To be or not to be? 1 Introduction
... that π1 (H) = Z⊗r . In this case all allowed charges on the dual weight lattice are topologically conserved. There is a perfect matching between topological sectors and points on the lattice determined by the quantization condition. The situation for the ’t Hooft-Polyakov case is an example of this ...
... that π1 (H) = Z⊗r . In this case all allowed charges on the dual weight lattice are topologically conserved. There is a perfect matching between topological sectors and points on the lattice determined by the quantization condition. The situation for the ’t Hooft-Polyakov case is an example of this ...
JJ Thomson and “Hidden” - Physics Department, Princeton University
... it is associated with the electric charge. He then noted that if the Ampèrian magnetic dipole were a small permanent magnet (in the field of an electric charge), and this magnet were demagnetized by “tapping,” the magnet would acquire the initial momentum (1) according to the argument of sec. 3.1, w ...
... it is associated with the electric charge. He then noted that if the Ampèrian magnetic dipole were a small permanent magnet (in the field of an electric charge), and this magnet were demagnetized by “tapping,” the magnet would acquire the initial momentum (1) according to the argument of sec. 3.1, w ...
physics course descriptions.pdf
... a number of alternative modes of energy generation - fossil fuels, biomass, wind, solar, hydro, and nuclear - and study the physical and technological aspects of each, and their societal, environmental and economic impacts over the construction and operational lifetimes. No previous study of physics ...
... a number of alternative modes of energy generation - fossil fuels, biomass, wind, solar, hydro, and nuclear - and study the physical and technological aspects of each, and their societal, environmental and economic impacts over the construction and operational lifetimes. No previous study of physics ...
Quantum Theory
... h, which has the value 6.626x10 J·s, is a proportionality constant called Planck’s constant. The amount of energy in a wave is then E = nhν, where n is the number of quanta in the wave. Thus, increasing the intensity of light increases the number of energy quanta it contains, not the energy of each ...
... h, which has the value 6.626x10 J·s, is a proportionality constant called Planck’s constant. The amount of energy in a wave is then E = nhν, where n is the number of quanta in the wave. Thus, increasing the intensity of light increases the number of energy quanta it contains, not the energy of each ...
Magnetic Flux Density (Cont`d)
... potential is viewed as an auxiliary function with no physical meaning. However, there are phenomena in quantum mechanics that suggest that the vector magnetic potential is a real (i.e., measurable) field. ...
... potential is viewed as an auxiliary function with no physical meaning. However, there are phenomena in quantum mechanics that suggest that the vector magnetic potential is a real (i.e., measurable) field. ...
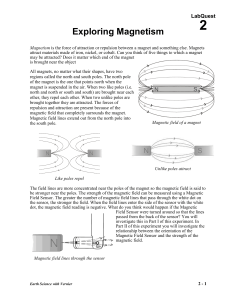
02 Expl Magnet LQ
... Magnetism is the force of attraction or repulsion between a magnet and something else. Magnets attract materials made of iron, nickel, or cobalt. Can you think of five things to which a magnet may be attracted? Does it matter which end of the magnet is brought near the object All magnets, no matter ...
... Magnetism is the force of attraction or repulsion between a magnet and something else. Magnets attract materials made of iron, nickel, or cobalt. Can you think of five things to which a magnet may be attracted? Does it matter which end of the magnet is brought near the object All magnets, no matter ...
glossary of terms
... This thesis will describe the software simulation process of real world physics in a 2D landscape. The physics characteristics and behaviors which will be simulated are electric charges and fields. An Android application will be built to simulate all of the above. Electric charge can be transferred ...
... This thesis will describe the software simulation process of real world physics in a 2D landscape. The physics characteristics and behaviors which will be simulated are electric charges and fields. An Android application will be built to simulate all of the above. Electric charge can be transferred ...
Are we there yet? A Journey to Understand and Predict Solar
... Unique role in solar physics research “The Sun would be a boring star if it had no magnetic field” ● Solar Flares are the most dramatic examples of the magnetic field's influence. Understanding the field's role in solar flares production requires: ● Understanding magnetic reconnection and other MHD ...
... Unique role in solar physics research “The Sun would be a boring star if it had no magnetic field” ● Solar Flares are the most dramatic examples of the magnetic field's influence. Understanding the field's role in solar flares production requires: ● Understanding magnetic reconnection and other MHD ...
Chapter 15
... The electric field is zero everywhere inside the conducting material Any excess charge on an isolated conductor resides entirely on its surface The electric field just outside a charged conductor is perpendicular to the conductor’s surface On an irregularly shaped conductor, the charge accumulates a ...
... The electric field is zero everywhere inside the conducting material Any excess charge on an isolated conductor resides entirely on its surface The electric field just outside a charged conductor is perpendicular to the conductor’s surface On an irregularly shaped conductor, the charge accumulates a ...
Electromagnetism

Electromagnetism is a branch of physics which involves the study of the electromagnetic force, a type of physical interaction that occurs between electrically charged particles. The electromagnetic force usually shows electromagnetic fields, such as electric fields, magnetic fields, and light. The electromagnetic force is one of the four fundamental interactions in nature. The other three fundamental interactions are the strong interaction, the weak interaction, and gravitation.The word electromagnetism is a compound form of two Greek terms, ἤλεκτρον, ēlektron, ""amber"", and μαγνῆτις λίθος magnētis lithos, which means ""magnesian stone"", a type of iron ore. The science of electromagnetic phenomena is defined in terms of the electromagnetic force, sometimes called the Lorentz force, which includes both electricity and magnetism as elements of one phenomenon.The electromagnetic force plays a major role in determining the internal properties of most objects encountered in daily life. Ordinary matter takes its form as a result of intermolecular forces between individual molecules in matter. Electrons are bound by electromagnetic wave mechanics into orbitals around atomic nuclei to form atoms, which are the building blocks of molecules. This governs the processes involved in chemistry, which arise from interactions between the electrons of neighboring atoms, which are in turn determined by the interaction between electromagnetic force and the momentum of the electrons.There are numerous mathematical descriptions of the electromagnetic field. In classical electrodynamics, electric fields are described as electric potential and electric current in Ohm's law, magnetic fields are associated with electromagnetic induction and magnetism, and Maxwell's equations describe how electric and magnetic fields are generated and altered by each other and by charges and currents.The theoretical implications of electromagnetism, in particular the establishment of the speed of light based on properties of the ""medium"" of propagation (permeability and permittivity), led to the development of special relativity by Albert Einstein in 1905.Although electromagnetism is considered one of the four fundamental forces, at high energy the weak force and electromagnetism are unified. In the history of the universe, during the quark epoch, the electroweak force split into the electromagnetic and weak forces.