THE HISTORY OF FRET: From conception through the labors of birth
... The basic FRET phenomenon involves the electrodynamic interaction between two molecules over distances that are large compared to their diameters; and this description requires the idea of an EM field (for FRET this is a dipole interaction, which arises from a multi-pole approximation to the Coulomb ...
... The basic FRET phenomenon involves the electrodynamic interaction between two molecules over distances that are large compared to their diameters; and this description requires the idea of an EM field (for FRET this is a dipole interaction, which arises from a multi-pole approximation to the Coulomb ...
Learn Physics by Programming in Haskell
... proficient in this subset of Haskell in about seven weeks, and can then apply it to problems in mechanics and electromagnetic theory. In the second part of the course, we use Haskell to express the ideas of Newtonian mechanics and electromagnetic theory. Here we want students to use the language as ...
... proficient in this subset of Haskell in about seven weeks, and can then apply it to problems in mechanics and electromagnetic theory. In the second part of the course, we use Haskell to express the ideas of Newtonian mechanics and electromagnetic theory. Here we want students to use the language as ...
VCE PHYSICS UNIT 3
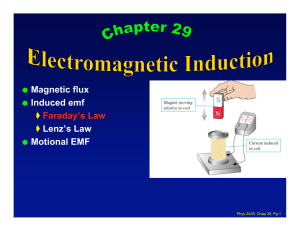
... All magnets have poles labelled as North and South: Like poles repel Unlike poles attract Magnets generate Fields in the space surrounding them. The concept of “a field” is an important concept in our study of Physics. A Field is defined as a “region of influence”. In a Magnetic Field, magnetically ...
... All magnets have poles labelled as North and South: Like poles repel Unlike poles attract Magnets generate Fields in the space surrounding them. The concept of “a field” is an important concept in our study of Physics. A Field is defined as a “region of influence”. In a Magnetic Field, magnetically ...
dielectric_micro
... dielectric surface charge density bound (induced) – these bound charges are not free to move as they are bound to the molecules. In the interior of the dielectric, the net dipole moment is zero because of the cancellation of the charges. This phenomenon is called polarization and the material is ...
... dielectric surface charge density bound (induced) – these bound charges are not free to move as they are bound to the molecules. In the interior of the dielectric, the net dipole moment is zero because of the cancellation of the charges. This phenomenon is called polarization and the material is ...
General Instructions
... Outline how Isaac Newton, in proposing the law of gravity, changed the way we think about the motion of the planets and motion of objects near the Earth’s surface. ...
... Outline how Isaac Newton, in proposing the law of gravity, changed the way we think about the motion of the planets and motion of objects near the Earth’s surface. ...
OBJECTIVES
... In the video lecture it was stated that the Tacoma Narrows Bridge collapse was caused by resonance. The driving force in that case, however, was not sinusoidal nor did it oscillate at the frequency of the steady state oscillations of the bridge. In fact the driving force was provided by a wind blowi ...
... In the video lecture it was stated that the Tacoma Narrows Bridge collapse was caused by resonance. The driving force in that case, however, was not sinusoidal nor did it oscillate at the frequency of the steady state oscillations of the bridge. In fact the driving force was provided by a wind blowi ...
Questions 9 and 10 refer to the following information
... (a) Using F = BIl, but current is parallel to the magnetic field so Force = zero. (b) The direction of the force on UV is UP and the force on WX is down. This produces a clockwise rotation. The torques depends of the separation of the lines of action of the two forces, which is a maximum in Figure 6 ...
... (a) Using F = BIl, but current is parallel to the magnetic field so Force = zero. (b) The direction of the force on UV is UP and the force on WX is down. This produces a clockwise rotation. The torques depends of the separation of the lines of action of the two forces, which is a maximum in Figure 6 ...
Experiment 5: Magnetic Fields of a Bar Magnet and of the Earth
... earth’s field), select AXIAL, and push the TARE button while the sensor is far away from the bar magnetic. Start taking data, and move the sensor towards one end of the bar magnet, with the probe on and parallel to the magnet axis. (Some find it easier to hold the sensor fixed and move the magnet.) ...
... earth’s field), select AXIAL, and push the TARE button while the sensor is far away from the bar magnetic. Start taking data, and move the sensor towards one end of the bar magnet, with the probe on and parallel to the magnet axis. (Some find it easier to hold the sensor fixed and move the magnet.) ...
Novel simulation methods for Coulomb and hydrodynamic interactions
... Part 1 is devoted to computer simulations of Brownian particles with hydrodynamic interactions. The main influence of the solvent on the dynamics of Brownian particles is that it mediates hydrodynamic interactions. In the method, this is simulated by numerical solution of the Navier–Stokes equation ...
... Part 1 is devoted to computer simulations of Brownian particles with hydrodynamic interactions. The main influence of the solvent on the dynamics of Brownian particles is that it mediates hydrodynamic interactions. In the method, this is simulated by numerical solution of the Navier–Stokes equation ...
Understanding and using the minus sign in Faraday`s law
... Two issues arise from the discussion above. Firstly, what does a negative sign for E actually mean? Secondly, is there a way in which we can teach students to use the minus sign in order to predict the direction of the induced current? This article deals with the second point first, since this is of ...
... Two issues arise from the discussion above. Firstly, what does a negative sign for E actually mean? Secondly, is there a way in which we can teach students to use the minus sign in order to predict the direction of the induced current? This article deals with the second point first, since this is of ...
Build the Simplest Electric Motor
... • A video of this demonstration, Build a Simple Motor is available online at www.flinnsci.com in Teacher Resource Videos, part of the Physical Science Minute Video Series. ...
... • A video of this demonstration, Build a Simple Motor is available online at www.flinnsci.com in Teacher Resource Videos, part of the Physical Science Minute Video Series. ...
berncatcaptions1
... Model 1. shows a chain of 40 jumbo gold paper clip links (from Staples), with three others with three different pairs of tangent points and tangents . Model 1A. shows the original chain compared to one with 20 paper clip links replaced by two black equal tangents with 20 links concentrated at their ...
... Model 1. shows a chain of 40 jumbo gold paper clip links (from Staples), with three others with three different pairs of tangent points and tangents . Model 1A. shows the original chain compared to one with 20 paper clip links replaced by two black equal tangents with 20 links concentrated at their ...
P. LeClair - MINT Center
... captured inside the barn and then proceed to exit the barn from the back door. Do both the runner and the ground observer agree that the runner makes it safely through the barn? Solution: Given the relative velocity between the reference frames v = 0.75c, we will have to account for length contracti ...
... captured inside the barn and then proceed to exit the barn from the back door. Do both the runner and the ground observer agree that the runner makes it safely through the barn? Solution: Given the relative velocity between the reference frames v = 0.75c, we will have to account for length contracti ...
Centripetal Force - thsicp-23
... •Centripetal Force relies on fiction to satisfy the 3rd law of motion. • Centripetal force is the action to the reaction of friction. • Centripetal force must be greater than friction for an object to negotiate a turn. If centripetal force is less than friction the object will veer off in a straight ...
... •Centripetal Force relies on fiction to satisfy the 3rd law of motion. • Centripetal force is the action to the reaction of friction. • Centripetal force must be greater than friction for an object to negotiate a turn. If centripetal force is less than friction the object will veer off in a straight ...
Electromagnetism

Electromagnetism is a branch of physics which involves the study of the electromagnetic force, a type of physical interaction that occurs between electrically charged particles. The electromagnetic force usually shows electromagnetic fields, such as electric fields, magnetic fields, and light. The electromagnetic force is one of the four fundamental interactions in nature. The other three fundamental interactions are the strong interaction, the weak interaction, and gravitation.The word electromagnetism is a compound form of two Greek terms, ἤλεκτρον, ēlektron, ""amber"", and μαγνῆτις λίθος magnētis lithos, which means ""magnesian stone"", a type of iron ore. The science of electromagnetic phenomena is defined in terms of the electromagnetic force, sometimes called the Lorentz force, which includes both electricity and magnetism as elements of one phenomenon.The electromagnetic force plays a major role in determining the internal properties of most objects encountered in daily life. Ordinary matter takes its form as a result of intermolecular forces between individual molecules in matter. Electrons are bound by electromagnetic wave mechanics into orbitals around atomic nuclei to form atoms, which are the building blocks of molecules. This governs the processes involved in chemistry, which arise from interactions between the electrons of neighboring atoms, which are in turn determined by the interaction between electromagnetic force and the momentum of the electrons.There are numerous mathematical descriptions of the electromagnetic field. In classical electrodynamics, electric fields are described as electric potential and electric current in Ohm's law, magnetic fields are associated with electromagnetic induction and magnetism, and Maxwell's equations describe how electric and magnetic fields are generated and altered by each other and by charges and currents.The theoretical implications of electromagnetism, in particular the establishment of the speed of light based on properties of the ""medium"" of propagation (permeability and permittivity), led to the development of special relativity by Albert Einstein in 1905.Although electromagnetism is considered one of the four fundamental forces, at high energy the weak force and electromagnetism are unified. In the history of the universe, during the quark epoch, the electroweak force split into the electromagnetic and weak forces.