Do now! - MrSimonPorter
... Do now! Can you continue with the ‘Draw the sentences’ from last lesson? This is to be FINISHED FOR HOMEWORK. Due next Friday 16th September. ...
... Do now! Can you continue with the ‘Draw the sentences’ from last lesson? This is to be FINISHED FOR HOMEWORK. Due next Friday 16th September. ...
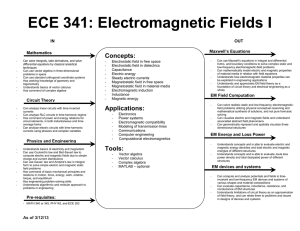
ECE 341: Electromagnetic Fields I Concepts: Maxwell’s Equations
... Understands basics of electricity and magnetism Can use Coulomb's law and Biot-Savart law to compute electric and magnetic fields due to simple charge and current distributions Can use Gauss’ law and Ampère’s law in integral form to solve simple electric and magnetic static field problems Has comman ...
... Understands basics of electricity and magnetism Can use Coulomb's law and Biot-Savart law to compute electric and magnetic fields due to simple charge and current distributions Can use Gauss’ law and Ampère’s law in integral form to solve simple electric and magnetic static field problems Has comman ...
TCAP Worksheet #9 – Magnets
... containing iron. • Magnets have a North and South pole. • Magnetism depends on the material’s atoms. ...
... containing iron. • Magnets have a North and South pole. • Magnetism depends on the material’s atoms. ...
6F05pp_L29 - University of Iowa Physics
... should be able to produce currents • He was correct with one important requirement the magnetic field must be changing in some way to induce a current • the phenomenon that a changing magnetic field can induce a current is called electromagnetic induction ...
... should be able to produce currents • He was correct with one important requirement the magnetic field must be changing in some way to induce a current • the phenomenon that a changing magnetic field can induce a current is called electromagnetic induction ...
Electricity Structured Reading: Intro to Electricity
... 19. What is an insulator? 20. Because clothing is an insulator, the _________________________ on each piece of clothing, creating ______________ electricity. 21. Why do clothes stuck together by static electricity eventually separate on their own. 22. Lightning is an example of _________ _________ . ...
... 19. What is an insulator? 20. Because clothing is an insulator, the _________________________ on each piece of clothing, creating ______________ electricity. 21. Why do clothes stuck together by static electricity eventually separate on their own. 22. Lightning is an example of _________ _________ . ...
High-Voltage Transmission
... under electrical pressure • Neutral wire: a current-carrying conductor NOT under electrical pressure (has volts) • Ground wire: a conducting wire that transmits current to the earth to minimize the danger of electrical shock ...
... under electrical pressure • Neutral wire: a current-carrying conductor NOT under electrical pressure (has volts) • Ground wire: a conducting wire that transmits current to the earth to minimize the danger of electrical shock ...
Michael Faraday (1791-1867) The laws of electricity and magnetism
... Electromagnetic induction • Faraday thought that if currents could produce magnetic fields, magnetic fields should be able to produce currents • He was correct with one important requirement Î the magnetic field must be changing in some way to induce a current • the phenomenon that a changing magnet ...
... Electromagnetic induction • Faraday thought that if currents could produce magnetic fields, magnetic fields should be able to produce currents • He was correct with one important requirement Î the magnetic field must be changing in some way to induce a current • the phenomenon that a changing magnet ...
Digital Design - Oakland University
... static electricity from 1746 – 1751 (including his lightning experiment) and became famous throughout Europe by describing these experiments in a series of letters to Peter Collinson. ...
... static electricity from 1746 – 1751 (including his lightning experiment) and became famous throughout Europe by describing these experiments in a series of letters to Peter Collinson. ...
1 Repetition on Maxwell`s Equations and Electromag
... Classical electrodynamic was essentially developed in the 19th century by Henry Cavendish (law of forces between electrical charges 1771), Charles Augustin de Coulomb, Hans Christian Ørsted, André Marie Ampère, Michael Faraday, James Clerk Maxwell (dynamical theory of the electromagnetic field 186 ...
... Classical electrodynamic was essentially developed in the 19th century by Henry Cavendish (law of forces between electrical charges 1771), Charles Augustin de Coulomb, Hans Christian Ørsted, André Marie Ampère, Michael Faraday, James Clerk Maxwell (dynamical theory of the electromagnetic field 186 ...
2 - WordPress.com
... Electricity + Magnetism Electric Current + Magnetism- are related Moving charged + magnetic fields An electrical current creates a magnetic field Grater the current – grater the magnetic field Electromagnets- a temporary magnet made by wrapping a wire coil carrying an electric current around and iro ...
... Electricity + Magnetism Electric Current + Magnetism- are related Moving charged + magnetic fields An electrical current creates a magnetic field Grater the current – grater the magnetic field Electromagnets- a temporary magnet made by wrapping a wire coil carrying an electric current around and iro ...
History of electromagnetic theory

For a chronological guide to this subject, see Timeline of electromagnetic theory.The history of electromagnetic theory begins with ancient measures to deal with atmospheric electricity, in particular lightning. People then had little understanding of electricity, and were unable to scientifically explain the phenomena. In the 19th century there was a unification of the history of electric theory with the history of magnetic theory. It became clear that electricity should be treated jointly with magnetism, because wherever electricity is in motion, magnetism is also present. Magnetism was not fully explained until the idea of magnetic induction was developed. Electricity was not fully explained until the idea of electric charge was developed.