Audio Alto
... impedance of few hundreds of ohms to low impedance (high current) output required by speakers. The output transistors are biased with an innovative dedicated circuit that keeps both output transistors biased during the whole signal phase (360°) reducing the low power related distortions (no typical ...
... impedance of few hundreds of ohms to low impedance (high current) output required by speakers. The output transistors are biased with an innovative dedicated circuit that keeps both output transistors biased during the whole signal phase (360°) reducing the low power related distortions (no typical ...
Dual Negative Regulated Charge Pump
... feedback resistor network (R3 and R4) are tied to the same 3.3V supply [5]. By means of negative feedback, the error amplifier will generate the required voltage to charge up the capacitor, CP, via the pMOS transistor. The pMOS and nMOS transistors, P1 and N1, are controlled by a non-overlapping clo ...
... feedback resistor network (R3 and R4) are tied to the same 3.3V supply [5]. By means of negative feedback, the error amplifier will generate the required voltage to charge up the capacitor, CP, via the pMOS transistor. The pMOS and nMOS transistors, P1 and N1, are controlled by a non-overlapping clo ...
Application Note Ceramic Surface Mount Amplifier 1. Introduction
... The base of the package is ceramic due to the power dissipated in the transistor. Using a ceramic package is the best way to transfer heat out of the transistor, and still keep the design low cost for the commercial market. A land grid array package was used so that the amplifiers can easily be sold ...
... The base of the package is ceramic due to the power dissipated in the transistor. Using a ceramic package is the best way to transfer heat out of the transistor, and still keep the design low cost for the commercial market. A land grid array package was used so that the amplifiers can easily be sold ...
Student Biographies
... The op amp is designed to sense the difference between the voltage signals applied to its two inputs (v2-v1), and multiply this by a number A, and cause the resulting voltage A (v2-v1) to appear at the output terminal relative to ground. Note that v1 and v2 are also implied to be relative to ground ...
... The op amp is designed to sense the difference between the voltage signals applied to its two inputs (v2-v1), and multiply this by a number A, and cause the resulting voltage A (v2-v1) to appear at the output terminal relative to ground. Note that v1 and v2 are also implied to be relative to ground ...
basic differential amplifier
... If the diff amp is not perfectly balanced, as is always the case in the real world, then the common-mode signal input will cause an output signal that then constitutes interference with the desired amplified signal. ...
... If the diff amp is not perfectly balanced, as is always the case in the real world, then the common-mode signal input will cause an output signal that then constitutes interference with the desired amplified signal. ...
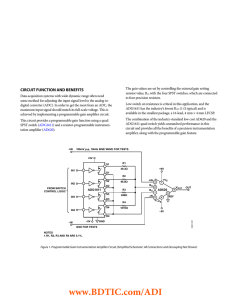
CIRCUIT FUNCTION AND BENEFITS
... Data acquisition systems with wide dynamic range often need some method for adjusting the input signal level to the analog-todigital converter (ADC). In order to get the most from an ADC, the maximum input signal should match its full-scale voltage. This is achieved by implementing a programmable ga ...
... Data acquisition systems with wide dynamic range often need some method for adjusting the input signal level to the analog-todigital converter (ADC). In order to get the most from an ADC, the maximum input signal should match its full-scale voltage. This is achieved by implementing a programmable ga ...
Improving common-mode rejection using the right
... methodologies to measure CMR, however, specify the minimum isolation capacitance CB at which the system must pass the required CMR specification. 3. Post-Conversion Processing There is a possibility that a residual common-mode signal can be removed from the input after the conversion using finite-im ...
... methodologies to measure CMR, however, specify the minimum isolation capacitance CB at which the system must pass the required CMR specification. 3. Post-Conversion Processing There is a possibility that a residual common-mode signal can be removed from the input after the conversion using finite-im ...
Negative feedback
Negative feedback occurs when some function of the output of a system, process, or mechanism is fed back in a manner that tends to reduce the fluctuations in the output, whether caused by changes in the input or by other disturbances.Whereas positive feedback tends to lead to instability via exponential growth, oscillation or chaotic behavior, negative feedback generally promotes stability. Negative feedback tends to promote a settling to equilibrium, and reduces the effects of perturbations. Negative feedback loops in which just the right amount of correction is applied with optimum timing can be very stable, accurate, and responsive.Negative feedback is widely used in mechanical and electronic engineering, but it also occurs naturally within living organisms, and can be seen in many other fields from chemistry and economics to physical systems such as the climate. General negative feedback systems are studied in control systems engineering.