Particle self-bunching in the Schwinger effect in spacetime
... Introduction: The vacuum of quantum electrodynamics (QED) is unstable against the formation of manybody states in the presence of an external electric field, manifesting itself as the creation of electron-positron pairs [1–3]. This effect has been a long-standing but still unobserved prediction as t ...
... Introduction: The vacuum of quantum electrodynamics (QED) is unstable against the formation of manybody states in the presence of an external electric field, manifesting itself as the creation of electron-positron pairs [1–3]. This effect has been a long-standing but still unobserved prediction as t ...
Final report - ECMI Modelling Week
... common to all of them was the fact that the z-value was fixed. This was done to further reduce the degrees of freedom in our problem and thereby reducing the computational time. Even with this simplification of the problem, each numerical experiment lasted up to 30 minutes. From the numerical experi ...
... common to all of them was the fact that the z-value was fixed. This was done to further reduce the degrees of freedom in our problem and thereby reducing the computational time. Even with this simplification of the problem, each numerical experiment lasted up to 30 minutes. From the numerical experi ...
introduction
... b) Paramagnetic:The phenomenon of paramagnetic occurs only in materials in which individual atoms or molecules have permanent magnetic moments. The susceptibility is positive and temperature dependent. It is of the order of 103 at room temperature and is proportional to 1/T. This kind of magnetic be ...
... b) Paramagnetic:The phenomenon of paramagnetic occurs only in materials in which individual atoms or molecules have permanent magnetic moments. The susceptibility is positive and temperature dependent. It is of the order of 103 at room temperature and is proportional to 1/T. This kind of magnetic be ...
Document
... This means that the electric field within the dielectric is less than it would be in air, allowing more charge to be stored for the same potential. ...
... This means that the electric field within the dielectric is less than it would be in air, allowing more charge to be stored for the same potential. ...
Electromagnetic force on a magnetic dipole inside
... fluid passes in the vicinity of the magnet (case (a)) must cause a much higher Lorentz force than a velocity profile, where most of the movement is far away from the magnet (case (b)). For these reasons, we will derive the velocity field of the annular flow in this section. Our problem is that of a ...
... fluid passes in the vicinity of the magnet (case (a)) must cause a much higher Lorentz force than a velocity profile, where most of the movement is far away from the magnet (case (b)). For these reasons, we will derive the velocity field of the annular flow in this section. Our problem is that of a ...
Electrostatics 12
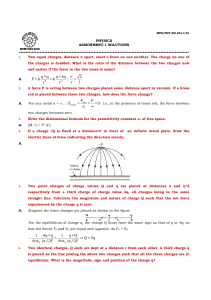
... Electric Field Rules for Drawing Electric Field Lines 1. The lines must originate on a positive charge (or infinity) and end on a negative charge (or infinity). 2. The number of lines drawn leaving a positive charge or approaching a negative charge is proportional to the magnitude of the charge. 3. ...
... Electric Field Rules for Drawing Electric Field Lines 1. The lines must originate on a positive charge (or infinity) and end on a negative charge (or infinity). 2. The number of lines drawn leaving a positive charge or approaching a negative charge is proportional to the magnitude of the charge. 3. ...
the faraday disk - Irreversiblesystems.com
... is a circumference or the speed v is constant, as it follows observing Fig.1 and Fig. 2 (see also the cases of Fig. 1' and Fig. 2'). The result (4) is surprising: even more so when we remember that "LORENTZ's force" is exclusively experimental. Moreover, in FRENET's trihedron the value v of speed is ...
... is a circumference or the speed v is constant, as it follows observing Fig.1 and Fig. 2 (see also the cases of Fig. 1' and Fig. 2'). The result (4) is surprising: even more so when we remember that "LORENTZ's force" is exclusively experimental. Moreover, in FRENET's trihedron the value v of speed is ...
Slide 1
... This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching their courses and assessing student learning. Dissemination or sale of any part of this work (including on the World Wide Web) will destroy the integrity of the work and is not permit ...
... This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching their courses and assessing student learning. Dissemination or sale of any part of this work (including on the World Wide Web) will destroy the integrity of the work and is not permit ...
Chapter14
... The polarity of induced voltage is determined by Lenz’s law. An induced voltage has the polarity that opposes the change causing the induction. Absolute polarity depends upon three points: Whether the flux is increasing or decreasing; The method of winding; Which end of the coil is the r ...
... The polarity of induced voltage is determined by Lenz’s law. An induced voltage has the polarity that opposes the change causing the induction. Absolute polarity depends upon three points: Whether the flux is increasing or decreasing; The method of winding; Which end of the coil is the r ...
Inhomogeneities in the Universe DESY, 2004
... As we shall see, the gravitational potential does not grow within linear perturbation theory. Hence initial fluctuations with an amplitude of » a few £ 10-5 are needed. During a phase of inflationary expansion of the universe such fluctuations emerge out of the quantum fluctuations of the inflation ...
... As we shall see, the gravitational potential does not grow within linear perturbation theory. Hence initial fluctuations with an amplitude of » a few £ 10-5 are needed. During a phase of inflationary expansion of the universe such fluctuations emerge out of the quantum fluctuations of the inflation ...
1m 12cm x =.12m 100cm F =BiLsinθ
... current. The extended fingers point in the direction of the magnetic, B, field. The palm points in the direction of the magnetic force exerted. You could also imagine a vector perpendicular to the palm that shows the direction of the force. Point the fingers of your right hand into the page. The thu ...
... current. The extended fingers point in the direction of the magnetic, B, field. The palm points in the direction of the magnetic force exerted. You could also imagine a vector perpendicular to the palm that shows the direction of the force. Point the fingers of your right hand into the page. The thu ...
Electromagnetism

Electromagnetism is a branch of physics which involves the study of the electromagnetic force, a type of physical interaction that occurs between electrically charged particles. The electromagnetic force usually shows electromagnetic fields, such as electric fields, magnetic fields, and light. The electromagnetic force is one of the four fundamental interactions in nature. The other three fundamental interactions are the strong interaction, the weak interaction, and gravitation.The word electromagnetism is a compound form of two Greek terms, ἤλεκτρον, ēlektron, ""amber"", and μαγνῆτις λίθος magnētis lithos, which means ""magnesian stone"", a type of iron ore. The science of electromagnetic phenomena is defined in terms of the electromagnetic force, sometimes called the Lorentz force, which includes both electricity and magnetism as elements of one phenomenon.The electromagnetic force plays a major role in determining the internal properties of most objects encountered in daily life. Ordinary matter takes its form as a result of intermolecular forces between individual molecules in matter. Electrons are bound by electromagnetic wave mechanics into orbitals around atomic nuclei to form atoms, which are the building blocks of molecules. This governs the processes involved in chemistry, which arise from interactions between the electrons of neighboring atoms, which are in turn determined by the interaction between electromagnetic force and the momentum of the electrons.There are numerous mathematical descriptions of the electromagnetic field. In classical electrodynamics, electric fields are described as electric potential and electric current in Ohm's law, magnetic fields are associated with electromagnetic induction and magnetism, and Maxwell's equations describe how electric and magnetic fields are generated and altered by each other and by charges and currents.The theoretical implications of electromagnetism, in particular the establishment of the speed of light based on properties of the ""medium"" of propagation (permeability and permittivity), led to the development of special relativity by Albert Einstein in 1905.Although electromagnetism is considered one of the four fundamental forces, at high energy the weak force and electromagnetism are unified. In the history of the universe, during the quark epoch, the electroweak force split into the electromagnetic and weak forces.