12-6
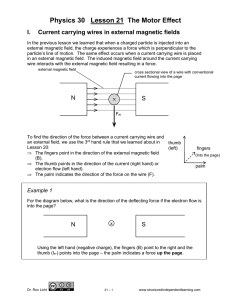
... For a long time, people knew only one source of magnetism from Iron. In 1821, a Danish physicist, Oersted noticed that an electrical wire carrying current made the near-by compass reorient. First clue of inter-relation between electricity and Magnetism. Ampere, Faraday established the nature of el ...
... For a long time, people knew only one source of magnetism from Iron. In 1821, a Danish physicist, Oersted noticed that an electrical wire carrying current made the near-by compass reorient. First clue of inter-relation between electricity and Magnetism. Ampere, Faraday established the nature of el ...
12: Electromagnetic Induction - SJHS-IB
... vary from maximum to zero as angle θ (between the normal to the coil and the field plane) goes from 90° to zero (as shown in the diagrams). ...
... vary from maximum to zero as angle θ (between the normal to the coil and the field plane) goes from 90° to zero (as shown in the diagrams). ...
First year - physics teacher
... The essence of science education is learning by doing. So practicals are inevitable in science learning. Through practical, it is aimed to develop various experimental skills such as preparation for the work, specificity and accuracy in carrying out the experiment, controlling variables, measurement ...
... The essence of science education is learning by doing. So practicals are inevitable in science learning. Through practical, it is aimed to develop various experimental skills such as preparation for the work, specificity and accuracy in carrying out the experiment, controlling variables, measurement ...
Physics 30 - Structured Independent Learning
... After Oersted’s discovery, Andre-Marie Ampere performed extensive experiments and did an insightful mathematical analysis of the magnetic field induced around a current carrying wire. In addition, he studied the forces between current carrying wires. The induced magnetic fields around the wires inte ...
... After Oersted’s discovery, Andre-Marie Ampere performed extensive experiments and did an insightful mathematical analysis of the magnetic field induced around a current carrying wire. In addition, he studied the forces between current carrying wires. The induced magnetic fields around the wires inte ...
7. Two fixed charges +4q and +q are kept at
... 14. Why is it necessary that the field lines from a point charge placed in the vicinity of a conductor must be normal to the surface of the conductor at every point ? 15. Electrostatic potential is constant throughout the volume of the conductor and has the same value on its surface. Why ? 16. If t ...
... 14. Why is it necessary that the field lines from a point charge placed in the vicinity of a conductor must be normal to the surface of the conductor at every point ? 15. Electrostatic potential is constant throughout the volume of the conductor and has the same value on its surface. Why ? 16. If t ...
Fundamental of Physics
... the shuttle is a sphere of radius 10 m, estimate the amount of charge it collects. 10. The charge is ...
... the shuttle is a sphere of radius 10 m, estimate the amount of charge it collects. 10. The charge is ...
magnetically coupled circuits
... • M12 = M 21 = M and is always a positive quantity. di • The induced voltage M may be positive or negative. dt • The choice of polarity is made by examining the way in which both coils are physically wound and applying Lenz’s law in conjunction with the right-hand-rule. • The procedure is inconvenie ...
... • M12 = M 21 = M and is always a positive quantity. di • The induced voltage M may be positive or negative. dt • The choice of polarity is made by examining the way in which both coils are physically wound and applying Lenz’s law in conjunction with the right-hand-rule. • The procedure is inconvenie ...
History of electromagnetic theory

For a chronological guide to this subject, see Timeline of electromagnetic theory.The history of electromagnetic theory begins with ancient measures to deal with atmospheric electricity, in particular lightning. People then had little understanding of electricity, and were unable to scientifically explain the phenomena. In the 19th century there was a unification of the history of electric theory with the history of magnetic theory. It became clear that electricity should be treated jointly with magnetism, because wherever electricity is in motion, magnetism is also present. Magnetism was not fully explained until the idea of magnetic induction was developed. Electricity was not fully explained until the idea of electric charge was developed.