Cosmological Constant Problem, Dark Energy, and the
... The observed value of Λ does raise an interesting question, usually referred to as the coincidence problem or “why now” problem. Vacuum energy, or anything behaving like it (which includes all options still allowed by current data) does not redshift like matter. In the past, vacuum energy was neglig ...
... The observed value of Λ does raise an interesting question, usually referred to as the coincidence problem or “why now” problem. Vacuum energy, or anything behaving like it (which includes all options still allowed by current data) does not redshift like matter. In the past, vacuum energy was neglig ...
Geometries, Band Gaps, Dipole Moments, Ionization Energies and
... band tuning. Techniques to precisely manipulate QDs and their derivatives at the molecular level are urgent to foster their applications in photovoltaics. QDs exist in the form of a large number of geometrical isomers due to a variety of possible atom arrangement patterns. In principle, these isomer ...
... band tuning. Techniques to precisely manipulate QDs and their derivatives at the molecular level are urgent to foster their applications in photovoltaics. QDs exist in the form of a large number of geometrical isomers due to a variety of possible atom arrangement patterns. In principle, these isomer ...
Griffiths-McCoy singularities in the random transverse-field Ising spin chain Ferenc Iglo´i
... correlations,13 and various probability distributions and scaling functions.11,14 Later, using simple expressions about the surface magnetization and the energy gap several exact results have been derived by making use of a mathematical analogy with surviving random walks,14 see also Ref. 15. In the ...
... correlations,13 and various probability distributions and scaling functions.11,14 Later, using simple expressions about the surface magnetization and the energy gap several exact results have been derived by making use of a mathematical analogy with surviving random walks,14 see also Ref. 15. In the ...
JOURNAL OF CONDENSED MATTER NUCLEAR SCIENCE Experiments and Methods in Cold Fusion
... of energy −E, the second option being mathematically as valid as the first. Neglecting the second possibility just amounts to miss half of the solutions of all our equations! Thus, it is certainly correct to argue that QFT convincingly demonstrated that positive and negative energy states cannot be ...
... of energy −E, the second option being mathematically as valid as the first. Neglecting the second possibility just amounts to miss half of the solutions of all our equations! Thus, it is certainly correct to argue that QFT convincingly demonstrated that positive and negative energy states cannot be ...
Characterizing Si: P quantum dot qubits with spin resonance
... to know the precise number of electron and nuclear spins bound to these dots, which can also help to identify appropriate spin transitions of the qubit and to deplete the dots down to the ideal regime of one electron occupation. Understanding the extent of the electron wavefunctions of the donor dot ...
... to know the precise number of electron and nuclear spins bound to these dots, which can also help to identify appropriate spin transitions of the qubit and to deplete the dots down to the ideal regime of one electron occupation. Understanding the extent of the electron wavefunctions of the donor dot ...
11th International Conference on Squeezed - icssur 2009
... Quantum tunneling and the time contraction, according to the new relativity theory of AlMosallami (A. K. AlMosallami) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19 Photon statistics in the macroscopic realm: methods to beat the lack of photoncounters (A. Andreoni). . . . . . . . ...
... Quantum tunneling and the time contraction, according to the new relativity theory of AlMosallami (A. K. AlMosallami) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19 Photon statistics in the macroscopic realm: methods to beat the lack of photoncounters (A. Andreoni). . . . . . . . ...
A Brief Analysis of the Mass-Energy Relation
... Although no mention of any relativistic derivation, in this regard, is made in the surveyed literature, it seems, at first glance, that there are two possible derivations of the relativistic formula for calculating the charge-to-mass ratio of J. J. Thomson's cathode-ray particle: The momentum-based ...
... Although no mention of any relativistic derivation, in this regard, is made in the surveyed literature, it seems, at first glance, that there are two possible derivations of the relativistic formula for calculating the charge-to-mass ratio of J. J. Thomson's cathode-ray particle: The momentum-based ...
Exciton Fine-Structure Splitting in Self- Assembled Lateral InAs/GaAs Quantum-Dot Molecular Structures
... correlation in the DQDs, namely, the lower-lying bright exciton state is in fact polarized along the [11̅0] axis that is perpendicular to the elongation axis (i.e [110]) of each of the two QDs constituting the DQD as shown in Fig.2(b) and 2(d). This finding thus rules out the effect of the shape-ind ...
... correlation in the DQDs, namely, the lower-lying bright exciton state is in fact polarized along the [11̅0] axis that is perpendicular to the elongation axis (i.e [110]) of each of the two QDs constituting the DQD as shown in Fig.2(b) and 2(d). This finding thus rules out the effect of the shape-ind ...
Monopoles in condensed matter physics
... Band Switching Band switching by basis change unitary transformation ...
... Band Switching Band switching by basis change unitary transformation ...
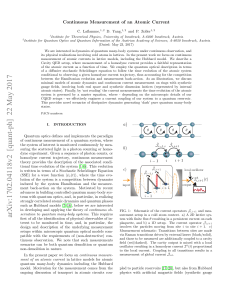
Continuous Measurement of an Atomic Current
... Quantum optics defines and implements the paradigm of continuous measurement of a quantum system, where the system of interest is monitored continuously by measuring the scattered light in a photon counting or homodyne experiment. Given a sequence of photon counts, or homodyne current trajectory, co ...
... Quantum optics defines and implements the paradigm of continuous measurement of a quantum system, where the system of interest is monitored continuously by measuring the scattered light in a photon counting or homodyne experiment. Given a sequence of photon counts, or homodyne current trajectory, co ...
Document
... superconductivity ferromagnetism and nonlinear optical properties. properties Because the presence of two cooperative properties in the same crystal lattice might result in new physical phenomena and novel applications, a particularly attractive goal is the design of molecular materials with two pro ...
... superconductivity ferromagnetism and nonlinear optical properties. properties Because the presence of two cooperative properties in the same crystal lattice might result in new physical phenomena and novel applications, a particularly attractive goal is the design of molecular materials with two pro ...
- Philsci
... for understanding of the so-called self-energy divergence. The problem was seemingly overcome with help of the known renormalization procedure in Electrodynamics but not in gravitational field theory. GRT was shown to be nonrenormalizable. Our analysis of the SRT mass-energy concept showed that, aft ...
... for understanding of the so-called self-energy divergence. The problem was seemingly overcome with help of the known renormalization procedure in Electrodynamics but not in gravitational field theory. GRT was shown to be nonrenormalizable. Our analysis of the SRT mass-energy concept showed that, aft ...
hybrid quantum computation - Centre for Quantum Technologies
... and discreteness of atomic spectroscopy. These ideas are now collectively known as the old quantum theory. In 1923, de Broglie introduced the concept of wave-particle duality, which was experimentally verified by Davisson and Germer in 1927. In 1926, Schrödinger established wave mechanics. This is ...
... and discreteness of atomic spectroscopy. These ideas are now collectively known as the old quantum theory. In 1923, de Broglie introduced the concept of wave-particle duality, which was experimentally verified by Davisson and Germer in 1927. In 1926, Schrödinger established wave mechanics. This is ...