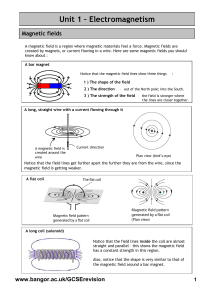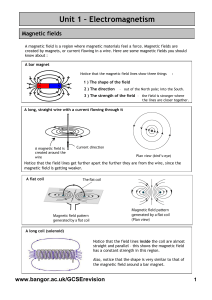
lab
... cart. When the cart is pulled along the track at a constant speed, the tension in the line is equal in magnitude to the frictional force. Find the mass of the cart. Tie one end of a string to the hook on the Force Sensor and the other end to the hook on the cart. Practice pulling the block and masse ...
... cart. When the cart is pulled along the track at a constant speed, the tension in the line is equal in magnitude to the frictional force. Find the mass of the cart. Tie one end of a string to the hook on the Force Sensor and the other end to the hook on the cart. Practice pulling the block and masse ...
Lecture 19
... • Negative charges moving • Positive charges moving clockwise experience CCW experience upward upward force force Equilibrium between electrostatic & magnetic forces: •VHUpper plate at lower • Upper plate at higher Fup = qvdrift B Fdown = qEinduced = q potential VH = vdrift Bw = "Hall Voltage" poten ...
... • Negative charges moving • Positive charges moving clockwise experience CCW experience upward upward force force Equilibrium between electrostatic & magnetic forces: •VHUpper plate at lower • Upper plate at higher Fup = qvdrift B Fdown = qEinduced = q potential VH = vdrift Bw = "Hall Voltage" poten ...
Classical Electrodynamics and Theory of Relativity
... the framework of the concept of near action Coulomb law (1.2) is treated as approximate law, which is exact only for the charges at rest that stayed at rest during sufficiently long time so that process of transmission of electric interaction has been terminated. Theory of electromagnetism has measu ...
... the framework of the concept of near action Coulomb law (1.2) is treated as approximate law, which is exact only for the charges at rest that stayed at rest during sufficiently long time so that process of transmission of electric interaction has been terminated. Theory of electromagnetism has measu ...
File - SPASH PHYSICS
... Who was the first to publish a book on electricity and magnetism and theorize that the Earth is a giant magnet? What were Benjamin Franklin’s contributions in the field of electricity? What did Michael Faraday contribute with respect to magnetism and electrical current? What did Charles Dufay contri ...
... Who was the first to publish a book on electricity and magnetism and theorize that the Earth is a giant magnet? What were Benjamin Franklin’s contributions in the field of electricity? What did Michael Faraday contribute with respect to magnetism and electrical current? What did Charles Dufay contri ...
Chapter 18
... • As the bar (with zero resistance) is pulled to the right with a constant velocity under the influence of an applied force, the free charges experience a magnetic force along the length of the bar • This force sets up an induced current because the charges are free to move in the closed path • The ...
... • As the bar (with zero resistance) is pulled to the right with a constant velocity under the influence of an applied force, the free charges experience a magnetic force along the length of the bar • This force sets up an induced current because the charges are free to move in the closed path • The ...
Chapter 20
... • As the bar (with zero resistance) is pulled to the right with a constant velocity under the influence of an applied force, the free charges experience a magnetic force along the length of the bar • This force sets up an induced current because the charges are free to move in the closed path • The ...
... • As the bar (with zero resistance) is pulled to the right with a constant velocity under the influence of an applied force, the free charges experience a magnetic force along the length of the bar • This force sets up an induced current because the charges are free to move in the closed path • The ...
Lab 25: Electric Fields
... distribution is the electroscope, which consists of two very light conducting leaves connected to a conducting rod or ball (Figure 25.2). When the charged rod on the left is brought closer to the ball, it attracts the negative charges and repels the positive charges within the conductor. The pr ...
... distribution is the electroscope, which consists of two very light conducting leaves connected to a conducting rod or ball (Figure 25.2). When the charged rod on the left is brought closer to the ball, it attracts the negative charges and repels the positive charges within the conductor. The pr ...
y - Copernicus.org
... Electron phase space holes (electron holes) are often observed in space plasma, and have also been observed in the laboratory. They are considered to be the stationary BGK (Bernstein-Greene-Kruskal) solution of the Vlasov and Poisson equations. In space-based measurements, they are positive potentia ...
... Electron phase space holes (electron holes) are often observed in space plasma, and have also been observed in the laboratory. They are considered to be the stationary BGK (Bernstein-Greene-Kruskal) solution of the Vlasov and Poisson equations. In space-based measurements, they are positive potentia ...
Biomedical Imaging II
... A 1H magnetic moment can couple (i.e., exchange energy with) the magnetic moments of other 1H nuclei in its vicinity These are called “spin-spin coupling” Spin-spin interactions occur when the magnetic field at a given 1H nucleus fluctuates Therefore, should the rates of these interaction depend on ...
... A 1H magnetic moment can couple (i.e., exchange energy with) the magnetic moments of other 1H nuclei in its vicinity These are called “spin-spin coupling” Spin-spin interactions occur when the magnetic field at a given 1H nucleus fluctuates Therefore, should the rates of these interaction depend on ...
Electromagnetism

Electromagnetism is a branch of physics which involves the study of the electromagnetic force, a type of physical interaction that occurs between electrically charged particles. The electromagnetic force usually shows electromagnetic fields, such as electric fields, magnetic fields, and light. The electromagnetic force is one of the four fundamental interactions in nature. The other three fundamental interactions are the strong interaction, the weak interaction, and gravitation.The word electromagnetism is a compound form of two Greek terms, ἤλεκτρον, ēlektron, ""amber"", and μαγνῆτις λίθος magnētis lithos, which means ""magnesian stone"", a type of iron ore. The science of electromagnetic phenomena is defined in terms of the electromagnetic force, sometimes called the Lorentz force, which includes both electricity and magnetism as elements of one phenomenon.The electromagnetic force plays a major role in determining the internal properties of most objects encountered in daily life. Ordinary matter takes its form as a result of intermolecular forces between individual molecules in matter. Electrons are bound by electromagnetic wave mechanics into orbitals around atomic nuclei to form atoms, which are the building blocks of molecules. This governs the processes involved in chemistry, which arise from interactions between the electrons of neighboring atoms, which are in turn determined by the interaction between electromagnetic force and the momentum of the electrons.There are numerous mathematical descriptions of the electromagnetic field. In classical electrodynamics, electric fields are described as electric potential and electric current in Ohm's law, magnetic fields are associated with electromagnetic induction and magnetism, and Maxwell's equations describe how electric and magnetic fields are generated and altered by each other and by charges and currents.The theoretical implications of electromagnetism, in particular the establishment of the speed of light based on properties of the ""medium"" of propagation (permeability and permittivity), led to the development of special relativity by Albert Einstein in 1905.Although electromagnetism is considered one of the four fundamental forces, at high energy the weak force and electromagnetism are unified. In the history of the universe, during the quark epoch, the electroweak force split into the electromagnetic and weak forces.