particle level: forces and fields
... 3. The equipotential lines (or surfaces in 3D) represent points that have the same electrostatic potential. 4. The equipotential lines and field lines must be normal (perpendicular) to each other at ...
... 3. The equipotential lines (or surfaces in 3D) represent points that have the same electrostatic potential. 4. The equipotential lines and field lines must be normal (perpendicular) to each other at ...
Electric Charges
... • Note: Since the permittivity of air is very close to that of free space (relative permittivity of air is 1.0005 ≈ 1), the force between the charges in air can be approximated as ...
... • Note: Since the permittivity of air is very close to that of free space (relative permittivity of air is 1.0005 ≈ 1), the force between the charges in air can be approximated as ...
7.1 Permanent Magnets
... the storage of data on audio and video tape as well as on computer disks. In the world of medicine, they are used in body scanners as well as a range of applications where they are attached to or implanted into the body. The home entertainment market relies on magnetic materials in applications such ...
... the storage of data on audio and video tape as well as on computer disks. In the world of medicine, they are used in body scanners as well as a range of applications where they are attached to or implanted into the body. The home entertainment market relies on magnetic materials in applications such ...
TIMSS Advanced 2015 Physics Framework
... Kinematics, dynamics (Newton’s three laws of motion), and the law of gravitation are important components of this area. The conservation of certain physical quantities, such as energy or momentum, is a fundamental concept in physics that is expressed by the laws of conservation (energy and momentum) ...
... Kinematics, dynamics (Newton’s three laws of motion), and the law of gravitation are important components of this area. The conservation of certain physical quantities, such as energy or momentum, is a fundamental concept in physics that is expressed by the laws of conservation (energy and momentum) ...
View File - UET Taxila
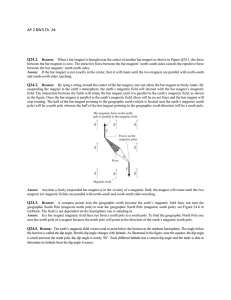
... Two circuits are not connected: no current? However, closing the switch we see that the compass’ needle moves and then goes back to its previous position Nothing happens when the current in the primary coil is steady But same thing happens when the switch is opened, except for the needle going in th ...
... Two circuits are not connected: no current? However, closing the switch we see that the compass’ needle moves and then goes back to its previous position Nothing happens when the current in the primary coil is steady But same thing happens when the switch is opened, except for the needle going in th ...
Aging and Stiffness
... An alternative analysis to the dynamic analysis of F=ma for understanding the mechanics of physical systems Provides insight into motion in terms of a combination of kinematics (displacement) and kinetics (force) Provides insight into muscle mechanics in terms of contraction types, roles of muscles, ...
... An alternative analysis to the dynamic analysis of F=ma for understanding the mechanics of physical systems Provides insight into motion in terms of a combination of kinematics (displacement) and kinetics (force) Provides insight into muscle mechanics in terms of contraction types, roles of muscles, ...
AP2 Unit 5 BW3
... pointing down with the same magnitude as the uniform magnetic field in the plane because the problem states that the total magnetic field is zero at point 1. When the magnetic field from the current is pointing down at point 1, then the magnetic field direction is clockwise around the wire. At point ...
... pointing down with the same magnitude as the uniform magnetic field in the plane because the problem states that the total magnetic field is zero at point 1. When the magnetic field from the current is pointing down at point 1, then the magnetic field direction is clockwise around the wire. At point ...
Millikan Oil Drop Derivation ··· Seth Hopper ··· 4/3/06 +
... The first term in square brackets will be a constant for the setup and need only be calculated once. The second term will be constant for each particular drop, but will have to be calculated again whenever a new drop is observed. (That is true only if the temperature, and thus η remain constant whi ...
... The first term in square brackets will be a constant for the setup and need only be calculated once. The second term will be constant for each particular drop, but will have to be calculated again whenever a new drop is observed. (That is true only if the temperature, and thus η remain constant whi ...
Chapter 16
... Lines – Positive Charge The equipotentials for a point charge are a family of spheres centered on the point charge The field lines are perpendicular to the electric potential at all ...
... Lines – Positive Charge The equipotentials for a point charge are a family of spheres centered on the point charge The field lines are perpendicular to the electric potential at all ...
Principle of Moments - iGCSE Science Courses
... • Describe the moment of a force as a measure of its turning effect and give everyday examples • Understand that increasing force or distance from the pivot increases the moment of a force • Calculate moment using the product force × perpendicular distance from the pivot • Apply the principle of mom ...
... • Describe the moment of a force as a measure of its turning effect and give everyday examples • Understand that increasing force or distance from the pivot increases the moment of a force • Calculate moment using the product force × perpendicular distance from the pivot • Apply the principle of mom ...
Interactions b/w hail and smaller ice crystals transfer e
... Electric Field: What are the magnitude and direction of the electric force on an electron (e=1.6x10-19 C) in a uniform electric field of strength 2000 N/C ...
... Electric Field: What are the magnitude and direction of the electric force on an electron (e=1.6x10-19 C) in a uniform electric field of strength 2000 N/C ...
Characteristic Properties of Plasma
... For regions of dimensions of the order of a centimetre and deviation from neutrality with densities of 10 18 m-3, fields of the order of 100 MV/m are created. Usually deviations from neutrality can be created in very small regions, such that the energy required to support the corresponding electric ...
... For regions of dimensions of the order of a centimetre and deviation from neutrality with densities of 10 18 m-3, fields of the order of 100 MV/m are created. Usually deviations from neutrality can be created in very small regions, such that the energy required to support the corresponding electric ...
Peaceful Uses of Fusion - Nuclear Sciences and Applications
... ionized material through these ends, then, in contrast with the other machines, one can circumvent the problem of heating a plasma which is already present. The open ends have another advantage: they allow one to study the particles which escape and, therefore, to determine what energy particles mus ...
... ionized material through these ends, then, in contrast with the other machines, one can circumvent the problem of heating a plasma which is already present. The open ends have another advantage: they allow one to study the particles which escape and, therefore, to determine what energy particles mus ...
Electromagnetism

Electromagnetism is a branch of physics which involves the study of the electromagnetic force, a type of physical interaction that occurs between electrically charged particles. The electromagnetic force usually shows electromagnetic fields, such as electric fields, magnetic fields, and light. The electromagnetic force is one of the four fundamental interactions in nature. The other three fundamental interactions are the strong interaction, the weak interaction, and gravitation.The word electromagnetism is a compound form of two Greek terms, ἤλεκτρον, ēlektron, ""amber"", and μαγνῆτις λίθος magnētis lithos, which means ""magnesian stone"", a type of iron ore. The science of electromagnetic phenomena is defined in terms of the electromagnetic force, sometimes called the Lorentz force, which includes both electricity and magnetism as elements of one phenomenon.The electromagnetic force plays a major role in determining the internal properties of most objects encountered in daily life. Ordinary matter takes its form as a result of intermolecular forces between individual molecules in matter. Electrons are bound by electromagnetic wave mechanics into orbitals around atomic nuclei to form atoms, which are the building blocks of molecules. This governs the processes involved in chemistry, which arise from interactions between the electrons of neighboring atoms, which are in turn determined by the interaction between electromagnetic force and the momentum of the electrons.There are numerous mathematical descriptions of the electromagnetic field. In classical electrodynamics, electric fields are described as electric potential and electric current in Ohm's law, magnetic fields are associated with electromagnetic induction and magnetism, and Maxwell's equations describe how electric and magnetic fields are generated and altered by each other and by charges and currents.The theoretical implications of electromagnetism, in particular the establishment of the speed of light based on properties of the ""medium"" of propagation (permeability and permittivity), led to the development of special relativity by Albert Einstein in 1905.Although electromagnetism is considered one of the four fundamental forces, at high energy the weak force and electromagnetism are unified. In the history of the universe, during the quark epoch, the electroweak force split into the electromagnetic and weak forces.