Casimir Forces in a Piston Geometry at Zero and Finite Temperatures
... A striking macroscopic manifestation of quantum electrodynamics is the attraction of neutral metals. In 1948 Casimir predicted that such a force results from the modification of the ground state energy of the photon field due to the presence of conducting boundary conditions [1]. The energy spectrum ...
... A striking macroscopic manifestation of quantum electrodynamics is the attraction of neutral metals. In 1948 Casimir predicted that such a force results from the modification of the ground state energy of the photon field due to the presence of conducting boundary conditions [1]. The energy spectrum ...
P. LeClair
... the initial energy, and derive a formula for the difference in terms of the initial charge and the two capacitances. Solution: This problem is easiest to start if you approach it from a conservation of energy & charge point of view. We have two capacitors. Initially, one capacitor stores a charge Q1 ...
... the initial energy, and derive a formula for the difference in terms of the initial charge and the two capacitances. Solution: This problem is easiest to start if you approach it from a conservation of energy & charge point of view. We have two capacitors. Initially, one capacitor stores a charge Q1 ...
Electric Potential Energy, Electric Potential and
... The potential difference (V) between two points is defined as the amount of work required to move a unit of positive charge from the point that is lower potential to the point that is at the higher potential. p. 195 - 196 ...
... The potential difference (V) between two points is defined as the amount of work required to move a unit of positive charge from the point that is lower potential to the point that is at the higher potential. p. 195 - 196 ...
Chapter 15
... • If a tree falls in the forest, and no one hears it…? • However: the concept of field will be extremely useful in understanding later chapters – Electric fields can generate magnetic fields and vice versa. (not just created by charge) – Electric and Magnetic fields are the medium of light waves (wa ...
... • If a tree falls in the forest, and no one hears it…? • However: the concept of field will be extremely useful in understanding later chapters – Electric fields can generate magnetic fields and vice versa. (not just created by charge) – Electric and Magnetic fields are the medium of light waves (wa ...
Alaska-SubstormChap
... • No imposed E-field; E-field is derived. • test 1: solve momentum equations and Maxwell’s equations using explicit method • test 2: use implicit method (increasing time step by 105 times) • test 3: include continuity and energy equations with ...
... • No imposed E-field; E-field is derived. • test 1: solve momentum equations and Maxwell’s equations using explicit method • test 2: use implicit method (increasing time step by 105 times) • test 3: include continuity and energy equations with ...
Physics v. 2016
... Electromagnetic Wave- A transverse wave consisting of oscillating electric and magnetic fields at right angles to each other (light wave); Sound- A longitudinal density wave created by a vibrating source; Wave- A disturbance or oscillation of matter or electromagnetic fields that travels through mat ...
... Electromagnetic Wave- A transverse wave consisting of oscillating electric and magnetic fields at right angles to each other (light wave); Sound- A longitudinal density wave created by a vibrating source; Wave- A disturbance or oscillation of matter or electromagnetic fields that travels through mat ...
Lecture 9 - web page for staff
... The current inside conductor creates the magnetic flux inside the material texture. This flux causes an internal inductance which combines with the external inductance to get the total inductance. Normally, the internal inductance can be neglected due to its small value compared to the external one. ...
... The current inside conductor creates the magnetic flux inside the material texture. This flux causes an internal inductance which combines with the external inductance to get the total inductance. Normally, the internal inductance can be neglected due to its small value compared to the external one. ...
NCEA Level 1 Science (90940) 2011 Assessment Schedule
... Net force is in the downwards direction and greater than zero. Forces are unbalanced. Explanation of motion Motion is acceleration towards ground. An unbalanced force is required to make an object’s speed change, therefore, as there is an unbalanced force greater than zero towards the ground, the pa ...
... Net force is in the downwards direction and greater than zero. Forces are unbalanced. Explanation of motion Motion is acceleration towards ground. An unbalanced force is required to make an object’s speed change, therefore, as there is an unbalanced force greater than zero towards the ground, the pa ...
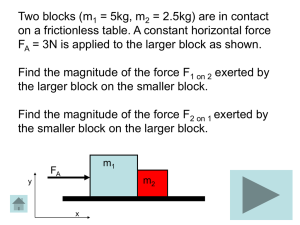
Tutorial_blocks
... •Newton’s 3rd law gave an important relation for the forces between blocks. This law explains the normal forces that the blocks exert on each other. •Blocks moving together have the same acceleration. •The applied force (FA) only acts on larger block. ...
... •Newton’s 3rd law gave an important relation for the forces between blocks. This law explains the normal forces that the blocks exert on each other. •Blocks moving together have the same acceleration. •The applied force (FA) only acts on larger block. ...
216KB - NZQA
... Net force is in the downwards direction and greater than zero. Forces are unbalanced. Explanation of motion Motion is acceleration towards ground. An unbalanced force is required to make an object’s speed change, therefore, as there is an unbalanced force greater than zero towards the ground, the pa ...
... Net force is in the downwards direction and greater than zero. Forces are unbalanced. Explanation of motion Motion is acceleration towards ground. An unbalanced force is required to make an object’s speed change, therefore, as there is an unbalanced force greater than zero towards the ground, the pa ...
9 - web page for staff
... The current inside conductor creates the magnetic flux inside the material texture. This flux causes an internal inductance which combines with the external inductance to get the total inductance. Normally, the internal inductance can be neglected due to its small value compared to the external one. ...
... The current inside conductor creates the magnetic flux inside the material texture. This flux causes an internal inductance which combines with the external inductance to get the total inductance. Normally, the internal inductance can be neglected due to its small value compared to the external one. ...
Document
... is arranged so that, just as the emf is about to change sign from positive to negative, the brushes cross the gap, and the polarity of the contacts is switched. The polarity of the contacts changes in phase with the polarity of the emf -- the two changes essentially cancel each other out, and the em ...
... is arranged so that, just as the emf is about to change sign from positive to negative, the brushes cross the gap, and the polarity of the contacts is switched. The polarity of the contacts changes in phase with the polarity of the emf -- the two changes essentially cancel each other out, and the em ...
Lecture 11: tokamak / vertical stability / beta limit
... (contamination of the machine) Tungsten has very high Z, but takes the heat loads very well ...
... (contamination of the machine) Tungsten has very high Z, but takes the heat loads very well ...
Electromagnetism

Electromagnetism is a branch of physics which involves the study of the electromagnetic force, a type of physical interaction that occurs between electrically charged particles. The electromagnetic force usually shows electromagnetic fields, such as electric fields, magnetic fields, and light. The electromagnetic force is one of the four fundamental interactions in nature. The other three fundamental interactions are the strong interaction, the weak interaction, and gravitation.The word electromagnetism is a compound form of two Greek terms, ἤλεκτρον, ēlektron, ""amber"", and μαγνῆτις λίθος magnētis lithos, which means ""magnesian stone"", a type of iron ore. The science of electromagnetic phenomena is defined in terms of the electromagnetic force, sometimes called the Lorentz force, which includes both electricity and magnetism as elements of one phenomenon.The electromagnetic force plays a major role in determining the internal properties of most objects encountered in daily life. Ordinary matter takes its form as a result of intermolecular forces between individual molecules in matter. Electrons are bound by electromagnetic wave mechanics into orbitals around atomic nuclei to form atoms, which are the building blocks of molecules. This governs the processes involved in chemistry, which arise from interactions between the electrons of neighboring atoms, which are in turn determined by the interaction between electromagnetic force and the momentum of the electrons.There are numerous mathematical descriptions of the electromagnetic field. In classical electrodynamics, electric fields are described as electric potential and electric current in Ohm's law, magnetic fields are associated with electromagnetic induction and magnetism, and Maxwell's equations describe how electric and magnetic fields are generated and altered by each other and by charges and currents.The theoretical implications of electromagnetism, in particular the establishment of the speed of light based on properties of the ""medium"" of propagation (permeability and permittivity), led to the development of special relativity by Albert Einstein in 1905.Although electromagnetism is considered one of the four fundamental forces, at high energy the weak force and electromagnetism are unified. In the history of the universe, during the quark epoch, the electroweak force split into the electromagnetic and weak forces.